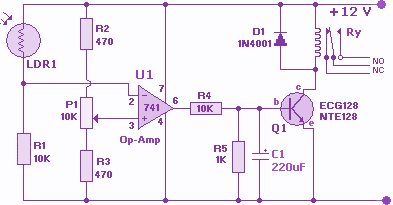
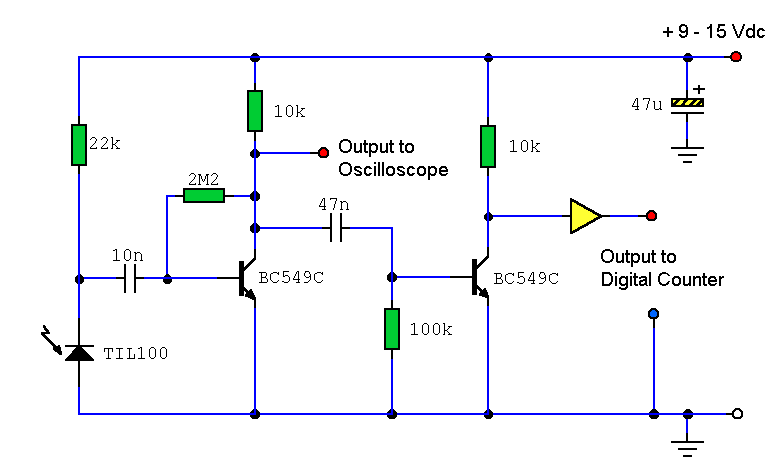
Photoresistor LDR light control switch circuit diagram
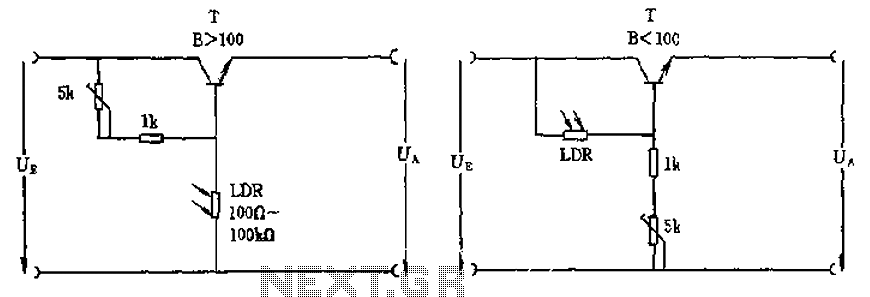
The circuit depicted involves a photoresistor (LDR) connected to a transistor, which operates at either a high or low level based on light conditions. The amplification factor of the transistor is 100, which is adequate for the application. The resistance of the photosensitive resistor varies between 100 ohms and 100k ohms, depending on the light intensity. For controlling high-power loads, Darlington transistors should be utilized.
The circuit utilizes a photoresistor (Light Dependent Resistor, LDR) as the primary sensor for detecting ambient light levels. The LDR exhibits a significant change in resistance based on the intensity of light falling on it; typically, its resistance decreases in bright light and increases in darkness. This property is crucial for the operation of the circuit, as it determines the behavior of the connected transistor.
In this configuration, the LDR is connected to the base of a standard bipolar junction transistor (BJT) with a gain factor (h_FE) of approximately 100. This transistor acts as a switch or amplifier, enabling the control of output signals based on the input from the LDR. When the LDR is exposed to light, its resistance drops, allowing current to flow into the base of the transistor, which in turn allows a larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter, effectively turning the transistor "on." Conversely, in low light conditions, the resistance of the LDR increases, reducing the base current and turning the transistor "off."
For applications requiring the control of higher power loads, such as motors or lamps, it is advisable to employ a Darlington pair configuration. A Darlington transistor consists of two BJTs connected in such a way that the current amplified by the first transistor is further amplified by the second. This configuration provides a much higher current gain, making it suitable for switching larger loads without requiring significant input current, thus enhancing the circuit's efficiency and reliability.
In summary, the circuit effectively utilizes an LDR to control a transistor's state based on light intensity, with the option to scale the design for higher power applications through the use of Darlington transistors, ensuring versatility and adaptability in various electronic applications. As shown in the circuit, there is the incident at the time, this circuit is connected with photoresistor LDR transistor is turned high or zero level. Amplification factor of tr ansistor B 100 is sufficient, the photosensitive resistor between 100 ~ 100k Europe, corresponding to the case when the light irradiation and dark. If you want to control high power loads should be used Darlington transistors.
The circuit utilizes a photoresistor (Light Dependent Resistor, LDR) as the primary sensor for detecting ambient light levels. The LDR exhibits a significant change in resistance based on the intensity of light falling on it; typically, its resistance decreases in bright light and increases in darkness. This property is crucial for the operation of the circuit, as it determines the behavior of the connected transistor.
In this configuration, the LDR is connected to the base of a standard bipolar junction transistor (BJT) with a gain factor (h_FE) of approximately 100. This transistor acts as a switch or amplifier, enabling the control of output signals based on the input from the LDR. When the LDR is exposed to light, its resistance drops, allowing current to flow into the base of the transistor, which in turn allows a larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter, effectively turning the transistor "on." Conversely, in low light conditions, the resistance of the LDR increases, reducing the base current and turning the transistor "off."
For applications requiring the control of higher power loads, such as motors or lamps, it is advisable to employ a Darlington pair configuration. A Darlington transistor consists of two BJTs connected in such a way that the current amplified by the first transistor is further amplified by the second. This configuration provides a much higher current gain, making it suitable for switching larger loads without requiring significant input current, thus enhancing the circuit's efficiency and reliability.
In summary, the circuit effectively utilizes an LDR to control a transistor's state based on light intensity, with the option to scale the design for higher power applications through the use of Darlington transistors, ensuring versatility and adaptability in various electronic applications. As shown in the circuit, there is the incident at the time, this circuit is connected with photoresistor LDR transistor is turned high or zero level. Amplification factor of tr ansistor B 100 is sufficient, the photosensitive resistor between 100 ~ 100k Europe, corresponding to the case when the light irradiation and dark. If you want to control high power loads should be used Darlington transistors.