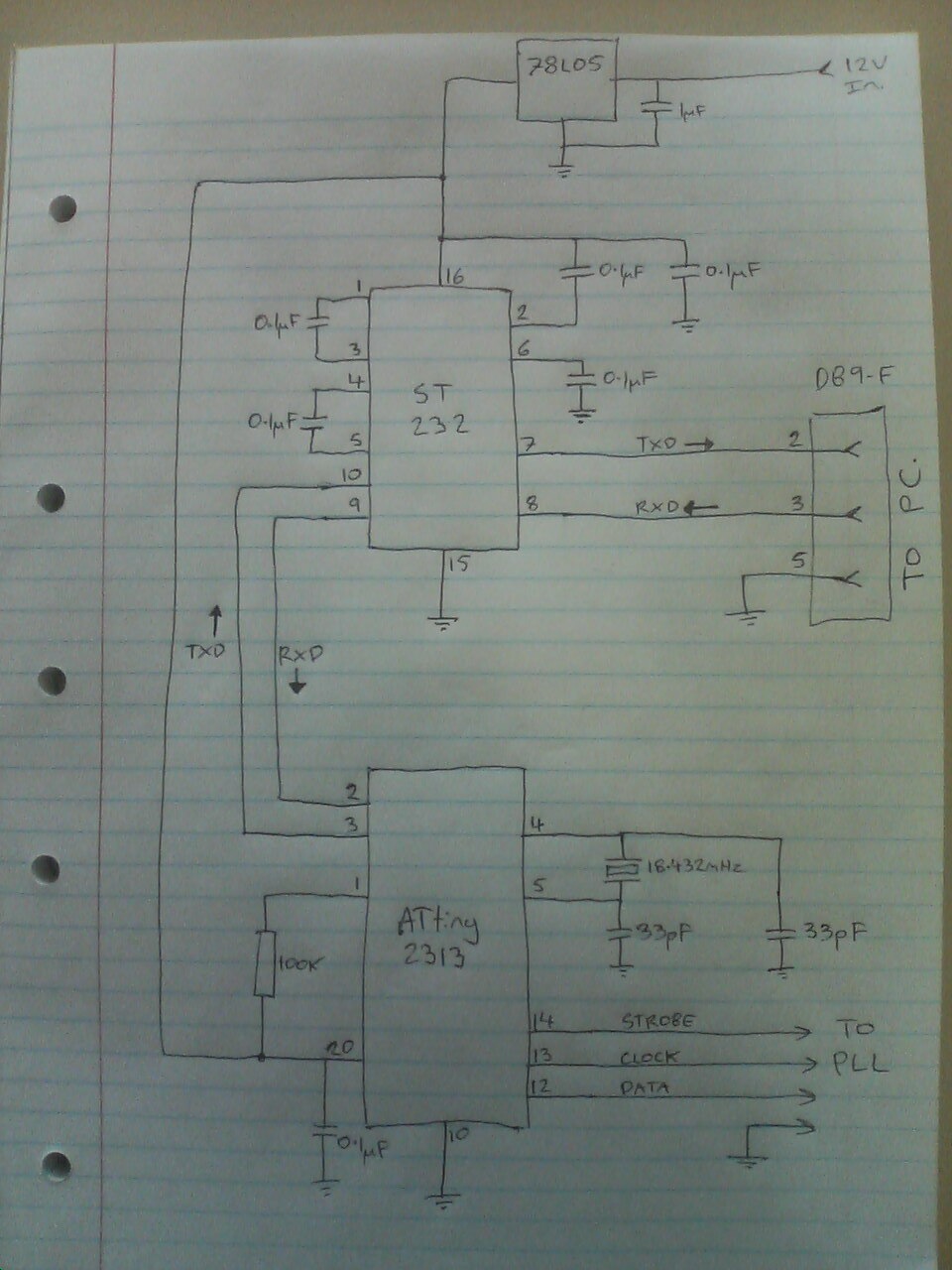
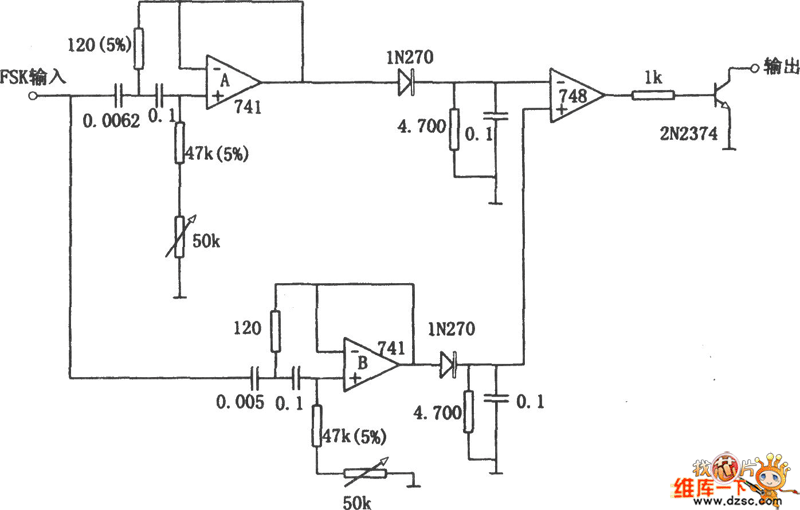
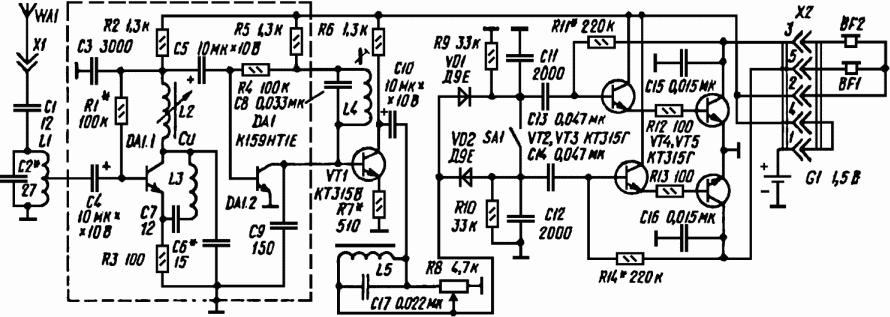
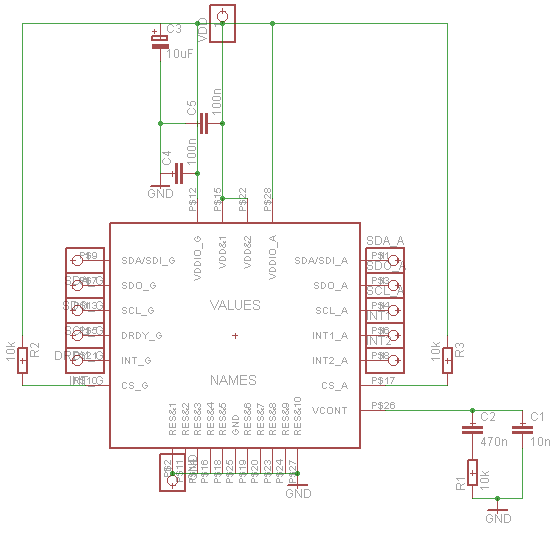
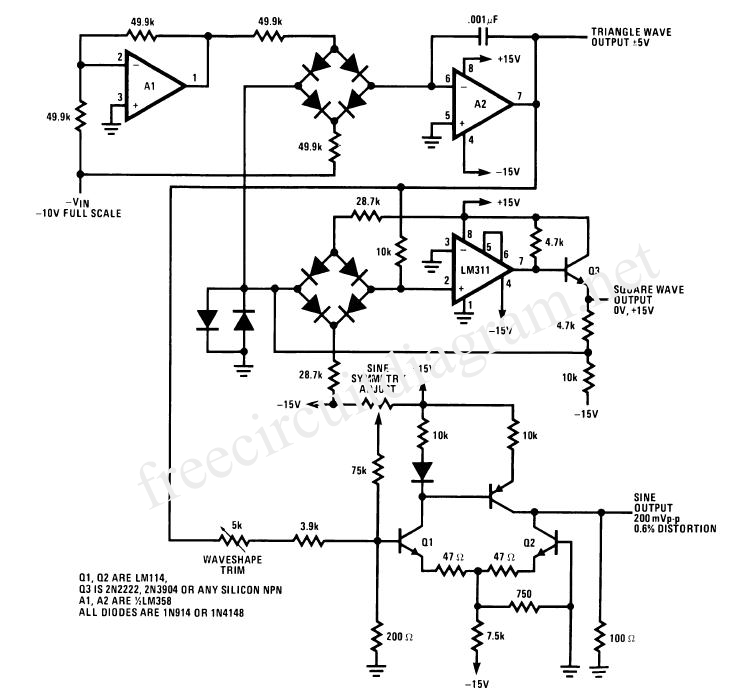
pll fm demodulator

This circuit is a Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) system designed to function as an FM demodulator. The output of the Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) tracks the FM signal, and since the input voltage of the VCO is proportional to its output frequency, the VCO input corresponds to the demodulated signal. In this example, an FM signal with a 10 kHz carrier frequency is modulated by a 400 Hz audio signal. The schematic diagram illustrates the connections of the CD4046B integrated circuit as an FM demodulator. The total amplitude of the FM signal is 500 mV, necessitating AC coupling to the signal input (terminal 14). Phase Comparator I is employed for this application due to the requirement for a PLL system with a center frequency matching the FM carrier frequency. Additionally, Phase Comparator I is advantageous in this context because of its high signal input noise rejection characteristics.
The FM demodulator circuit utilizing the CD4046B PLL integrates a VCO, phase comparator, and feedback loop to achieve demodulation of frequency-modulated signals. The VCO generates a frequency output that is adjusted based on the input voltage, which corresponds to the frequency of the incoming FM signal. In this setup, the 10 kHz carrier frequency is effectively tracked by the VCO, enabling the extraction of the modulating 400 Hz audio signal.
AC coupling is implemented at the input to ensure that only the varying component of the FM signal is processed, blocking any DC offset that may interfere with the demodulation process. The choice of Phase Comparator I is critical as it allows for the comparison of the phase of the VCO output with the incoming FM signal. This phase comparison is essential for maintaining lock and ensuring that the VCO output remains synchronized with the carrier frequency of the FM signal.
The circuit's design leverages the high signal-input-noise-rejection capabilities of Phase Comparator I, which enhances the overall performance of the demodulator by minimizing the impact of noise on the demodulated output. As a result, this PLL-based FM demodulator is suitable for various applications where reliable demodulation of FM signals is required, such as in radio receivers and communication systems. The schematic provides a clear representation of the connections and components involved, facilitating understanding and implementation of the circuit in practical applications.This is a circuit about PLL system that can be used to implement an FM demodulator. Since the VCO output tracks the FM signal, and the VCO input voltage is proportional to the VCO output frequency, then the VCO input will be equal to the demodulated signal. This is the figure of the circuit. For this example, an FM signal consisting of a 10-kHz ca rrier frequency was modulated by a 400-Hz audio signal. The schematic diagram shows the connections of the CD4046B as an FM demodulator. The total FM signal amplitude is 500 mV, therefore, the signal must be ac coupled to the signal input (terminal 14). Phase comparator I is used for this application because a PLL system with a center frequency equal to the FM carrier frequency is needed.
Phase comparator I lends itself to this application also because of its high signal-input-noise-rejection characteristics. 🔗 External reference
The FM demodulator circuit utilizing the CD4046B PLL integrates a VCO, phase comparator, and feedback loop to achieve demodulation of frequency-modulated signals. The VCO generates a frequency output that is adjusted based on the input voltage, which corresponds to the frequency of the incoming FM signal. In this setup, the 10 kHz carrier frequency is effectively tracked by the VCO, enabling the extraction of the modulating 400 Hz audio signal.
AC coupling is implemented at the input to ensure that only the varying component of the FM signal is processed, blocking any DC offset that may interfere with the demodulation process. The choice of Phase Comparator I is critical as it allows for the comparison of the phase of the VCO output with the incoming FM signal. This phase comparison is essential for maintaining lock and ensuring that the VCO output remains synchronized with the carrier frequency of the FM signal.
The circuit's design leverages the high signal-input-noise-rejection capabilities of Phase Comparator I, which enhances the overall performance of the demodulator by minimizing the impact of noise on the demodulated output. As a result, this PLL-based FM demodulator is suitable for various applications where reliable demodulation of FM signals is required, such as in radio receivers and communication systems. The schematic provides a clear representation of the connections and components involved, facilitating understanding and implementation of the circuit in practical applications.This is a circuit about PLL system that can be used to implement an FM demodulator. Since the VCO output tracks the FM signal, and the VCO input voltage is proportional to the VCO output frequency, then the VCO input will be equal to the demodulated signal. This is the figure of the circuit. For this example, an FM signal consisting of a 10-kHz ca rrier frequency was modulated by a 400-Hz audio signal. The schematic diagram shows the connections of the CD4046B as an FM demodulator. The total FM signal amplitude is 500 mV, therefore, the signal must be ac coupled to the signal input (terminal 14). Phase comparator I is used for this application because a PLL system with a center frequency equal to the FM carrier frequency is needed.
Phase comparator I lends itself to this application also because of its high signal-input-noise-rejection characteristics. 🔗 External reference