Portable Solar Powered Lantern Circuit
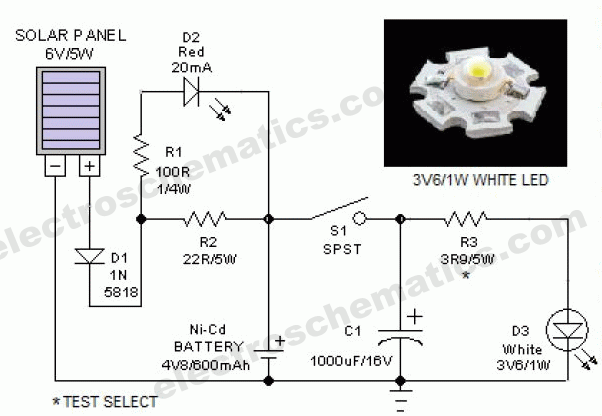
The 5W/6V solar panel can achieve a maximum current of approximately 500 to 800mA, peaking at 800mA during noon. Limiting the current to 150mA appears inefficient. A 1W panel can supply around 160mA during peak performance for up to 6 hours; however, for worst-case scenarios, a 2W panel may be more suitable, potentially reducing overall costs. A 1W LED can produce approximately 80 to 100 lumens, which can be achieved by using a series of two LEDs in strings, with ten strings operating at 8mA for enhanced brightness, thereby reducing total consumption to 80mA. The battery can sustain illumination for 6 hours, providing approximately 100 lumens (each LED produces 4 to 5 lumens). An additional current-limiting resistor in series with each string can increase the output to 6 lumens. However, the circuit may become overly complex with too many components, especially after the SPST switch, leading to inefficiencies in the 5W resistors.
The circuit design utilizes a 5W/6V solar panel as the primary energy source, capable of providing a peak current of 800mA under optimal sunlight conditions. To maximize efficiency, the system can be designed to operate at a lower current draw, ideally around 150mA, although this may not fully utilize the panel's capacity. A more practical approach would involve integrating a 1W solar panel, which can deliver approximately 160mA during peak sunlight hours for a duration of 6 hours. This allows for flexibility in design, particularly in applications where energy consumption needs to be minimized.
For the lighting component, a series configuration of two LEDs per string can be employed, with ten strings connected in parallel. Each string operates at 8mA, resulting in a total current draw of 80mA. This configuration not only enhances brightness but also ensures that the system remains within the operational limits of the solar panel and battery. The total light output from this arrangement can reach approximately 100 lumens, with each LED contributing between 4 to 5 lumens. To optimize performance, a current-limiting resistor can be added in series with each string to fine-tune the brightness, potentially increasing the output to 6 lumens per LED.
The incorporation of an SPST switch allows for manual control of the circuit, enabling the user to turn the system on or off as needed. However, care should be taken to minimize the number of components in the circuit to avoid excessive voltage drops and power loss, particularly through resistors. A well-designed circuit should balance the number of components with the desired performance, ensuring that the overall system remains efficient and cost-effective while providing reliable illumination.The panel 5W/6v Wp will have a max current of approx 500 to 800mA peaking at 800mA at noon. by restricting it to 150mA seems sheer waste. you can use a 1W panel to provide you 160mA at peak performance of 6 hours, to cover for the worst case scenario maybe 2W would be fine. thus reducing the cost of the panel. The 1W LED will give approx 80 to 1 00 Lumens this can be provided by use of a series of 2 LED`s in a strings and have 10 strings each string @8mA for Ultra brightness so the consumption is reduced to 80mA. the battery would last for 6 hours providing illumination of approx 100 Lumens (each LED @4/5 Lumens and you can get 6 Lumens by adding a current limiting resistor in series with each string Too many components after the SPST warming the circuit wasting it in the 5W resistors
🔗 External reference
The circuit design utilizes a 5W/6V solar panel as the primary energy source, capable of providing a peak current of 800mA under optimal sunlight conditions. To maximize efficiency, the system can be designed to operate at a lower current draw, ideally around 150mA, although this may not fully utilize the panel's capacity. A more practical approach would involve integrating a 1W solar panel, which can deliver approximately 160mA during peak sunlight hours for a duration of 6 hours. This allows for flexibility in design, particularly in applications where energy consumption needs to be minimized.
For the lighting component, a series configuration of two LEDs per string can be employed, with ten strings connected in parallel. Each string operates at 8mA, resulting in a total current draw of 80mA. This configuration not only enhances brightness but also ensures that the system remains within the operational limits of the solar panel and battery. The total light output from this arrangement can reach approximately 100 lumens, with each LED contributing between 4 to 5 lumens. To optimize performance, a current-limiting resistor can be added in series with each string to fine-tune the brightness, potentially increasing the output to 6 lumens per LED.
The incorporation of an SPST switch allows for manual control of the circuit, enabling the user to turn the system on or off as needed. However, care should be taken to minimize the number of components in the circuit to avoid excessive voltage drops and power loss, particularly through resistors. A well-designed circuit should balance the number of components with the desired performance, ensuring that the overall system remains efficient and cost-effective while providing reliable illumination.The panel 5W/6v Wp will have a max current of approx 500 to 800mA peaking at 800mA at noon. by restricting it to 150mA seems sheer waste. you can use a 1W panel to provide you 160mA at peak performance of 6 hours, to cover for the worst case scenario maybe 2W would be fine. thus reducing the cost of the panel. The 1W LED will give approx 80 to 1 00 Lumens this can be provided by use of a series of 2 LED`s in a strings and have 10 strings each string @8mA for Ultra brightness so the consumption is reduced to 80mA. the battery would last for 6 hours providing illumination of approx 100 Lumens (each LED @4/5 Lumens and you can get 6 Lumens by adding a current limiting resistor in series with each string Too many components after the SPST warming the circuit wasting it in the 5W resistors
🔗 External reference