Positive and negative from a battery LT1010

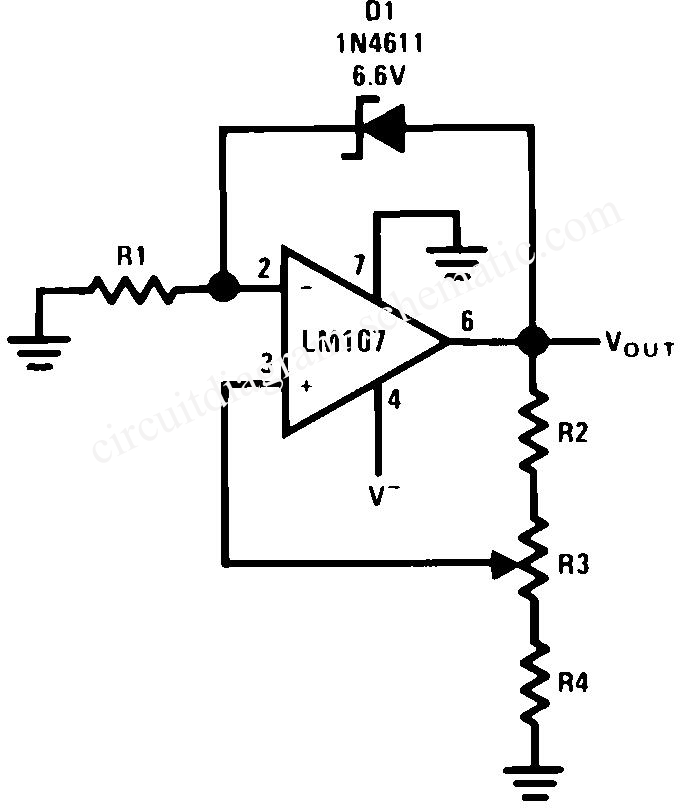
A common need in many systems is to obtain positive and negative supplies from a single battery. Where current requirements are small, the circuit shown is a simple solution. It provides symmetrical +&- output voltages, both equal to one half the input voltage. The output voltages are referenced to pin 3, output common. If the input voltage between pin 8 and pin 5 exceeds 6 V, pin 6 should also be connected to pin 3, as shown by the dashed line. More: Higher current requirements are served by an LT1010 buffer. The splitter circuit can source or sink up to +&- 150mA with only 5mA quiescent current. The output capacitor, C2, can be made as large as necessary to absorb current transients. An input capacitor.
The described circuit serves as a voltage splitter, generating both positive and negative supply voltages from a single input voltage source, typically a battery. This configuration is particularly useful in applications where dual supply voltages are required but space and simplicity are paramount. The circuit operates by utilizing the input voltage and dividing it evenly to produce two symmetrical outputs, each at half the input voltage.
The output voltages are referenced to a common point, designated as pin 3, which serves as the ground reference for the output. The design allows for flexibility in the input voltage range; however, it is crucial that when the input voltage between pins 8 and 5 exceeds 6 V, an additional connection from pin 6 to pin 3 is necessary. This connection ensures proper operation and stability of the circuit under higher voltage conditions.
For applications demanding higher current output, the inclusion of an LT1010 buffer enhances the circuit's capability. This buffer can effectively handle current loads of up to ±150 mA while maintaining a low quiescent current of just 5 mA, making it efficient for battery-powered devices.
The output capacitor, C2, plays a vital role in the circuit by smoothing out voltage fluctuations and absorbing transient currents that may occur during operation. The size of C2 can be adjusted based on the specific requirements of the application, allowing for greater flexibility in managing load changes.
Additionally, an input capacitor is mentioned, which is critical for filtering and stabilizing the input voltage, further improving the overall performance of the voltage splitter circuit. Proper selection and sizing of both input and output capacitors are essential for optimizing transient response and maintaining stable output voltages under varying load conditions.A common need in many systems is to obtain positive and negative supplies from a single battery. Where current requirements are small, the circuit shown is a simple solution. It provides symmetrical +&- output voltages, both equal to one half the input voltage. The output voltages are referenced to pin 3, output common. If the input voltage between pin 8 and pin 5 exceeds 6 V, pin 6 should also be connected to pin 3, as shown by the dashed line. Higher current requirements are served by an LT1010 buffer.The splitter circuit can source or sink up to +&- 150mA with only 5mA quiescent current. The output capacitor, C2, can be made as large as necessary to absorb current transients. An input capacito 🔗 External reference
The described circuit serves as a voltage splitter, generating both positive and negative supply voltages from a single input voltage source, typically a battery. This configuration is particularly useful in applications where dual supply voltages are required but space and simplicity are paramount. The circuit operates by utilizing the input voltage and dividing it evenly to produce two symmetrical outputs, each at half the input voltage.
The output voltages are referenced to a common point, designated as pin 3, which serves as the ground reference for the output. The design allows for flexibility in the input voltage range; however, it is crucial that when the input voltage between pins 8 and 5 exceeds 6 V, an additional connection from pin 6 to pin 3 is necessary. This connection ensures proper operation and stability of the circuit under higher voltage conditions.
For applications demanding higher current output, the inclusion of an LT1010 buffer enhances the circuit's capability. This buffer can effectively handle current loads of up to ±150 mA while maintaining a low quiescent current of just 5 mA, making it efficient for battery-powered devices.
The output capacitor, C2, plays a vital role in the circuit by smoothing out voltage fluctuations and absorbing transient currents that may occur during operation. The size of C2 can be adjusted based on the specific requirements of the application, allowing for greater flexibility in managing load changes.
Additionally, an input capacitor is mentioned, which is critical for filtering and stabilizing the input voltage, further improving the overall performance of the voltage splitter circuit. Proper selection and sizing of both input and output capacitors are essential for optimizing transient response and maintaining stable output voltages under varying load conditions.A common need in many systems is to obtain positive and negative supplies from a single battery. Where current requirements are small, the circuit shown is a simple solution. It provides symmetrical +&- output voltages, both equal to one half the input voltage. The output voltages are referenced to pin 3, output common. If the input voltage between pin 8 and pin 5 exceeds 6 V, pin 6 should also be connected to pin 3, as shown by the dashed line. Higher current requirements are served by an LT1010 buffer.The splitter circuit can source or sink up to +&- 150mA with only 5mA quiescent current. The output capacitor, C2, can be made as large as necessary to absorb current transients. An input capacito 🔗 External reference