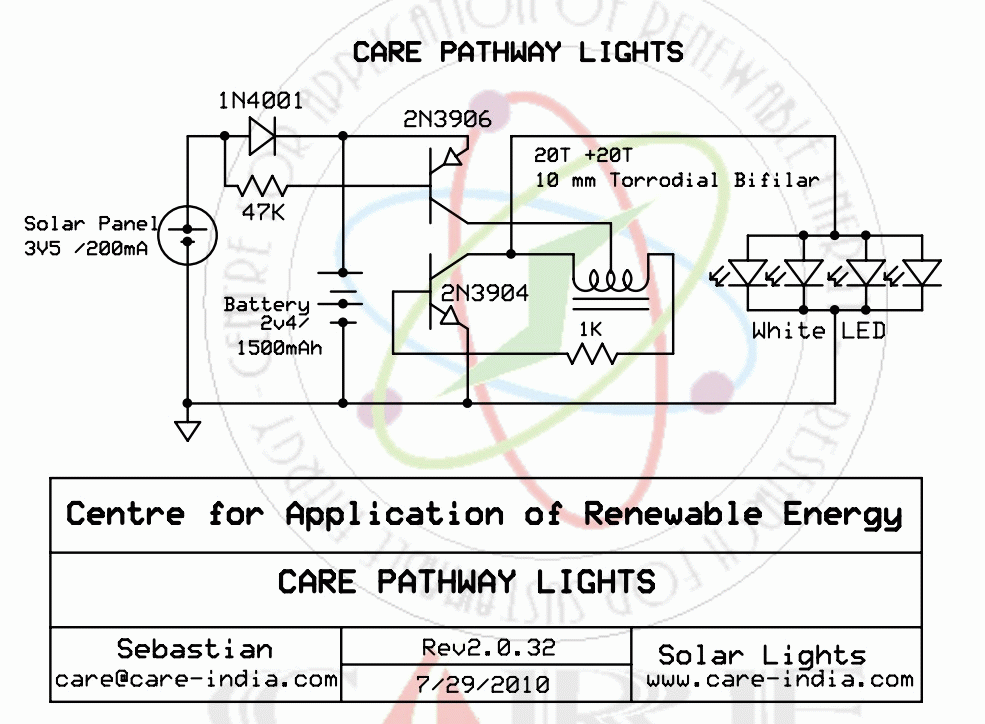
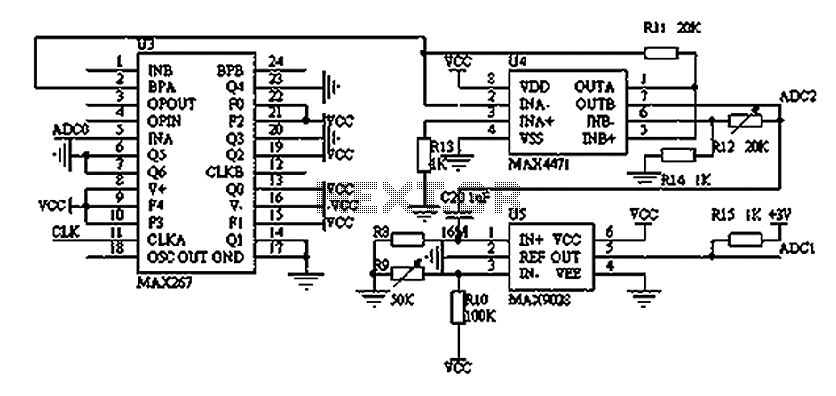
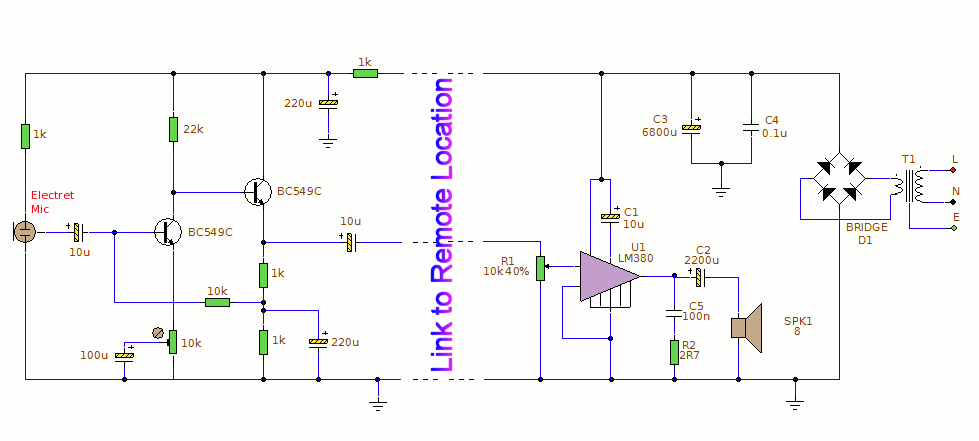
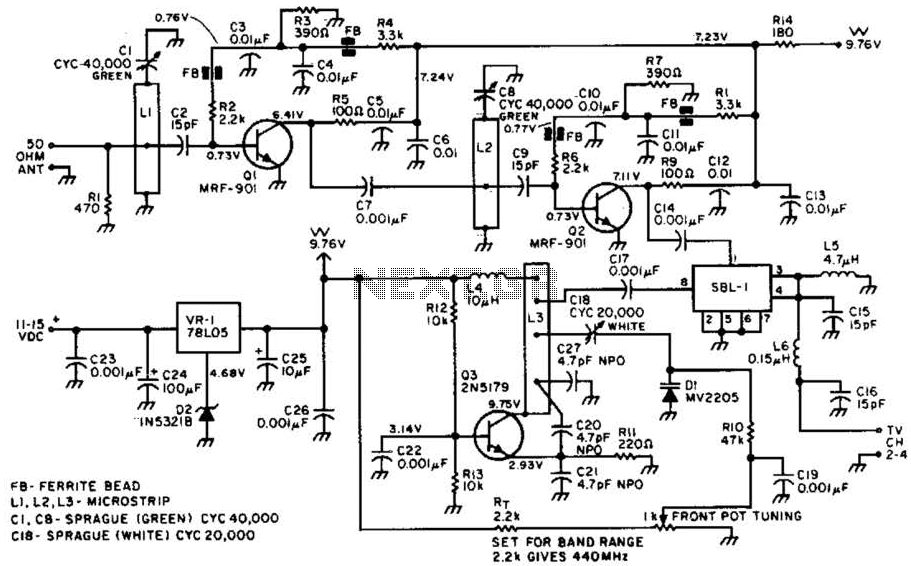
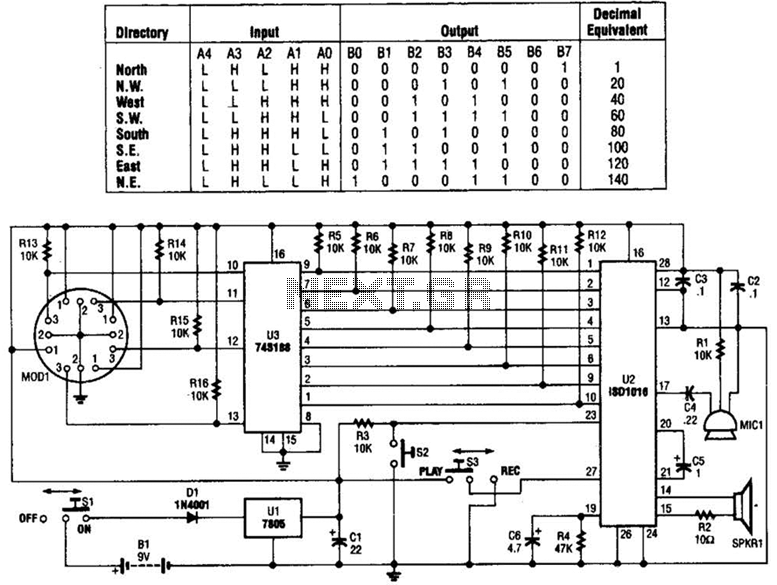
Power Amlifier 40W Class A circuit
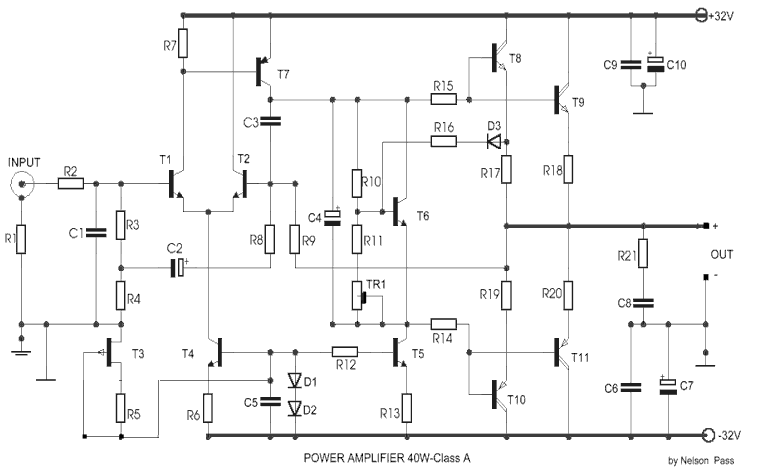
This is an audio power amplifier that delivers 40 W at 8 ohms in Class A operation. The power transistors are continuously active, enabling a substantial current to flow.
The audio power amplifier described operates in Class A mode, which is known for its linearity and low distortion, making it suitable for high-fidelity audio applications. In this configuration, the amplifier maintains the output transistors in an "always on" state, allowing them to conduct current continuously. This results in a quiescent current that is relatively high, leading to improved signal fidelity but also increased power consumption and heat generation.
The output stage of the amplifier is designed to deliver 40 watts of power into an 8-ohm load, which is a standard impedance for many audio speakers. The choice of Class A operation provides excellent sound quality, as it minimizes crossover distortion, a common issue in other amplifier classes, particularly Class B and Class AB.
To ensure optimal performance, the amplifier circuit includes various components such as biasing networks to set the operating point of the transistors, feedback loops to stabilize gain and improve linearity, and protection circuits to prevent damage from overcurrent or overheating. The power supply must be robust enough to handle the continuous current demand, which is essential for maintaining performance during dynamic audio signals.
Thermal management is also a critical aspect of the design. Heat sinks or other cooling mechanisms are typically incorporated to dissipate the heat generated by the power transistors during operation. This ensures reliability and longevity of the amplifier, especially under prolonged use at high output levels.
Overall, this audio power amplifier is engineered to deliver high-quality sound reproduction with significant power output, making it suitable for various audio applications, including home audio systems and professional sound reinforcement.This is an audio power amplifier, with its final stage giving 40 W/8 ? at Class A. The power transistors, are always ON, allowing a very high current to flow.. 🔗 External reference
The audio power amplifier described operates in Class A mode, which is known for its linearity and low distortion, making it suitable for high-fidelity audio applications. In this configuration, the amplifier maintains the output transistors in an "always on" state, allowing them to conduct current continuously. This results in a quiescent current that is relatively high, leading to improved signal fidelity but also increased power consumption and heat generation.
The output stage of the amplifier is designed to deliver 40 watts of power into an 8-ohm load, which is a standard impedance for many audio speakers. The choice of Class A operation provides excellent sound quality, as it minimizes crossover distortion, a common issue in other amplifier classes, particularly Class B and Class AB.
To ensure optimal performance, the amplifier circuit includes various components such as biasing networks to set the operating point of the transistors, feedback loops to stabilize gain and improve linearity, and protection circuits to prevent damage from overcurrent or overheating. The power supply must be robust enough to handle the continuous current demand, which is essential for maintaining performance during dynamic audio signals.
Thermal management is also a critical aspect of the design. Heat sinks or other cooling mechanisms are typically incorporated to dissipate the heat generated by the power transistors during operation. This ensures reliability and longevity of the amplifier, especially under prolonged use at high output levels.
Overall, this audio power amplifier is engineered to deliver high-quality sound reproduction with significant power output, making it suitable for various audio applications, including home audio systems and professional sound reinforcement.This is an audio power amplifier, with its final stage giving 40 W/8 ? at Class A. The power transistors, are always ON, allowing a very high current to flow.. 🔗 External reference