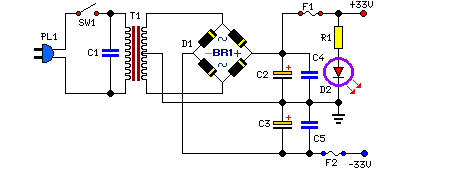
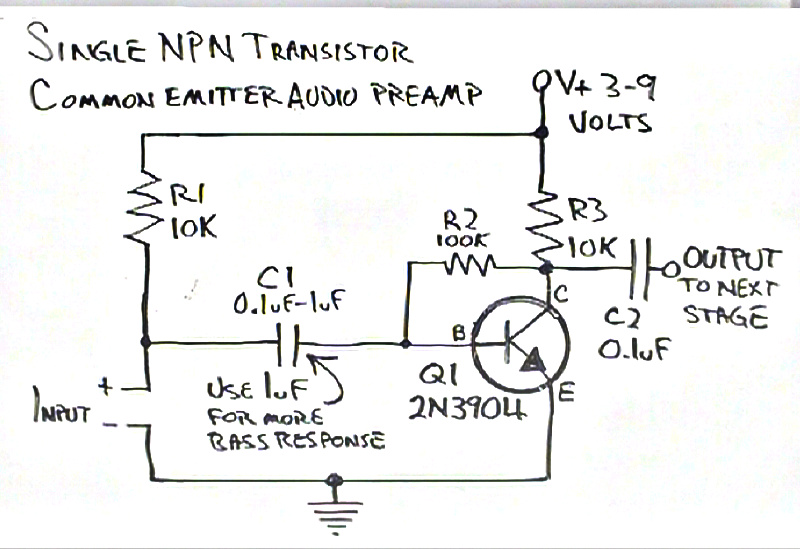
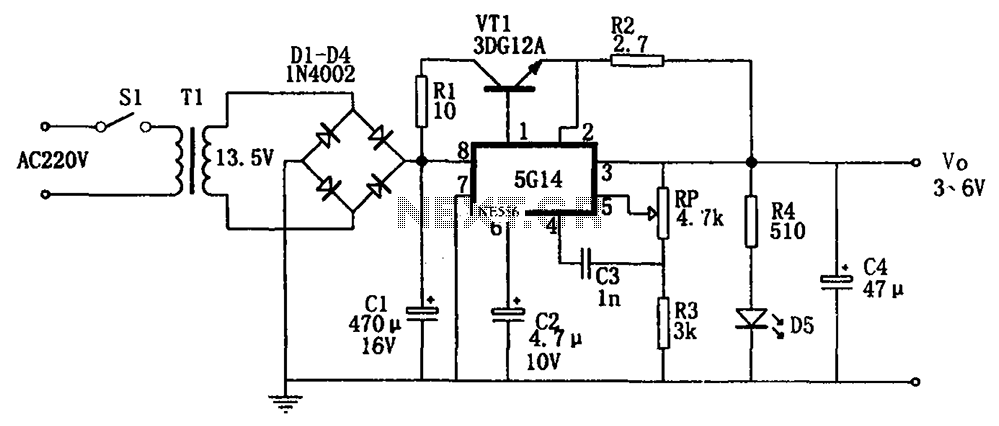
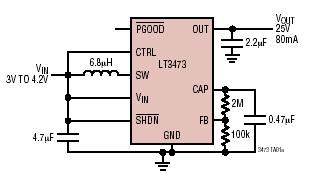
power amp 100w with v mosfet
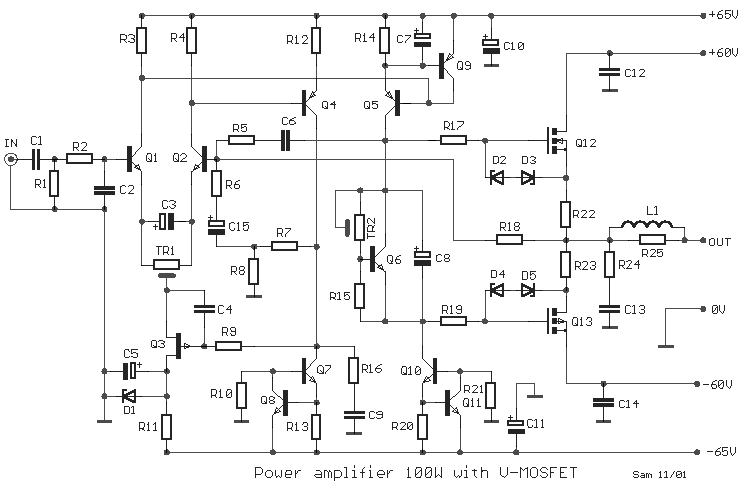
One design employs the exit transistor technology of V-MOSFETs. These transistors provide numerous advantages over standard bipolar transistors, including high speed, thermal stability, and low distortion.
V-MOSFETs, or Vertical Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors, are a specific type of MOSFET that utilizes a vertical structure to enhance performance characteristics. In electronic circuit design, these components are often favored for their superior switching speeds, which are essential in high-frequency applications such as RF amplifiers and digital circuits.
The thermal stability of V-MOSFETs is another significant advantage, as they can operate effectively over a wider range of temperatures without the risk of thermal runaway, a common issue with bipolar transistors. This stability is critical in applications where the operating environment may vary significantly, ensuring consistent performance.
Low distortion is a key characteristic of V-MOSFETs, making them ideal for audio applications where signal fidelity is paramount. The reduced distortion levels contribute to cleaner sound reproduction in amplifiers, making them a preferred choice for high-fidelity audio systems.
In circuit design, the integration of V-MOSFETs can lead to more compact and efficient designs due to their smaller size compared to bipolar transistors. This compactness allows for higher density layouts, which is particularly beneficial in modern electronic devices where space is at a premium.
Overall, the use of V-MOSFET technology in circuit design enhances performance, reliability, and efficiency, making it a valuable choice for engineers looking to optimize their electronic systems.One still designing that it uses in the exit transistor of technology V-mosfet. This transistors to us offer a lot of virtues concerning the simple bipolar transistors, as high speeds, thermic stability, low distortion etc.. 🔗 External reference
V-MOSFETs, or Vertical Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors, are a specific type of MOSFET that utilizes a vertical structure to enhance performance characteristics. In electronic circuit design, these components are often favored for their superior switching speeds, which are essential in high-frequency applications such as RF amplifiers and digital circuits.
The thermal stability of V-MOSFETs is another significant advantage, as they can operate effectively over a wider range of temperatures without the risk of thermal runaway, a common issue with bipolar transistors. This stability is critical in applications where the operating environment may vary significantly, ensuring consistent performance.
Low distortion is a key characteristic of V-MOSFETs, making them ideal for audio applications where signal fidelity is paramount. The reduced distortion levels contribute to cleaner sound reproduction in amplifiers, making them a preferred choice for high-fidelity audio systems.
In circuit design, the integration of V-MOSFETs can lead to more compact and efficient designs due to their smaller size compared to bipolar transistors. This compactness allows for higher density layouts, which is particularly beneficial in modern electronic devices where space is at a premium.
Overall, the use of V-MOSFET technology in circuit design enhances performance, reliability, and efficiency, making it a valuable choice for engineers looking to optimize their electronic systems.One still designing that it uses in the exit transistor of technology V-mosfet. This transistors to us offer a lot of virtues concerning the simple bipolar transistors, as high speeds, thermic stability, low distortion etc.. 🔗 External reference