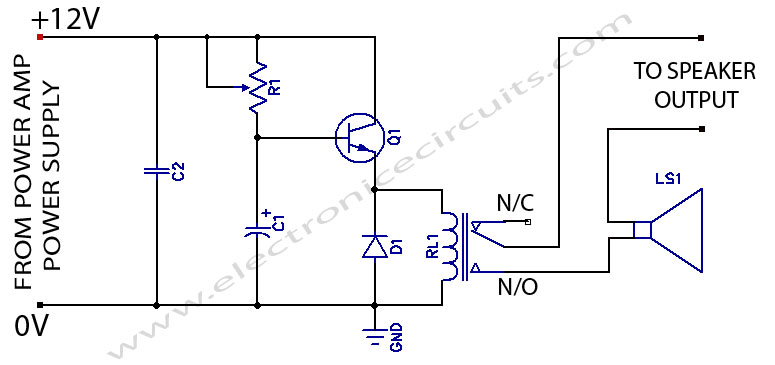
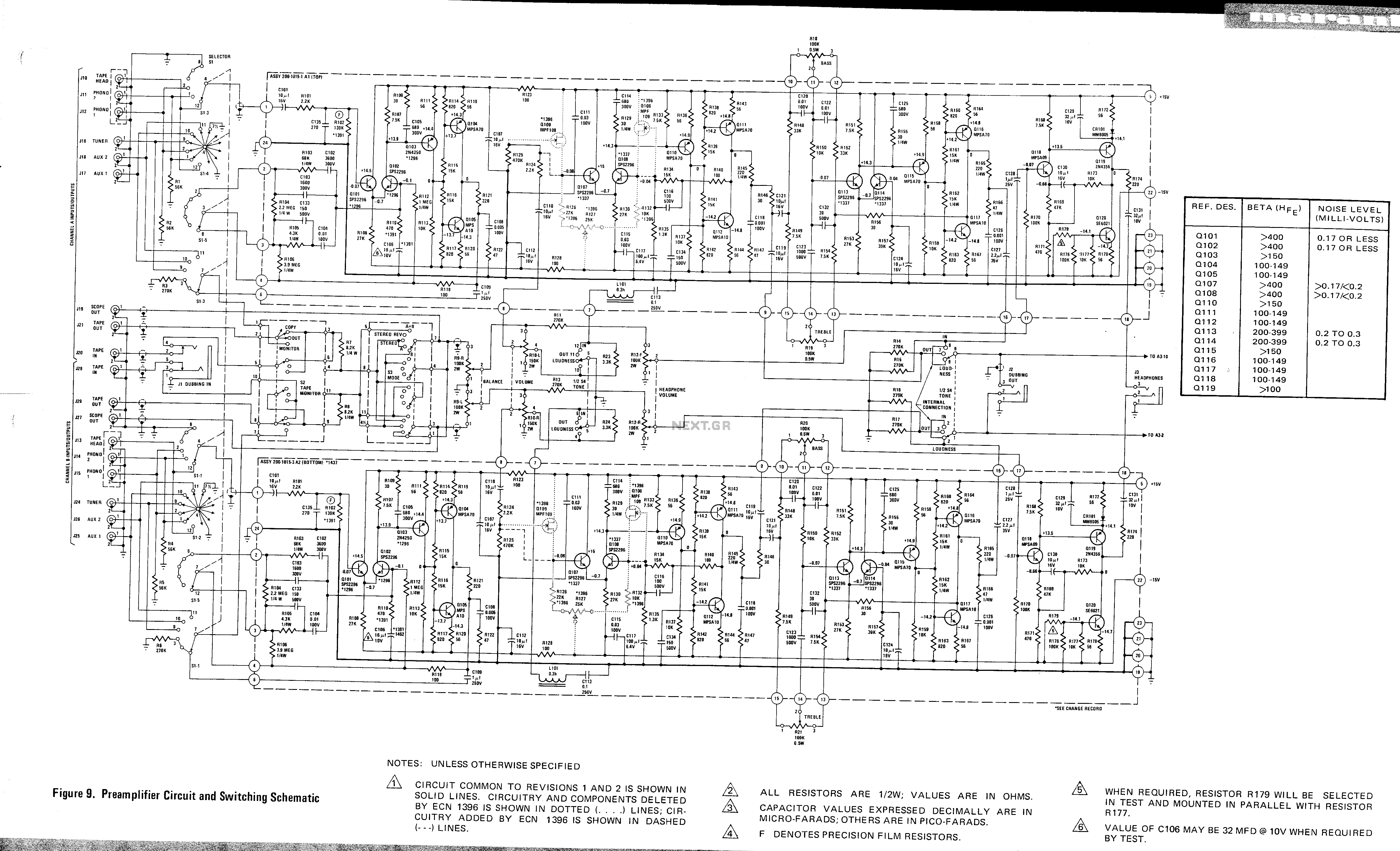
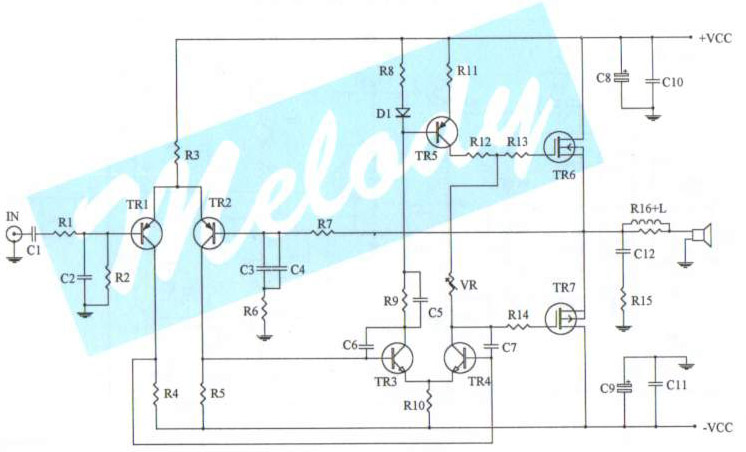
power amplifier 60w
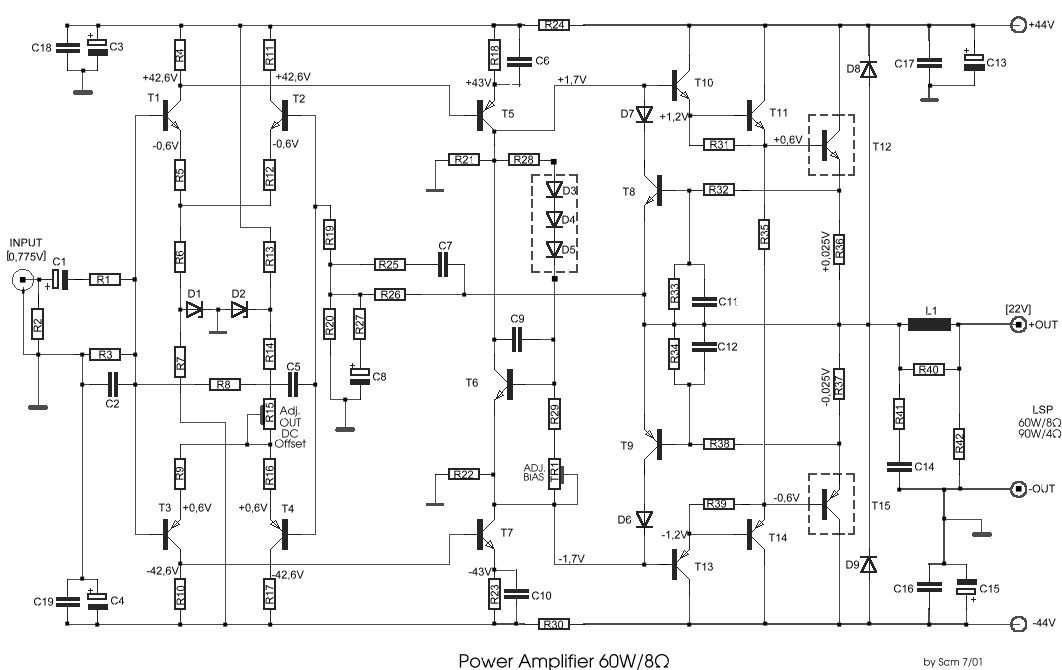
This circuit was designed and manufactured in the 1980s. Since then, it has operated without issues. There are no specific construction challenges, aside from the usual considerations: attention to the power supply requirements, selection of an appropriate heatsink, and proper matching of driver transistors.
The circuit is a product of the technological advancements of the 1980s, characterized by its robust design and reliability. It incorporates a straightforward architecture that ensures stable performance over time. The power supply section is crucial, as it must provide a consistent voltage and current to the circuit. Careful selection of components, such as capacitors and voltage regulators, is necessary to maintain the integrity of the power supply under varying load conditions.
The heatsink is another critical component, as it dissipates heat generated by the circuit during operation. An inadequate heatsink can lead to overheating, which may compromise the performance and longevity of the circuit. The selection process involves calculating the thermal resistance required to keep the junction temperature of the transistors within safe limits, taking into account the maximum power dissipation.
Driver transistors play a vital role in interfacing different sections of the circuit. Proper matching of these transistors ensures optimal signal integrity and minimizes distortion. The circuit design should consider parameters such as the current gain and switching speed of the transistors to achieve the desired performance.
Overall, the circuit reflects the engineering principles of its time, emphasizing reliability, efficiency, and ease of maintenance. It serves as a testament to the design practices of the 1980s, showcasing how thoughtful design considerations can lead to enduring performance.This circuit was designed and manufactured the `80`s. From then it works without problem. It does not present any particular constructional problem, beyond known: the attention in the provided force of power supply - choice suitable heatsink and good matching of drivers transistor.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is a product of the technological advancements of the 1980s, characterized by its robust design and reliability. It incorporates a straightforward architecture that ensures stable performance over time. The power supply section is crucial, as it must provide a consistent voltage and current to the circuit. Careful selection of components, such as capacitors and voltage regulators, is necessary to maintain the integrity of the power supply under varying load conditions.
The heatsink is another critical component, as it dissipates heat generated by the circuit during operation. An inadequate heatsink can lead to overheating, which may compromise the performance and longevity of the circuit. The selection process involves calculating the thermal resistance required to keep the junction temperature of the transistors within safe limits, taking into account the maximum power dissipation.
Driver transistors play a vital role in interfacing different sections of the circuit. Proper matching of these transistors ensures optimal signal integrity and minimizes distortion. The circuit design should consider parameters such as the current gain and switching speed of the transistors to achieve the desired performance.
Overall, the circuit reflects the engineering principles of its time, emphasizing reliability, efficiency, and ease of maintenance. It serves as a testament to the design practices of the 1980s, showcasing how thoughtful design considerations can lead to enduring performance.This circuit was designed and manufactured the `80`s. From then it works without problem. It does not present any particular constructional problem, beyond known: the attention in the provided force of power supply - choice suitable heatsink and good matching of drivers transistor.. 🔗 External reference