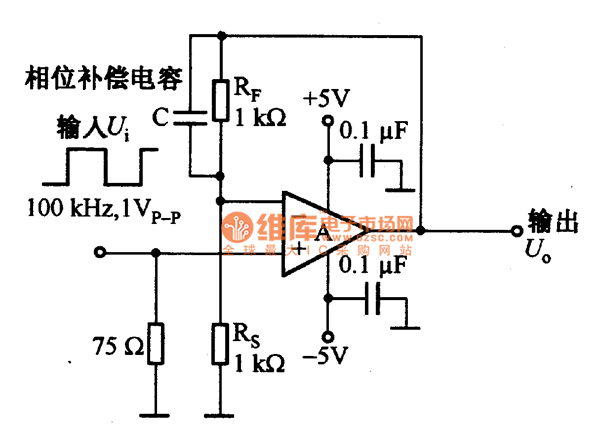
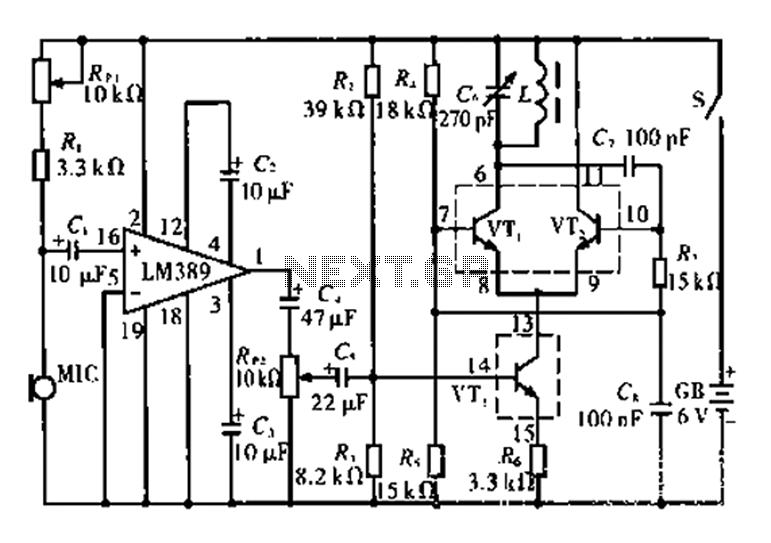
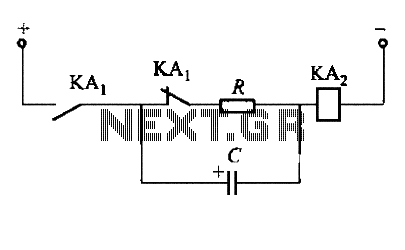
Low-noise switching power supply schematic circuit diagram
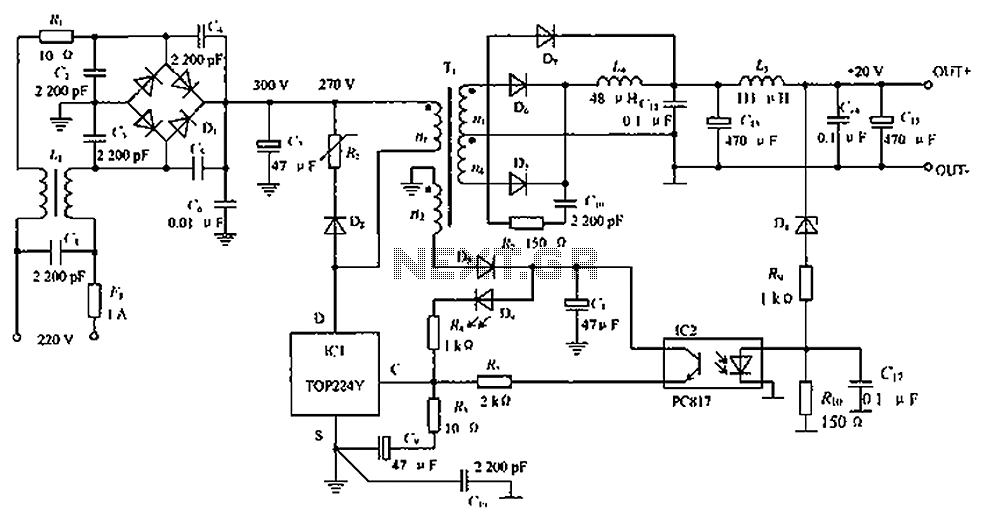
The circuit depicted in the figure is designed to achieve a higher power output by modifying specific components. On the left side of the figure, components R1, L1, D1, and capacitors C1 to C7 form a conventional filtering and rectifying circuit that produces a DC voltage of approximately 30V for the DC-DC converter. The rightmost section of the circuit contains L5, C11, and other standard LC filter components. The voltage feedback circuit, composed of IC2, D8, R9, and R10, creates a closed-loop structure to maintain a stable output voltage. The central part of the DC-DC converter focuses on effectively managing noise reduction within the circuit.
The circuit operates by first converting an AC input into a DC voltage using the rectifying components. The arrangement of R1, L1, D1, and the capacitors (C1 to C7) ensures that the voltage is smoothed and filtered to achieve the desired 30V output. The LC filter on the right, consisting of L5 and C11, further refines the output by attenuating any high-frequency noise that may have been introduced during the conversion process.
The feedback mechanism, facilitated by IC2, D8, R9, and R10, plays a crucial role in maintaining voltage regulation. The feedback loop monitors the output voltage and adjusts the switching elements of the DC-DC converter to ensure that the output remains stable under varying load conditions. This closed-loop control is essential for applications where voltage stability is critical.
In the central section of the circuit, careful attention is given to noise management. This may involve the use of additional filtering components or layout considerations to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure that the circuit operates efficiently. Proper disposal of noise is vital for the reliability of the power supply, particularly in sensitive electronic applications.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes efficient power conversion, stable output voltage, and effective noise reduction, making it suitable for various applications requiring reliable DC power. Circuit shown in Figure, the circuit can achieve greater power output, just change the part of the device. FIG circuit R1 to the left, L1, D1, C1 to C7 are conventional common mode filtering and rectifying circuit to obtain a DC voltage of about 30V DC-DC converter circuit for use; rightmost circuit L5, C11 and other ordinary LC filter circuit; IC2, D8, R9, R10 voltage feedback circuit composition, form a closed loop structure, stable power supply output voltage; the middle part of the DC-DC converter, the key to reducing noise in this circuit is a part of proper disposal.
The circuit operates by first converting an AC input into a DC voltage using the rectifying components. The arrangement of R1, L1, D1, and the capacitors (C1 to C7) ensures that the voltage is smoothed and filtered to achieve the desired 30V output. The LC filter on the right, consisting of L5 and C11, further refines the output by attenuating any high-frequency noise that may have been introduced during the conversion process.
The feedback mechanism, facilitated by IC2, D8, R9, and R10, plays a crucial role in maintaining voltage regulation. The feedback loop monitors the output voltage and adjusts the switching elements of the DC-DC converter to ensure that the output remains stable under varying load conditions. This closed-loop control is essential for applications where voltage stability is critical.
In the central section of the circuit, careful attention is given to noise management. This may involve the use of additional filtering components or layout considerations to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure that the circuit operates efficiently. Proper disposal of noise is vital for the reliability of the power supply, particularly in sensitive electronic applications.
Overall, this circuit design emphasizes efficient power conversion, stable output voltage, and effective noise reduction, making it suitable for various applications requiring reliable DC power. Circuit shown in Figure, the circuit can achieve greater power output, just change the part of the device. FIG circuit R1 to the left, L1, D1, C1 to C7 are conventional common mode filtering and rectifying circuit to obtain a DC voltage of about 30V DC-DC converter circuit for use; rightmost circuit L5, C11 and other ordinary LC filter circuit; IC2, D8, R9, R10 voltage feedback circuit composition, form a closed loop structure, stable power supply output voltage; the middle part of the DC-DC converter, the key to reducing noise in this circuit is a part of proper disposal.