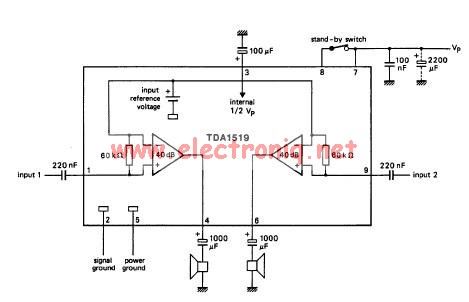
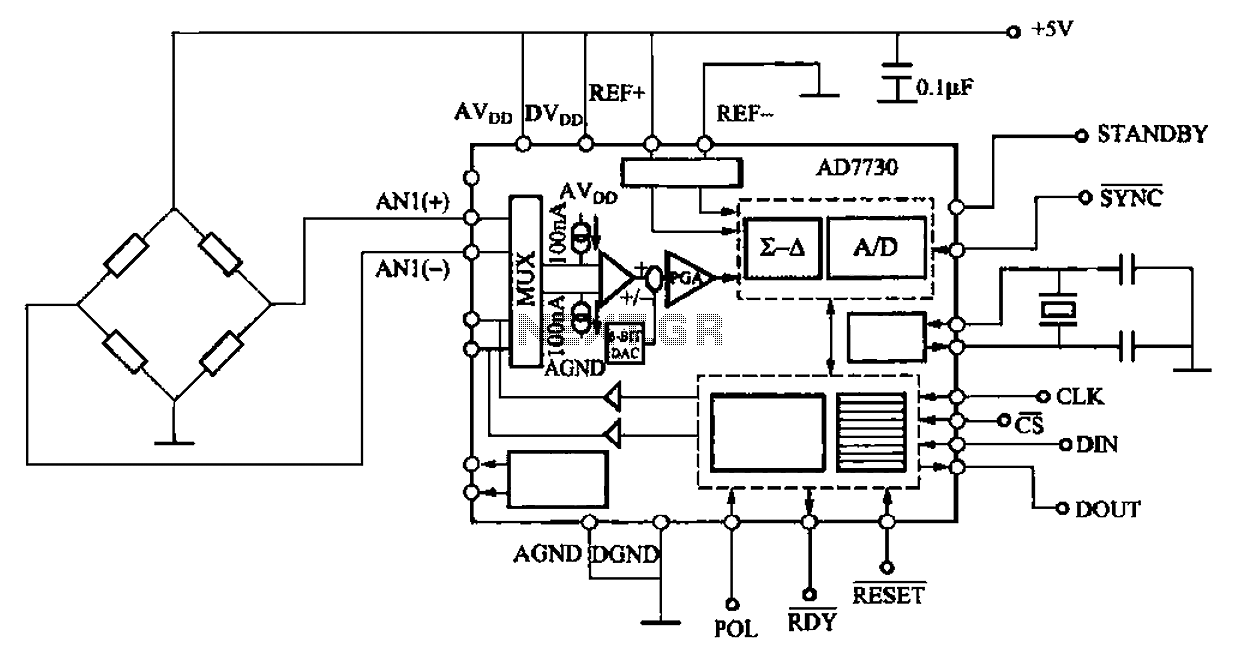
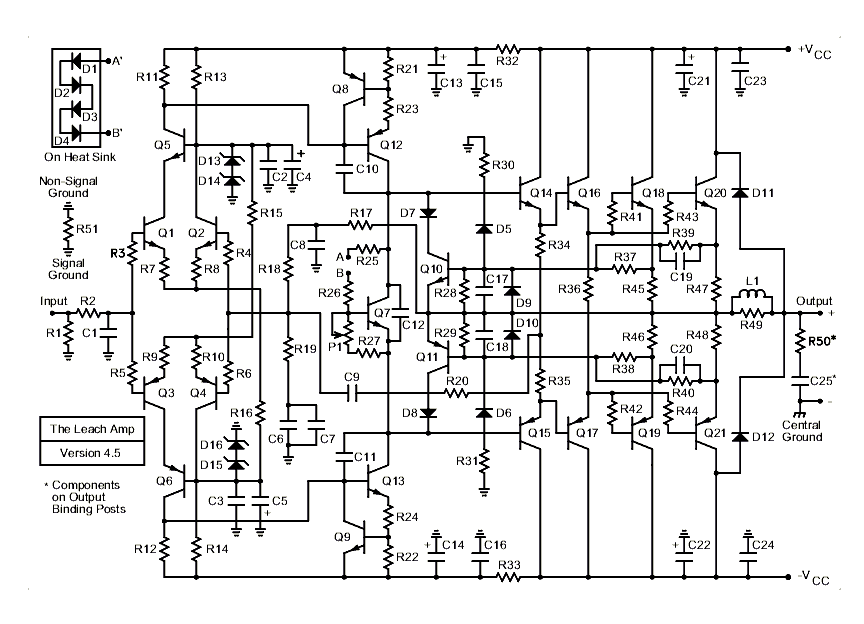
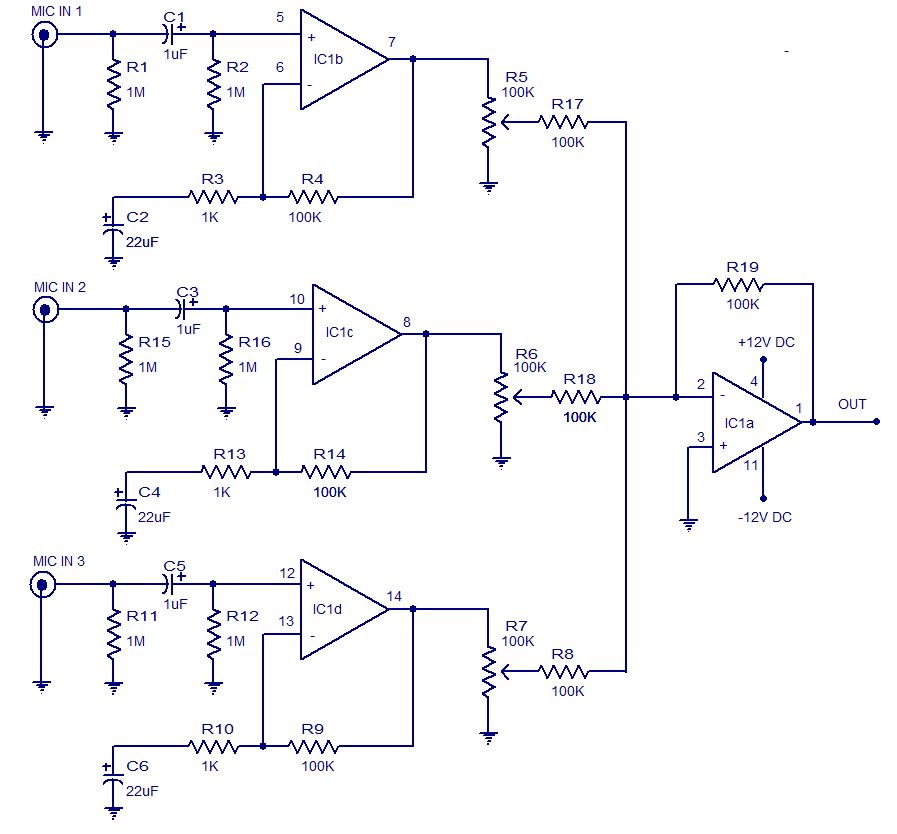
Practical digital amplifier TL084
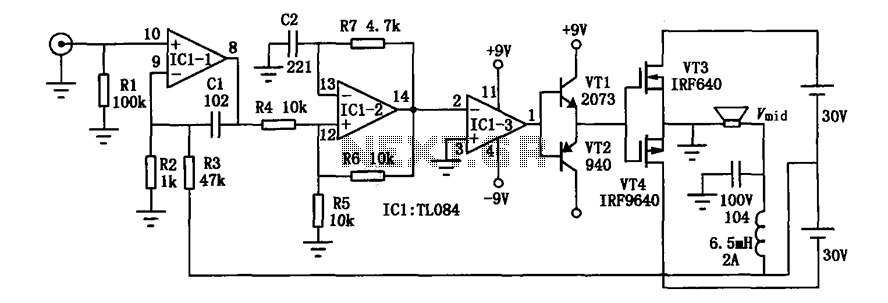
A conventional digital home theater amplifier necessitates a dedicated integrated circuit, which is often produced by a limited number of manufacturers, resulting in higher costs. This circuit element can be produced using standard components, delivering a power output of 50W. It exhibits minimal power consumption under no-load conditions and achieves a full-load efficiency of approximately 85%, demonstrating practical value. However, the final stage power supply is floating, which may lead to poor electromagnetic compatibility. Additionally, the 200kHz carrier is not adequately filtered, and improvements are needed in distortion levels and signal-to-noise ratio.
The described digital home theater amplifier utilizes a dedicated integrated circuit that is essential for its operation. The reliance on a limited number of manufacturers for these integrated circuits often leads to increased production costs. However, the circuit can be designed using standard components, allowing for a power output of 50W, which is suitable for home theater applications.
The amplifier is engineered to operate efficiently, with a no-load power consumption that is nearly negligible. Its full-load efficiency of around 85% indicates that it can deliver substantial power while minimizing energy waste. This efficiency is crucial for maintaining low operational costs and ensuring the longevity of the components used.
Despite its advantages, the amplifier's floating final stage power supply presents challenges in terms of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). This can lead to interference issues, which may affect overall performance. The design should consider incorporating additional filtering and shielding techniques to mitigate these problems.
Furthermore, the presence of a 200kHz carrier signal that is not effectively filtered can introduce unwanted artifacts into the audio output. This can manifest as distortion and a diminished signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), both of which are critical parameters in audio quality. To enhance the performance of the amplifier, it is advisable to implement advanced filtering techniques, such as low-pass filters or active filtering circuits, to eliminate the carrier signal and improve overall sound fidelity.
In conclusion, while the conventional digital home theater amplifier demonstrates practical value through its efficient design and power output, attention must be given to its electromagnetic compatibility and signal integrity. By addressing these issues, the performance and reliability of the amplifier can be significantly enhanced, making it a more competitive option in the market.Conventional digital home theater amplifier requires the use of a dedicated integrated circuit, and such a small integrated circuit manufacturers, the price is higher. This cir cuit element can be an ordinary production, power is 50W, when almost no-load power consumption, full load efficiency of about 85%, has some practical value. But its final stage power supply with floating, electromagnetic compatibility circuit can be poor. Since 200kHz carrier is not filtered out clean, distortion and signal to noise ratio and other indicators have yet to be improved.
The described digital home theater amplifier utilizes a dedicated integrated circuit that is essential for its operation. The reliance on a limited number of manufacturers for these integrated circuits often leads to increased production costs. However, the circuit can be designed using standard components, allowing for a power output of 50W, which is suitable for home theater applications.
The amplifier is engineered to operate efficiently, with a no-load power consumption that is nearly negligible. Its full-load efficiency of around 85% indicates that it can deliver substantial power while minimizing energy waste. This efficiency is crucial for maintaining low operational costs and ensuring the longevity of the components used.
Despite its advantages, the amplifier's floating final stage power supply presents challenges in terms of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). This can lead to interference issues, which may affect overall performance. The design should consider incorporating additional filtering and shielding techniques to mitigate these problems.
Furthermore, the presence of a 200kHz carrier signal that is not effectively filtered can introduce unwanted artifacts into the audio output. This can manifest as distortion and a diminished signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), both of which are critical parameters in audio quality. To enhance the performance of the amplifier, it is advisable to implement advanced filtering techniques, such as low-pass filters or active filtering circuits, to eliminate the carrier signal and improve overall sound fidelity.
In conclusion, while the conventional digital home theater amplifier demonstrates practical value through its efficient design and power output, attention must be given to its electromagnetic compatibility and signal integrity. By addressing these issues, the performance and reliability of the amplifier can be significantly enhanced, making it a more competitive option in the market.Conventional digital home theater amplifier requires the use of a dedicated integrated circuit, and such a small integrated circuit manufacturers, the price is higher. This cir cuit element can be an ordinary production, power is 50W, when almost no-load power consumption, full load efficiency of about 85%, has some practical value. But its final stage power supply with floating, electromagnetic compatibility circuit can be poor. Since 200kHz carrier is not filtered out clean, distortion and signal to noise ratio and other indicators have yet to be improved.