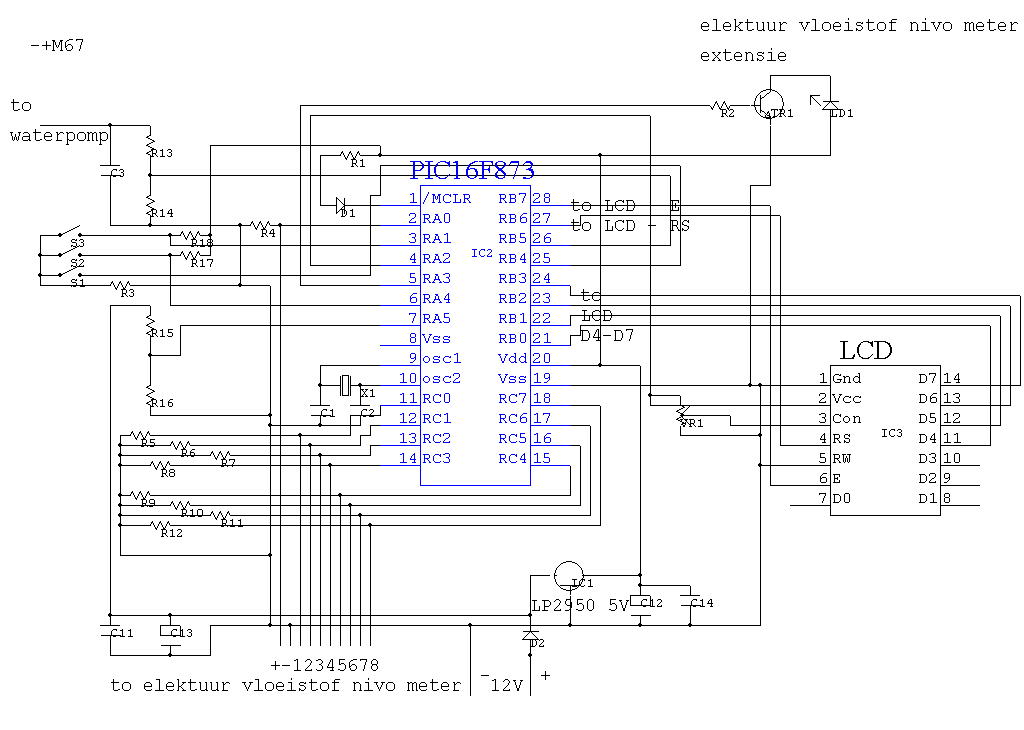
Precision photodiode level detector
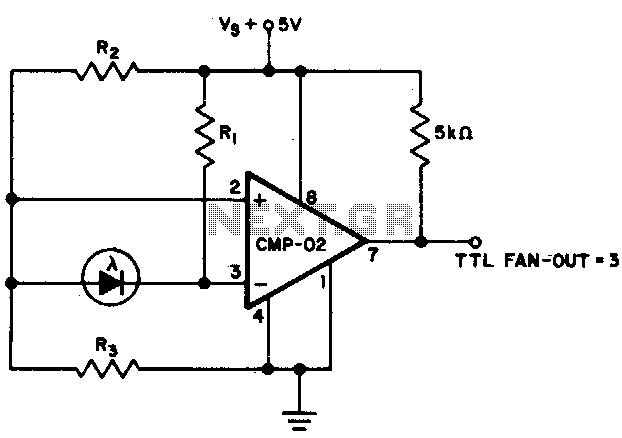
The output state changes at a photodiode current of 0 µA. For R1 = 2 MΩ, R2 = R3 = 5 MΩ.
The described circuit likely involves a photodiode used in conjunction with resistors R1, R2, and R3 to create a voltage divider or a similar configuration that influences the output state based on the current generated by the photodiode. When light strikes the photodiode, it generates a current that varies with the intensity of the light. The critical point mentioned is when this current reaches 0 µA, indicating a threshold at which the output state transitions.
In this configuration, R1, with a resistance of 2 MΩ, may serve as a load resistor for the photodiode. The values of R2 and R3, both at 5 MΩ, suggest they could be configured as pull-up or pull-down resistors, or they might be part of a feedback loop in an operational amplifier setup.
The output state change at 0 µA indicates that the circuit is designed to detect the absence of light or a very low light condition. This output could be used in various applications such as light-sensing alarms, automatic lighting systems, or in optical communication systems where the presence or absence of light signals a state change.
The overall performance of this circuit will depend on the characteristics of the photodiode, including its responsivity and the wavelength of light it is designed to detect, as well as the power supply and any additional components that may be included in the circuit for signal conditioning or amplification. Proper selection and placement of components will ensure that the circuit operates effectively at the specified thresholds and provides reliable output states in response to varying light conditions.The output state changes at a photo diode current of 0 µA For Rl = 2 M, R2 = R3 = 5 M.
The described circuit likely involves a photodiode used in conjunction with resistors R1, R2, and R3 to create a voltage divider or a similar configuration that influences the output state based on the current generated by the photodiode. When light strikes the photodiode, it generates a current that varies with the intensity of the light. The critical point mentioned is when this current reaches 0 µA, indicating a threshold at which the output state transitions.
In this configuration, R1, with a resistance of 2 MΩ, may serve as a load resistor for the photodiode. The values of R2 and R3, both at 5 MΩ, suggest they could be configured as pull-up or pull-down resistors, or they might be part of a feedback loop in an operational amplifier setup.
The output state change at 0 µA indicates that the circuit is designed to detect the absence of light or a very low light condition. This output could be used in various applications such as light-sensing alarms, automatic lighting systems, or in optical communication systems where the presence or absence of light signals a state change.
The overall performance of this circuit will depend on the characteristics of the photodiode, including its responsivity and the wavelength of light it is designed to detect, as well as the power supply and any additional components that may be included in the circuit for signal conditioning or amplification. Proper selection and placement of components will ensure that the circuit operates effectively at the specified thresholds and provides reliable output states in response to varying light conditions.The output state changes at a photo diode current of 0 µA For Rl = 2 M, R2 = R3 = 5 M.