Fluid level meter version 2
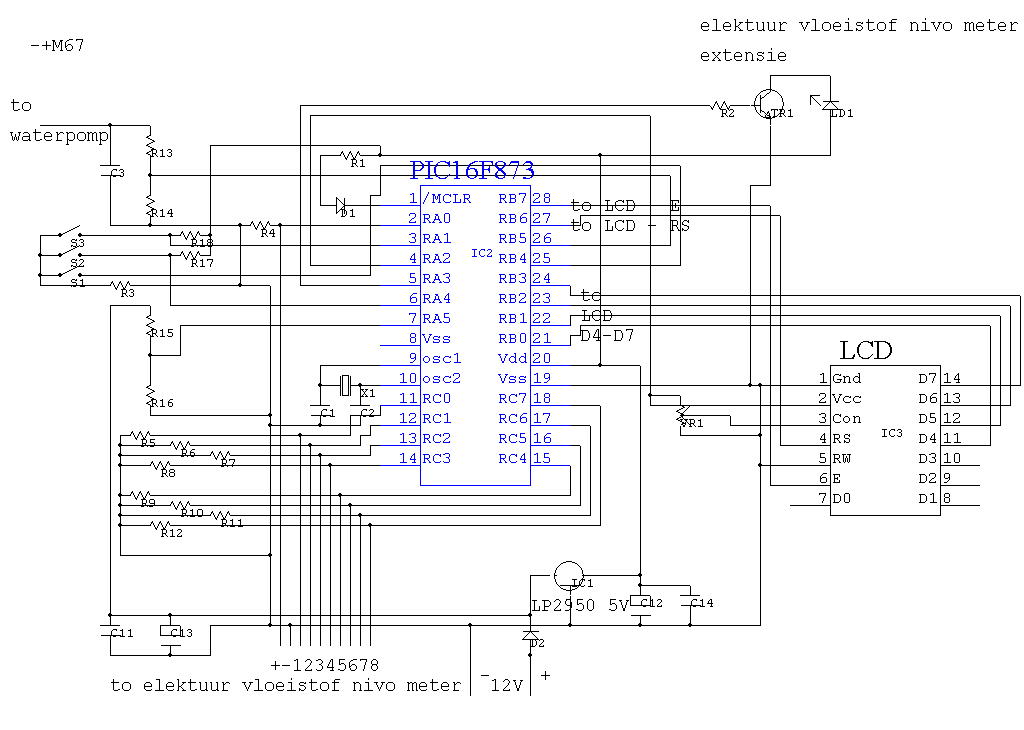
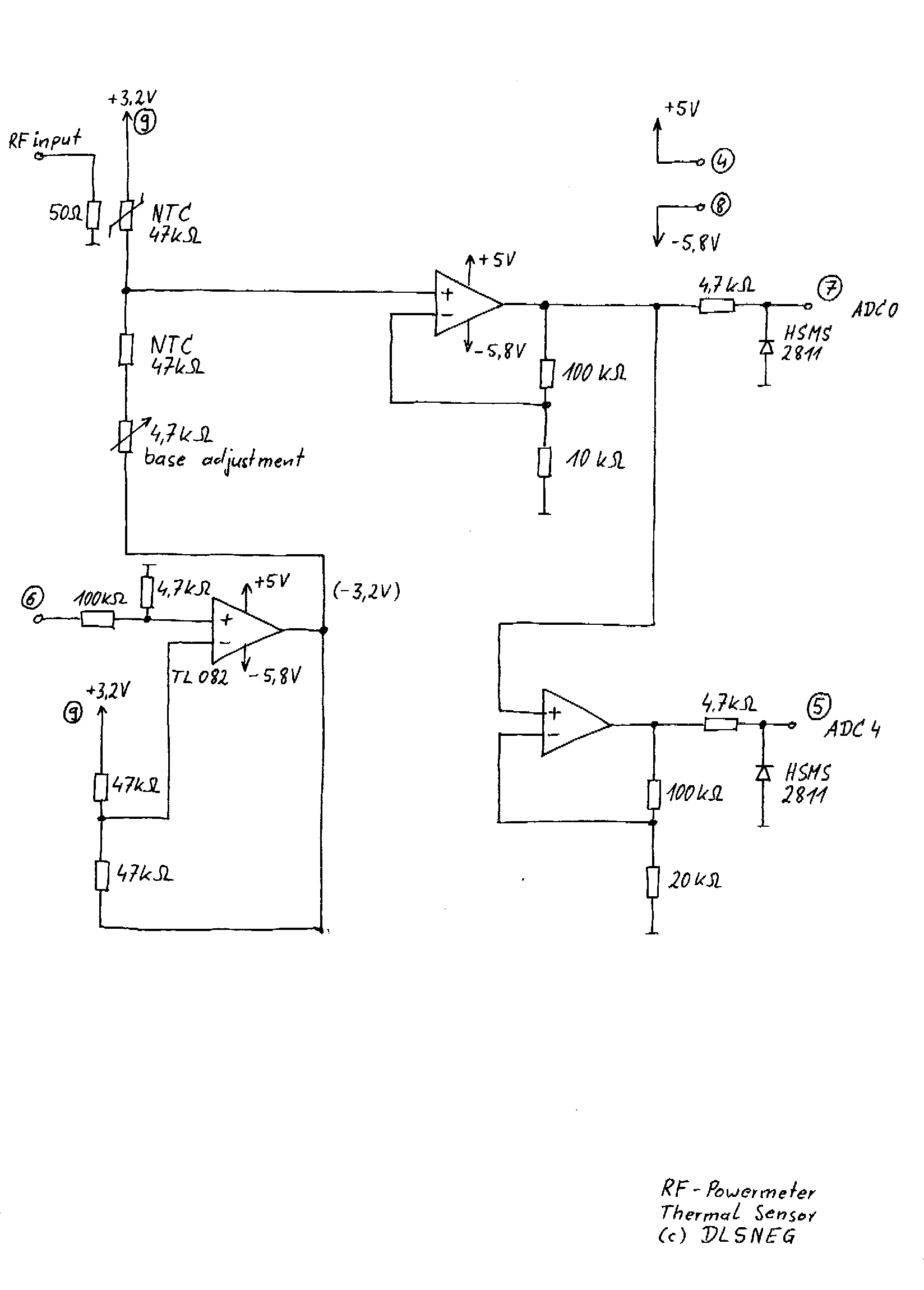
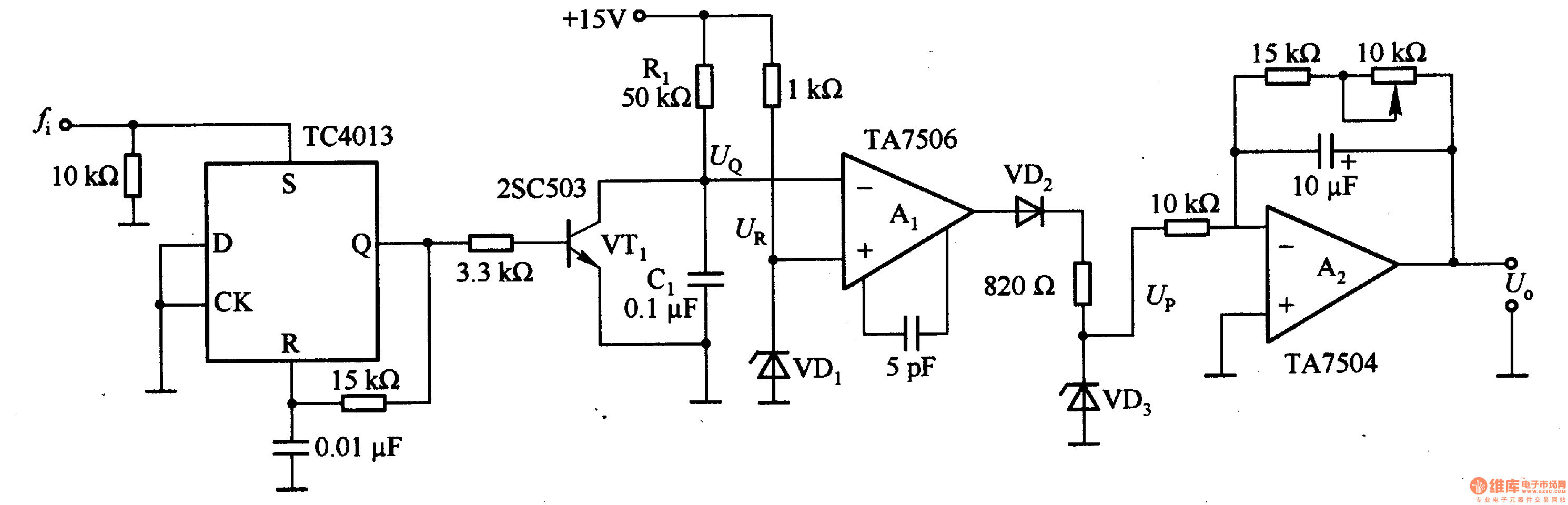
IC4 serves as a counter and oscillator combination, which is the pivotal component of the circuit. The oscillator generates an AC signal that is output on pin 7. This signal is routed through a voltage divider composed of resistors R3 and R4 to pin 3 of IC5, which functions as a multiplexer. Additionally, the same AC signal is directed to a rectifier/demodulator constructed with diodes D1 and resistors R1 and R5. The rectified output is then compared with a constant voltage using IC2, an operational amplifier. When a selected electrode is submerged in water, it introduces an additional load on the AC signal, resulting in a slight decrease in the output from the demodulator. The comparator responds to this change by adjusting its output level. This process occurs rapidly, as the multiplexer is designed to handle one electrode at a time, connecting the AC signal to the chosen electrode.
IC4 functions as a critical counter and oscillator combination within the circuit architecture, facilitating the generation of an alternating current (AC) signal essential for subsequent processing. The oscillator's output, available at pin 7, is integral to the operation of the system. The AC signal is modified by a voltage divider network comprising resistors R3 and R4, which attenuates the signal before it is fed into pin 3 of IC5, a multiplexer that selectively routes the signal to various electrodes.
Simultaneously, the AC signal is also directed to a rectifier/demodulator circuit, which consists of diode D1 and resistors R1 and R5. This configuration converts the AC signal into a direct current (DC) voltage that can be analyzed for variations. The rectified signal is then compared against a stable reference voltage using IC2, which operates as a comparator in this scenario.
The operational dynamics of this system become particularly relevant when an electrode is submerged in water. The introduction of water creates an additional capacitive load on the AC signal, leading to a measurable decrease in the output voltage from the demodulator. This reduction is detected by the comparator, which subsequently alters its output level in response to the change. The rapid response of the system is facilitated by the multiplexer, which is designed to connect the AC signal to one electrode at a time, ensuring that the circuit can effectively monitor multiple electrodes in quick succession. This design allows for efficient and accurate detection of changes in the environment around the electrodes, particularly in applications involving liquid detection.IC4 is a counter/oscillator combination and is the key element in the circuit. The oscillator outputs its AC signal on pin 7. This signal is lead (through voltage divider R3/R4) to pin 3 of IC5 (multiplexer IC) which is used as an input. The same signal is also lead to the rectifier/demodulator build up with D1/R1/R5. The resulting rectified signal is compared (with IC2, an opamp) with a constant voltage. If a selected electrode is under water, there will be an extra load on the AC signal, which causes the output of the demodulator to drop a little bit.
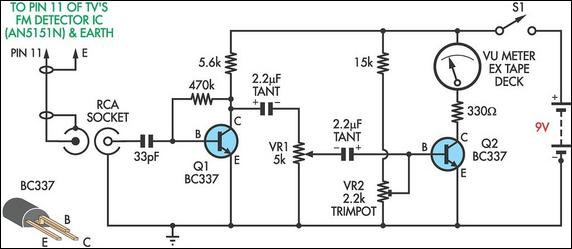
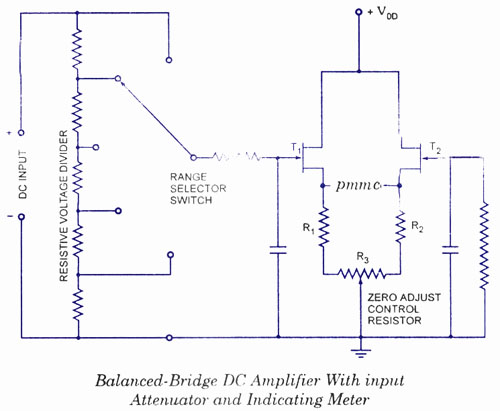
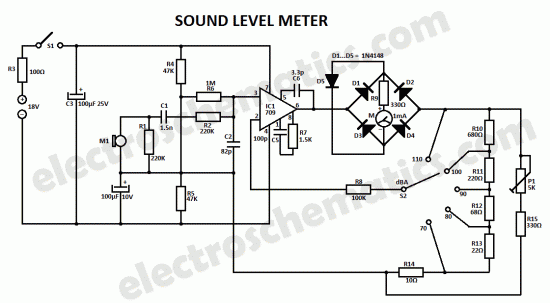
The comparator will react by changing its output level. All this takes a fraction of a second because the multiplexer will only handle one electrode at a time by connecting the AC signal to the selected electrode. 🔗 External reference
IC4 functions as a critical counter and oscillator combination within the circuit architecture, facilitating the generation of an alternating current (AC) signal essential for subsequent processing. The oscillator's output, available at pin 7, is integral to the operation of the system. The AC signal is modified by a voltage divider network comprising resistors R3 and R4, which attenuates the signal before it is fed into pin 3 of IC5, a multiplexer that selectively routes the signal to various electrodes.
Simultaneously, the AC signal is also directed to a rectifier/demodulator circuit, which consists of diode D1 and resistors R1 and R5. This configuration converts the AC signal into a direct current (DC) voltage that can be analyzed for variations. The rectified signal is then compared against a stable reference voltage using IC2, which operates as a comparator in this scenario.
The operational dynamics of this system become particularly relevant when an electrode is submerged in water. The introduction of water creates an additional capacitive load on the AC signal, leading to a measurable decrease in the output voltage from the demodulator. This reduction is detected by the comparator, which subsequently alters its output level in response to the change. The rapid response of the system is facilitated by the multiplexer, which is designed to connect the AC signal to one electrode at a time, ensuring that the circuit can effectively monitor multiple electrodes in quick succession. This design allows for efficient and accurate detection of changes in the environment around the electrodes, particularly in applications involving liquid detection.IC4 is a counter/oscillator combination and is the key element in the circuit. The oscillator outputs its AC signal on pin 7. This signal is lead (through voltage divider R3/R4) to pin 3 of IC5 (multiplexer IC) which is used as an input. The same signal is also lead to the rectifier/demodulator build up with D1/R1/R5. The resulting rectified signal is compared (with IC2, an opamp) with a constant voltage. If a selected electrode is under water, there will be an extra load on the AC signal, which causes the output of the demodulator to drop a little bit.
The comparator will react by changing its output level. All this takes a fraction of a second because the multiplexer will only handle one electrode at a time by connecting the AC signal to the selected electrode. 🔗 External reference