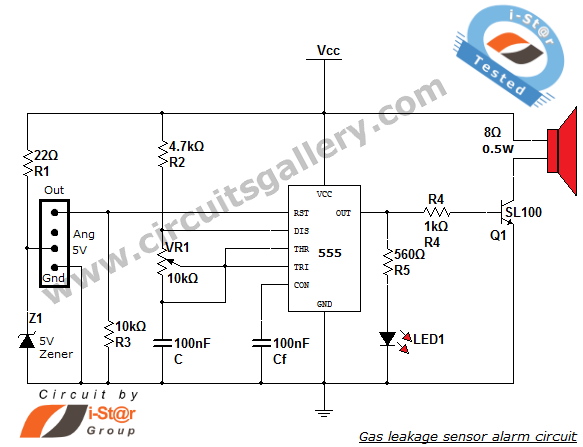
Project
The LM56 Thermostat project circuit diagram involves determining the values of resistors R1, R2, and R3 for the temperature points VT1 and VT2 using specific equations. This electronic circuit featuring the IC LM56 serves as a simple reference project. The LM56 is a low-power, dual-output thermostat characterized by its stable trip temperature points, VT1 and VT2, which are established by dividing the internal reference voltage of 1.250 volts from the LM56 IC using three external resistors (R1, R2, and R3). The LM56 IC provides two digital outputs; output 1 becomes low when the temperature exceeds T1 and returns high when the temperature falls below T1, adjusted by a hysteresis value. The IC LM56 includes several beneficial features, such as an internal voltage reference, an internal temperature sensor, and two internal voltage comparators.
The LM56 Thermostat circuit utilizes the LM56 integrated circuit, which is designed for low-power applications requiring temperature control. The primary function of this circuit is to monitor temperature and provide corresponding digital outputs based on predefined threshold levels. The circuit operates by utilizing a voltage divider configuration formed by the resistors R1, R2, and R3, which sets the reference voltage levels for the temperature thresholds VT1 and VT2.
In the circuit, the internal voltage reference of the LM56 (1.250 volts) is divided down to create the reference voltages that correspond to the desired temperature set points. The values of R1, R2, and R3 can be calculated using the following equations:
1. VT1 = Vref * (R2 / (R1 + R2))
2. VT2 = Vref * (R3 / (R2 + R3))
Where Vref is the internal reference voltage of the LM56. The output behavior of the LM56 is defined such that when the measured temperature exceeds the upper threshold (T1), output 1 transitions to a low state, indicating that the temperature is above the setpoint. Conversely, when the temperature drops below T1, output 1 returns to a high state, allowing for control actions or notifications to be triggered.
The hysteresis feature is essential for preventing rapid toggling of the output state around the threshold temperature, providing stability in the control system. The internal temperature sensor and voltage comparators enhance the functionality of the LM56, allowing for precise temperature monitoring and control.
This circuit can be utilized in various applications, such as HVAC systems, refrigeration units, and other temperature-sensitive equipment, where reliable temperature regulation is crucial. The design simplicity and effectiveness of the LM56 thermostat make it an excellent choice for engineers and hobbyists seeking to implement temperature control solutions in their projects.The values of LM56 Thermostat project Circuit diagram of R1, R2 and R3 for the points of travel, VT1 and VT2 can be determined using the subsequent equations. This thermostat of electronic circuit with IC LM56 diagram what simple project, you can use as reference.
As you know, IC LM56 is correct double output thermostat low power characterized by National Semiconductors. trip temperature stable 2 points called VT1 and VT2 are made with dividing the LM56 IC 1, 250 reference internal voltage volts by three outside resistors (R1, R2 and R3) component. There are 2 digital outputs for LM56 IC which is that output1 becomes weak when the temperature increases over T1 and goes high when the temperature decreases below (temperature T1 ±Hysteresis).
Component IC LM56 has a variety of useful features as internal voltage reference internal temperature sensor, 2 internal voltage comparators, etc. 🔗 External reference
The LM56 Thermostat circuit utilizes the LM56 integrated circuit, which is designed for low-power applications requiring temperature control. The primary function of this circuit is to monitor temperature and provide corresponding digital outputs based on predefined threshold levels. The circuit operates by utilizing a voltage divider configuration formed by the resistors R1, R2, and R3, which sets the reference voltage levels for the temperature thresholds VT1 and VT2.
In the circuit, the internal voltage reference of the LM56 (1.250 volts) is divided down to create the reference voltages that correspond to the desired temperature set points. The values of R1, R2, and R3 can be calculated using the following equations:
1. VT1 = Vref * (R2 / (R1 + R2))
2. VT2 = Vref * (R3 / (R2 + R3))
Where Vref is the internal reference voltage of the LM56. The output behavior of the LM56 is defined such that when the measured temperature exceeds the upper threshold (T1), output 1 transitions to a low state, indicating that the temperature is above the setpoint. Conversely, when the temperature drops below T1, output 1 returns to a high state, allowing for control actions or notifications to be triggered.
The hysteresis feature is essential for preventing rapid toggling of the output state around the threshold temperature, providing stability in the control system. The internal temperature sensor and voltage comparators enhance the functionality of the LM56, allowing for precise temperature monitoring and control.
This circuit can be utilized in various applications, such as HVAC systems, refrigeration units, and other temperature-sensitive equipment, where reliable temperature regulation is crucial. The design simplicity and effectiveness of the LM56 thermostat make it an excellent choice for engineers and hobbyists seeking to implement temperature control solutions in their projects.The values of LM56 Thermostat project Circuit diagram of R1, R2 and R3 for the points of travel, VT1 and VT2 can be determined using the subsequent equations. This thermostat of electronic circuit with IC LM56 diagram what simple project, you can use as reference.
As you know, IC LM56 is correct double output thermostat low power characterized by National Semiconductors. trip temperature stable 2 points called VT1 and VT2 are made with dividing the LM56 IC 1, 250 reference internal voltage volts by three outside resistors (R1, R2 and R3) component. There are 2 digital outputs for LM56 IC which is that output1 becomes weak when the temperature increases over T1 and goes high when the temperature decreases below (temperature T1 ±Hysteresis).
Component IC LM56 has a variety of useful features as internal voltage reference internal temperature sensor, 2 internal voltage comparators, etc. 🔗 External reference