Pulse Width Modulator Using 555 IC
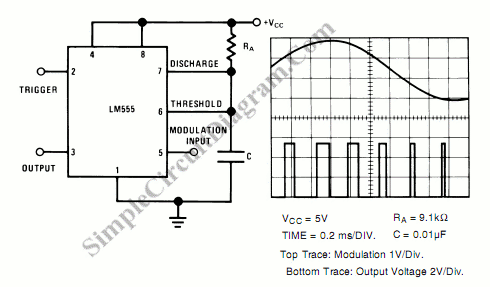
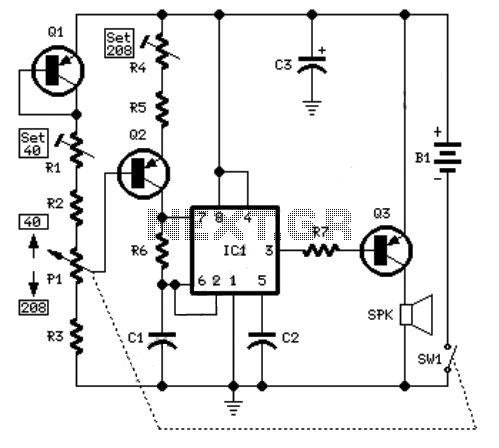
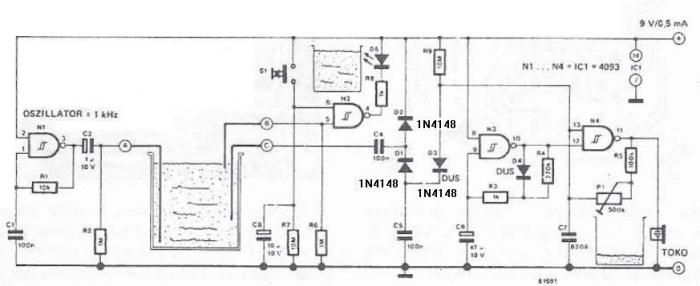
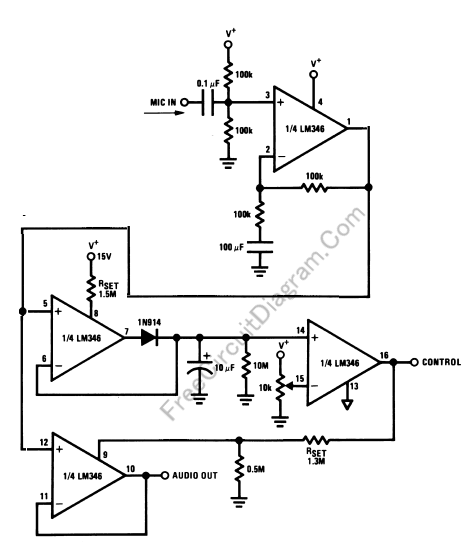
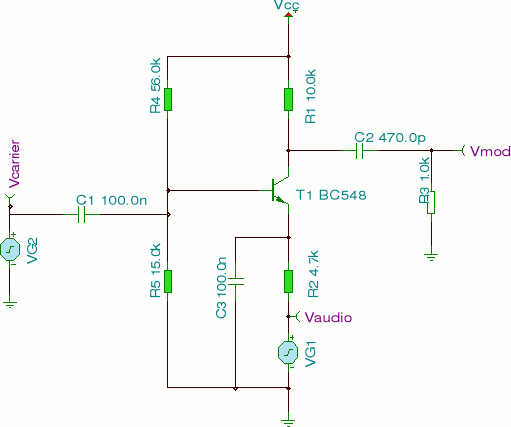
A simple pulse modulator circuit can be constructed using a 555 integrated circuit (IC). The 555 chip features a special modulator input located at pin 5. Below is the schematic diagram of the circuit.
The pulse modulator circuit utilizing the 555 IC operates in astable mode, generating a continuous square wave output. The frequency and duty cycle of the output pulse can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values connected to pins 6 (threshold) and 2 (trigger). The modulator input at pin 5 allows for external modulation of the pulse width, enabling dynamic control over the output signal.
In this configuration, an external voltage can be applied to pin 5, which influences the timing characteristics of the 555 timer. This modulation input can be used for various applications, such as amplitude modulation in communication systems or for generating variable duty cycles in pulse-width modulation (PWM) applications.
The circuit typically includes the following components:
- A 555 timer IC
- Two resistors (R1 and R2) for setting the timing intervals
- A capacitor (C1) to determine the frequency of the output waveform
- An external voltage source connected to pin 5 for modulation
- Output connections for the modulated pulse signal
The schematic diagram would illustrate the connections between these components, showing the configuration necessary for the desired operation. The output waveform can be monitored using an oscilloscope, allowing for adjustments to be made to the resistors and capacitor values to achieve the desired frequency and duty cycle.A very simple pulse modulator circuit can be built using 555 IC. In 555 chip, a special modulator input is available at pin 5. Here is the schematic diagram of.. 🔗 External reference
The pulse modulator circuit utilizing the 555 IC operates in astable mode, generating a continuous square wave output. The frequency and duty cycle of the output pulse can be adjusted by selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values connected to pins 6 (threshold) and 2 (trigger). The modulator input at pin 5 allows for external modulation of the pulse width, enabling dynamic control over the output signal.
In this configuration, an external voltage can be applied to pin 5, which influences the timing characteristics of the 555 timer. This modulation input can be used for various applications, such as amplitude modulation in communication systems or for generating variable duty cycles in pulse-width modulation (PWM) applications.
The circuit typically includes the following components:
- A 555 timer IC
- Two resistors (R1 and R2) for setting the timing intervals
- A capacitor (C1) to determine the frequency of the output waveform
- An external voltage source connected to pin 5 for modulation
- Output connections for the modulated pulse signal
The schematic diagram would illustrate the connections between these components, showing the configuration necessary for the desired operation. The output waveform can be monitored using an oscilloscope, allowing for adjustments to be made to the resistors and capacitor values to achieve the desired frequency and duty cycle.A very simple pulse modulator circuit can be built using 555 IC. In 555 chip, a special modulator input is available at pin 5. Here is the schematic diagram of.. 🔗 External reference