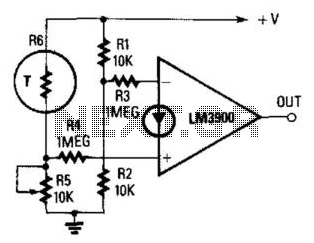
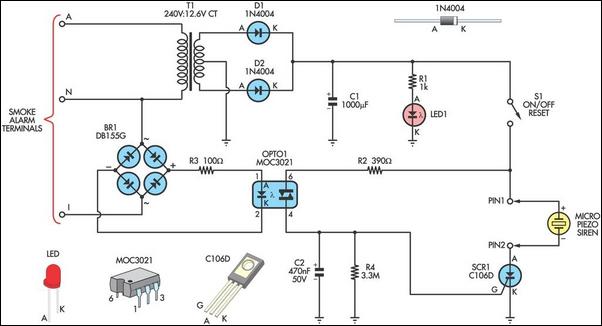
Remote on-off switch
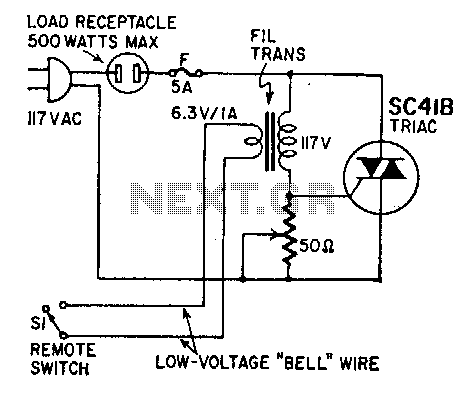
This circuit facilitates power control without the need for line-voltage switch leads. The primary winding of a 6-volt filament transformer is connected between the gate and one of the main terminals of a triac. The secondary winding is linked to a remote switch via standard low-voltage wiring. When the switch is open, the transformer blocks gate current, thereby preventing the triac from firing and supplying power to the equipment. Conversely, closing the switch short-circuits the secondary winding, causing the transformer to saturate and trigger the triac.
The circuit utilizes a triac for efficient power control in low-voltage applications. The triac operates by allowing current to flow in either direction when it is triggered, making it suitable for alternating current (AC) loads. The 6-volt filament transformer serves a dual purpose: it provides isolation from the high-voltage AC line and generates the necessary gate current to trigger the triac.
In this configuration, the primary winding of the transformer is strategically connected to the gate terminal of the triac. The gate voltage is crucial for turning the triac on, and the transformer ensures that this gate voltage is only present when the remote switch is closed. When the switch is open, the primary winding does not receive any voltage, effectively blocking any current from reaching the gate of the triac. This state keeps the triac in an off condition, preventing power from being delivered to the load.
When the remote switch is closed, a short circuit is created across the secondary winding of the transformer. This action leads to the saturation of the transformer, which induces a voltage in the primary winding. The induced voltage provides sufficient gate current to the triac, turning it on and allowing current to flow through the load. The circuit design emphasizes safety and simplicity, ensuring that the high-voltage components are isolated from the user while still allowing for remote control of the power supply.
Overall, this circuit is an effective solution for applications that require remote power control without direct handling of line-voltage components, enhancing both safety and operational convenience.This circuit provides power control without running line-voltage switch leads. The primary of a 6-volt filament transformer is connected between the gate and one of the main terminals of a triac. The secondary is connected to the remote switch through ordinary low-voltage line. With switch open, transformer blocks gate current, prevents the triac from firing and applying power to the equipment
Closingthe switch short-circuits the secondary, causing the transformer to saturate and trigger the triac.
The circuit utilizes a triac for efficient power control in low-voltage applications. The triac operates by allowing current to flow in either direction when it is triggered, making it suitable for alternating current (AC) loads. The 6-volt filament transformer serves a dual purpose: it provides isolation from the high-voltage AC line and generates the necessary gate current to trigger the triac.
In this configuration, the primary winding of the transformer is strategically connected to the gate terminal of the triac. The gate voltage is crucial for turning the triac on, and the transformer ensures that this gate voltage is only present when the remote switch is closed. When the switch is open, the primary winding does not receive any voltage, effectively blocking any current from reaching the gate of the triac. This state keeps the triac in an off condition, preventing power from being delivered to the load.
When the remote switch is closed, a short circuit is created across the secondary winding of the transformer. This action leads to the saturation of the transformer, which induces a voltage in the primary winding. The induced voltage provides sufficient gate current to the triac, turning it on and allowing current to flow through the load. The circuit design emphasizes safety and simplicity, ensuring that the high-voltage components are isolated from the user while still allowing for remote control of the power supply.
Overall, this circuit is an effective solution for applications that require remote power control without direct handling of line-voltage components, enhancing both safety and operational convenience.This circuit provides power control without running line-voltage switch leads. The primary of a 6-volt filament transformer is connected between the gate and one of the main terminals of a triac. The secondary is connected to the remote switch through ordinary low-voltage line. With switch open, transformer blocks gate current, prevents the triac from firing and applying power to the equipment
Closingthe switch short-circuits the secondary, causing the transformer to saturate and trigger the triac.