REMOTE TV VOLUME CONTROL
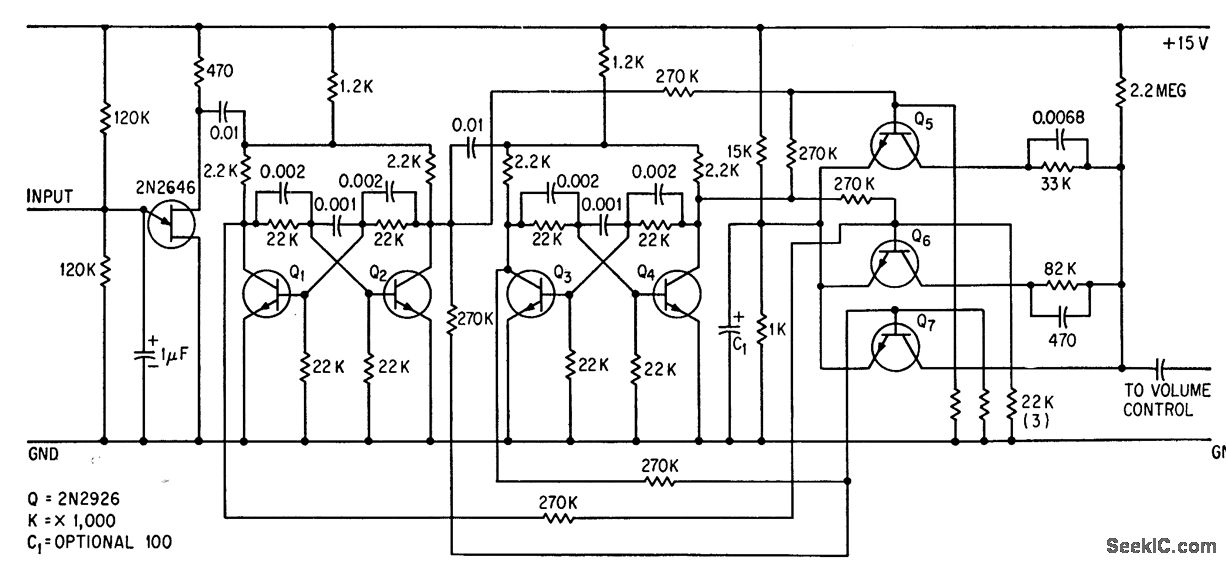
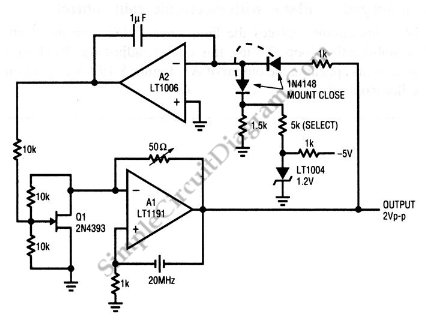
Ultrasonic bursts from a handheld transmitter are detected by a microphone and processed by a UJT threshold detector (2N2646), which generates a trigger pulse. Two cascaded bistable dividers manage three transistors that are connected across the volume control, allowing for full volume (no shunting) and three reduced volume levels.
The circuit operates by utilizing ultrasonic signals emitted from a handheld transmitter. Upon detection by the microphone, these signals are converted into electrical impulses. The UJT threshold detector (2N2646) is pivotal in this process, as it identifies the incoming signal and generates a corresponding trigger pulse. This pulse is essential for the operation of the subsequent bistable dividers.
The two cascaded bistable dividers serve as a control mechanism for the volume adjustment. Each divider can be set to toggle between states, which in turn activates the transistors responsible for modulating the volume output. The transistors are strategically placed across the volume control pathway, allowing for full volume when no shunting occurs, and enabling three distinct lower volume levels when activated.
This configuration provides a versatile solution for volume control in audio applications, particularly in scenarios where remote operation is desired. The use of ultrasonic signals allows for non-invasive control, minimizing the need for physical interaction with the volume control knob. The design emphasizes efficiency and user convenience, making it suitable for various electronic devices that require adjustable sound output.Ultrasonic bursts from handheld transmitter are picked up by microphone and fed to ujt threshold detector 2N2646 that also generates trigger pulse. Two cascaded bistable dividers control three transistors shunted across volume control, to give full volume (no shunting) and three lower volume levels.
-J. H. Phelps, Transistors Instead of Relays Tune TV Volume, Electronics, 37:9, p 32-33. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing ultrasonic signals emitted from a handheld transmitter. Upon detection by the microphone, these signals are converted into electrical impulses. The UJT threshold detector (2N2646) is pivotal in this process, as it identifies the incoming signal and generates a corresponding trigger pulse. This pulse is essential for the operation of the subsequent bistable dividers.
The two cascaded bistable dividers serve as a control mechanism for the volume adjustment. Each divider can be set to toggle between states, which in turn activates the transistors responsible for modulating the volume output. The transistors are strategically placed across the volume control pathway, allowing for full volume when no shunting occurs, and enabling three distinct lower volume levels when activated.
This configuration provides a versatile solution for volume control in audio applications, particularly in scenarios where remote operation is desired. The use of ultrasonic signals allows for non-invasive control, minimizing the need for physical interaction with the volume control knob. The design emphasizes efficiency and user convenience, making it suitable for various electronic devices that require adjustable sound output.Ultrasonic bursts from handheld transmitter are picked up by microphone and fed to ujt threshold detector 2N2646 that also generates trigger pulse. Two cascaded bistable dividers control three transistors shunted across volume control, to give full volume (no shunting) and three lower volume levels.
-J. H. Phelps, Transistors Instead of Relays Tune TV Volume, Electronics, 37:9, p 32-33. 🔗 External reference