Light control automatic energy-saving LED lights circuit
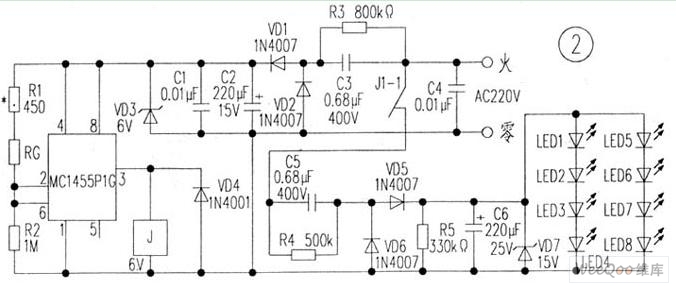
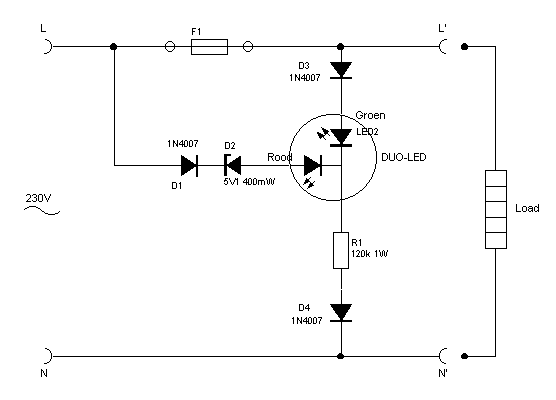
The circuit is depicted in Figure 1, while the electrical schematic diagram is presented in Figure 2. The AC voltage of 220V is reduced by components C3 and R3. The diodes VD1 and VD2 rectify the voltage, and capacitors C2 and C1 filter the output to obtain a smooth direct current. A voltage-regulator diode stabilizes the output voltage at 6V, which powers the MC1455P1G and a photosensitive resistor. During the daytime, the photosensitive resistor R...
The circuit operates by first stepping down the high voltage AC input of 220V through a resistor-capacitor (RC) network consisting of C3 and R3. This reduction is crucial for protecting downstream components from high voltage. The resulting AC voltage is then passed through two diodes, VD1 and VD2, configured in a bridge rectifier arrangement. This configuration allows for the conversion of the AC voltage into pulsating DC voltage.
Following rectification, the capacitors C2 and C1 play a vital role in smoothing the pulsating DC. C2 is typically larger and serves to filter out the majority of the ripple, while C1 provides additional filtering to ensure a more stable DC output. The combined effect of these capacitors is to produce a smooth, steady voltage supply suitable for sensitive electronic components.
The voltage-regulator diode is essential for maintaining a consistent output voltage of 6V. This regulated voltage is crucial for the proper operation of the MC1455P1G, which is a timer IC used in various applications, including timing and pulse generation. The MC1455P1G requires a stable voltage to function correctly, and the regulator ensures that fluctuations in the input voltage do not affect its performance.
Additionally, the circuit includes a photosensitive resistor, which is sensitive to light levels. During the daytime, the resistance of this component decreases, allowing more current to flow through the circuit. This feature can be used in applications such as light-activated switches or automatic lighting systems, where the circuit responds to ambient light levels.
Overall, this schematic illustrates a well-designed power supply and control circuit that effectively manages high voltage AC input, converts it to a stable low voltage DC output, and incorporates a light-sensitive element for responsive operation in varying light conditions.Circuit is shown in Figure 1,electrical schematic diagram is shown in Figure 2. The voltage AC220V is reduced by C3,R3 discharges,VD1 and VD2 rectify,C2 and C1 filter and get a smooth direct current,the voltage-regulator diode stabilizes the voltage in 6V and supplys the power for MC1455P1G and photosensitive resistor.In the daytime,photosensitive resistor R.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by first stepping down the high voltage AC input of 220V through a resistor-capacitor (RC) network consisting of C3 and R3. This reduction is crucial for protecting downstream components from high voltage. The resulting AC voltage is then passed through two diodes, VD1 and VD2, configured in a bridge rectifier arrangement. This configuration allows for the conversion of the AC voltage into pulsating DC voltage.
Following rectification, the capacitors C2 and C1 play a vital role in smoothing the pulsating DC. C2 is typically larger and serves to filter out the majority of the ripple, while C1 provides additional filtering to ensure a more stable DC output. The combined effect of these capacitors is to produce a smooth, steady voltage supply suitable for sensitive electronic components.
The voltage-regulator diode is essential for maintaining a consistent output voltage of 6V. This regulated voltage is crucial for the proper operation of the MC1455P1G, which is a timer IC used in various applications, including timing and pulse generation. The MC1455P1G requires a stable voltage to function correctly, and the regulator ensures that fluctuations in the input voltage do not affect its performance.
Additionally, the circuit includes a photosensitive resistor, which is sensitive to light levels. During the daytime, the resistance of this component decreases, allowing more current to flow through the circuit. This feature can be used in applications such as light-activated switches or automatic lighting systems, where the circuit responds to ambient light levels.
Overall, this schematic illustrates a well-designed power supply and control circuit that effectively manages high voltage AC input, converts it to a stable low voltage DC output, and incorporates a light-sensitive element for responsive operation in varying light conditions.Circuit is shown in Figure 1,electrical schematic diagram is shown in Figure 2. The voltage AC220V is reduced by C3,R3 discharges,VD1 and VD2 rectify,C2 and C1 filter and get a smooth direct current,the voltage-regulator diode stabilizes the voltage in 6V and supplys the power for MC1455P1G and photosensitive resistor.In the daytime,photosensitive resistor R.. 🔗 External reference