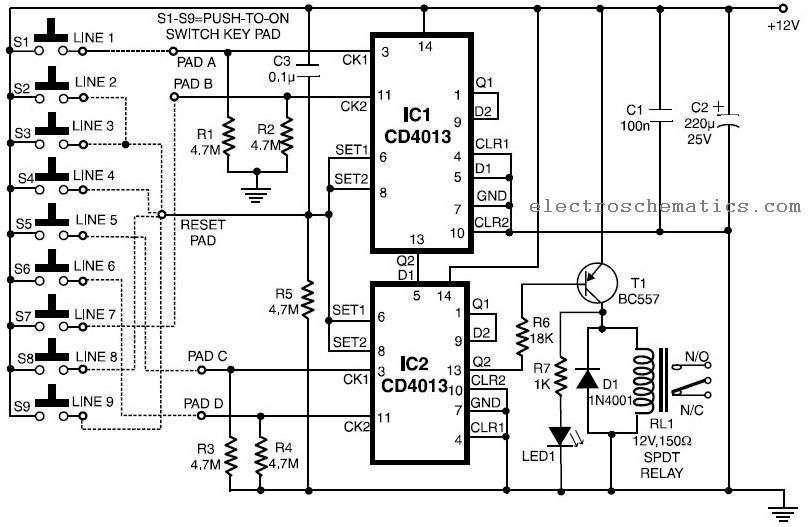
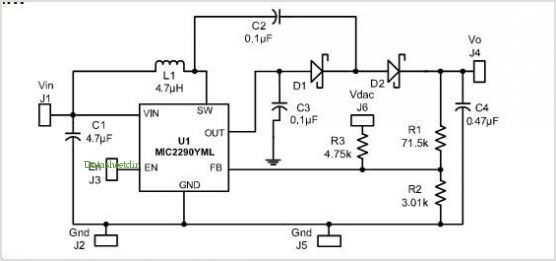
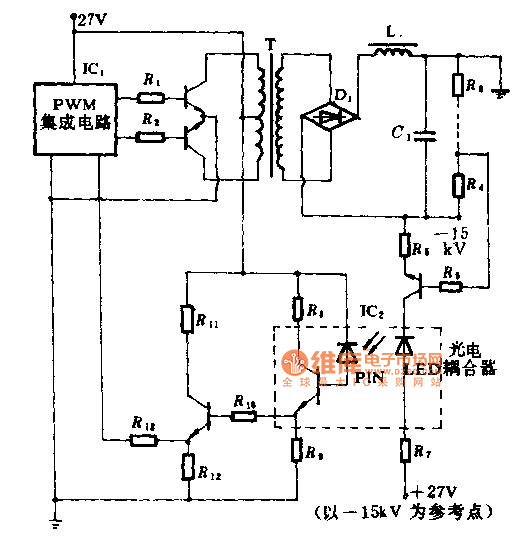
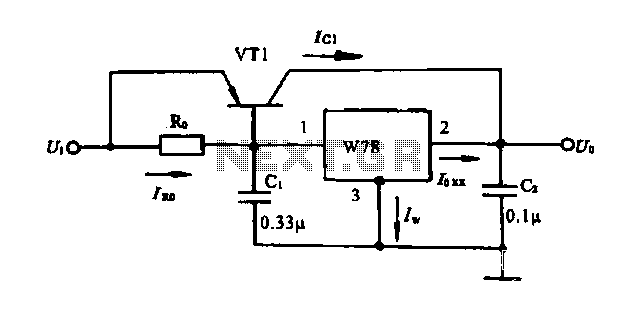
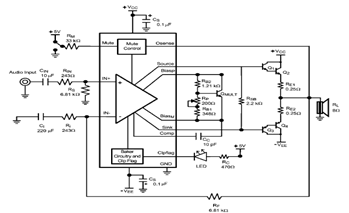
Resolver Application Data

Application notes on resolvers as devices for velocity and position encoding, including potentiometers, incremental encoders, absolute encoders, resolvers, and inductosyns.
Resolvers are electromechanical devices that convert angular position or velocity into an electrical signal. They are commonly used in applications requiring precise measurement of rotational position and speed. Potentiometers serve a similar function but are typically less accurate and are often used in less demanding applications. Incremental encoders provide information about the position and direction of movement but do not retain absolute position information when power is lost. In contrast, absolute encoders provide a unique position value for each distinct shaft position, ensuring that the position is known even after a power interruption.
The resolver operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction and typically consists of a rotor and stator. The rotor is connected to the shaft whose position is being measured, while the stator is excited with an alternating current. The output signals from the resolver can be converted into digital signals through analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for further processing in control systems.
Inductosyns are another type of position sensor that utilize inductive principles to determine angular displacement. They are known for their durability and resistance to environmental factors, making them suitable for harsh conditions.
These devices are integral in various applications, including robotics, aerospace, and industrial automation, where accurate position and velocity feedback are critical for performance and control. The selection of the appropriate encoding device depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as accuracy, resolution, environmental conditions, and cost considerations.Application Notes, Resolvers as Velocity and Position Encoding Devices, Potentiometer, Incremental encoder, Absolute encoder, Resolver, Inductosyn. 🔗 External reference
Resolvers are electromechanical devices that convert angular position or velocity into an electrical signal. They are commonly used in applications requiring precise measurement of rotational position and speed. Potentiometers serve a similar function but are typically less accurate and are often used in less demanding applications. Incremental encoders provide information about the position and direction of movement but do not retain absolute position information when power is lost. In contrast, absolute encoders provide a unique position value for each distinct shaft position, ensuring that the position is known even after a power interruption.
The resolver operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction and typically consists of a rotor and stator. The rotor is connected to the shaft whose position is being measured, while the stator is excited with an alternating current. The output signals from the resolver can be converted into digital signals through analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for further processing in control systems.
Inductosyns are another type of position sensor that utilize inductive principles to determine angular displacement. They are known for their durability and resistance to environmental factors, making them suitable for harsh conditions.
These devices are integral in various applications, including robotics, aerospace, and industrial automation, where accurate position and velocity feedback are critical for performance and control. The selection of the appropriate encoding device depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as accuracy, resolution, environmental conditions, and cost considerations.Application Notes, Resolvers as Velocity and Position Encoding Devices, Potentiometer, Incremental encoder, Absolute encoder, Resolver, Inductosyn. 🔗 External reference