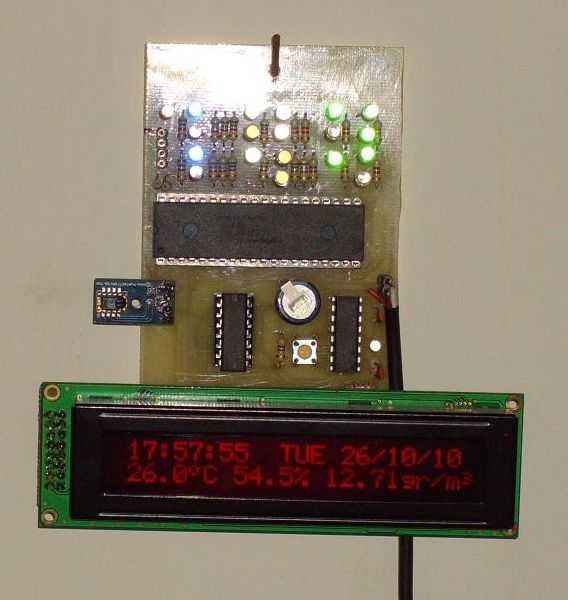
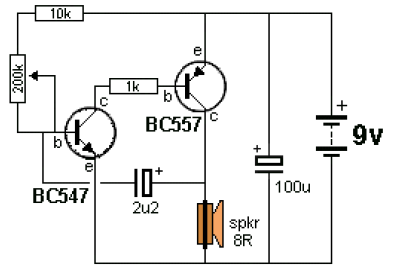
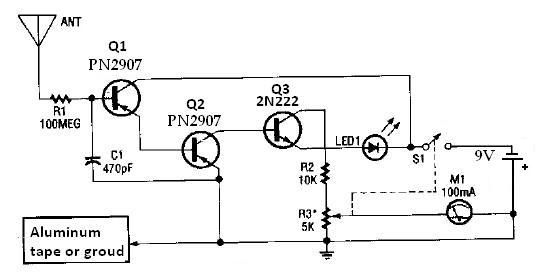
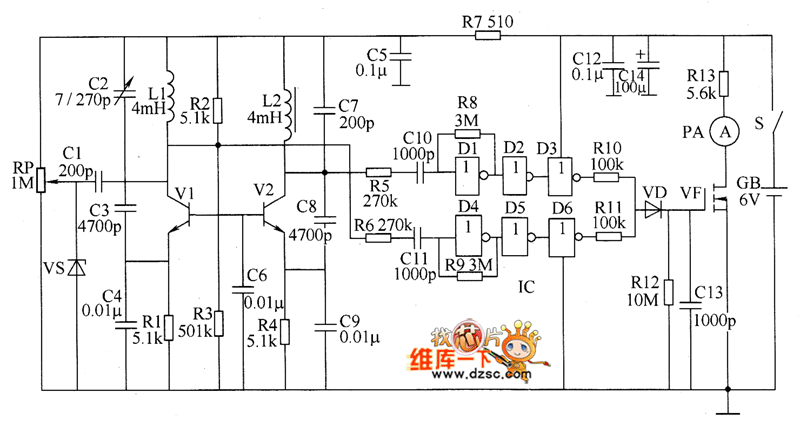
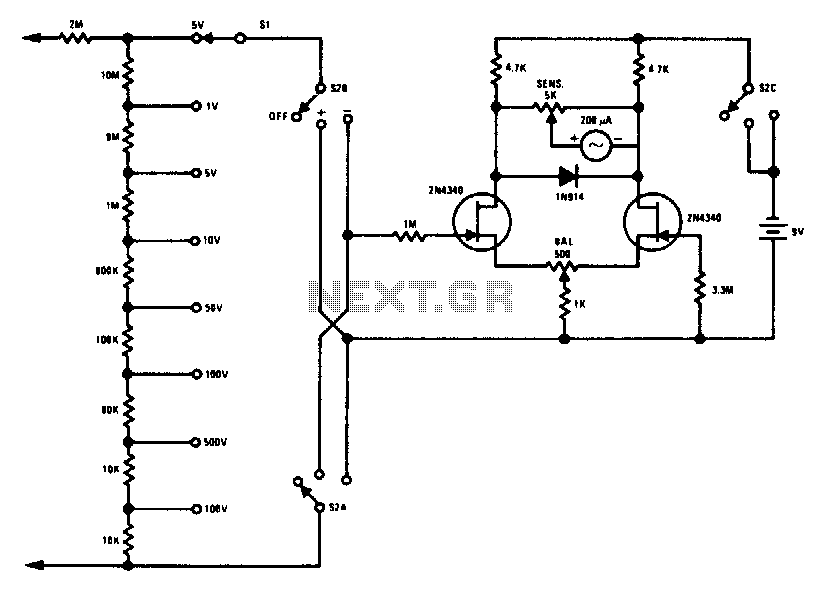
Schematic Diagram of Dashboard Digital Voltmeter
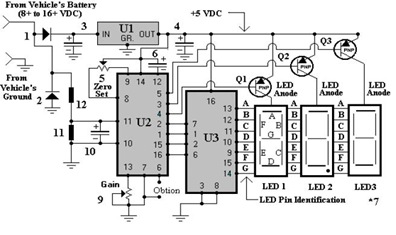
To create a dashboard digital voltmeter circuit diagram that includes a parts list, PCB layout, and component placement, a full PDF article is available for download.
The dashboard digital voltmeter circuit is designed to provide an accurate measurement of voltage levels and display them on a digital interface. The primary components of the circuit typically include a microcontroller, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), a display module (such as a 7-segment display or an LCD), resistors, capacitors, and a voltage reference.
The microcontroller serves as the central processing unit, interpreting the voltage readings from the ADC and controlling the display output. The ADC converts the analog voltage signal into a digital format that the microcontroller can process. It is crucial to select an ADC with sufficient resolution to ensure accurate voltage readings.
The display module is responsible for visually presenting the measured voltage. Depending on the complexity of the design, the display can be configured to show additional information such as battery status or voltage range. The choice of display technology (LED, LCD, etc.) will depend on the desired visibility and power consumption requirements.
The PCB layout is essential for ensuring that the components are arranged efficiently and that signal integrity is maintained. Proper placement of components can minimize noise and interference, which is particularly important in sensitive measurement applications. The PCB should also include appropriate traces for power distribution and signal routing.
In addition to the schematic diagram, a comprehensive parts list should be provided, detailing each component's specifications, such as resistance values, capacitance, and power ratings. This list aids in sourcing components and ensures compatibility within the circuit.
Overall, the design of a dashboard digital voltmeter circuit requires careful consideration of component selection, layout design, and functionality to achieve a reliable and accurate measurement tool.If you want to to try to make a Dashboard Digital Voltmeter Circuit Diagram including part lists, the PCB building and the placement of the components, you may download the article in full pdf here 🔗 External reference
The dashboard digital voltmeter circuit is designed to provide an accurate measurement of voltage levels and display them on a digital interface. The primary components of the circuit typically include a microcontroller, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), a display module (such as a 7-segment display or an LCD), resistors, capacitors, and a voltage reference.
The microcontroller serves as the central processing unit, interpreting the voltage readings from the ADC and controlling the display output. The ADC converts the analog voltage signal into a digital format that the microcontroller can process. It is crucial to select an ADC with sufficient resolution to ensure accurate voltage readings.
The display module is responsible for visually presenting the measured voltage. Depending on the complexity of the design, the display can be configured to show additional information such as battery status or voltage range. The choice of display technology (LED, LCD, etc.) will depend on the desired visibility and power consumption requirements.
The PCB layout is essential for ensuring that the components are arranged efficiently and that signal integrity is maintained. Proper placement of components can minimize noise and interference, which is particularly important in sensitive measurement applications. The PCB should also include appropriate traces for power distribution and signal routing.
In addition to the schematic diagram, a comprehensive parts list should be provided, detailing each component's specifications, such as resistance values, capacitance, and power ratings. This list aids in sourcing components and ensures compatibility within the circuit.
Overall, the design of a dashboard digital voltmeter circuit requires careful consideration of component selection, layout design, and functionality to achieve a reliable and accurate measurement tool.If you want to to try to make a Dashboard Digital Voltmeter Circuit Diagram including part lists, the PCB building and the placement of the components, you may download the article in full pdf here 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713