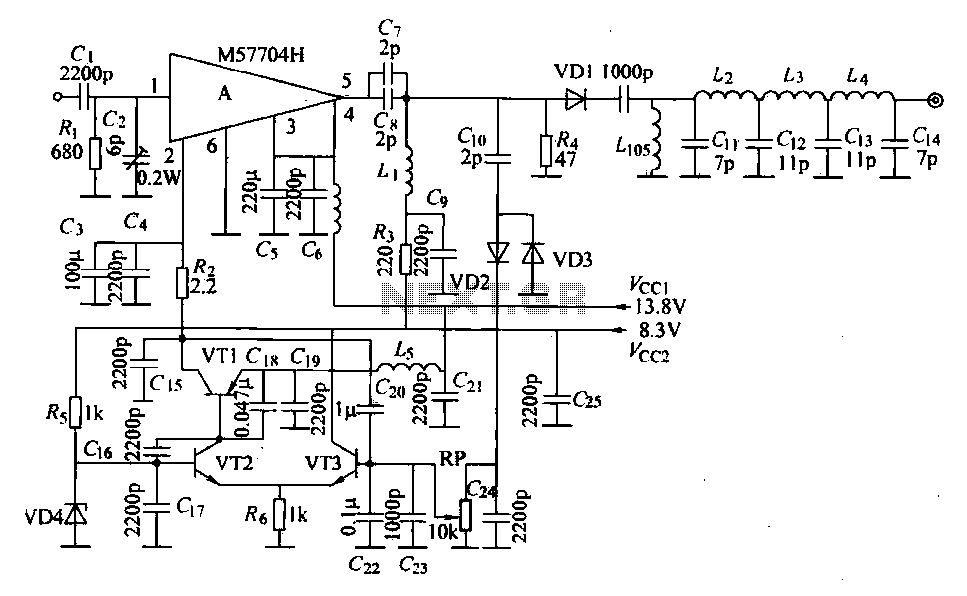
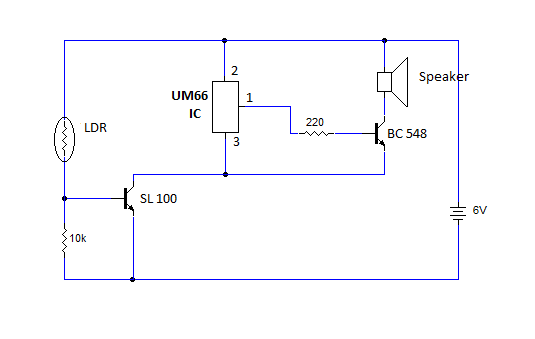
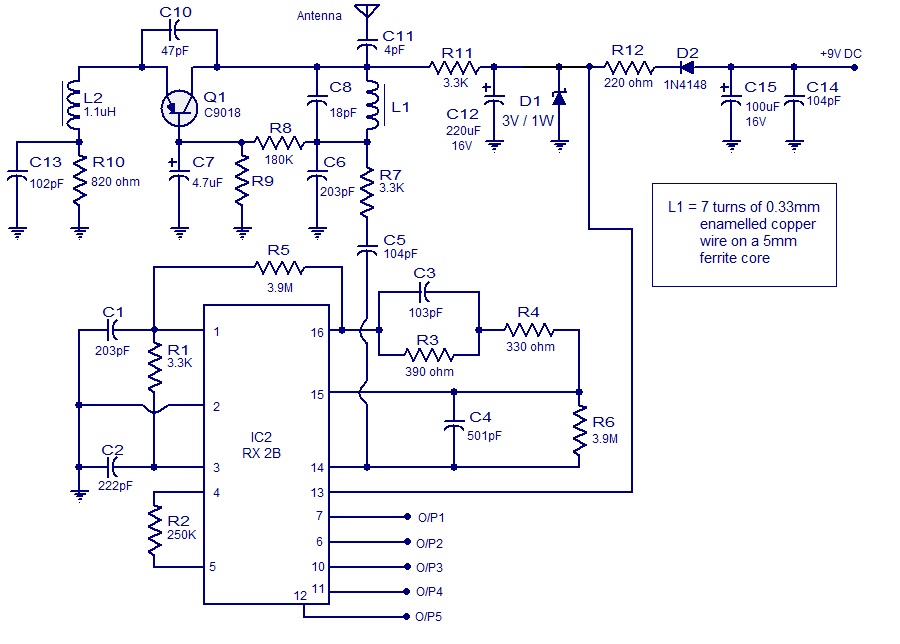
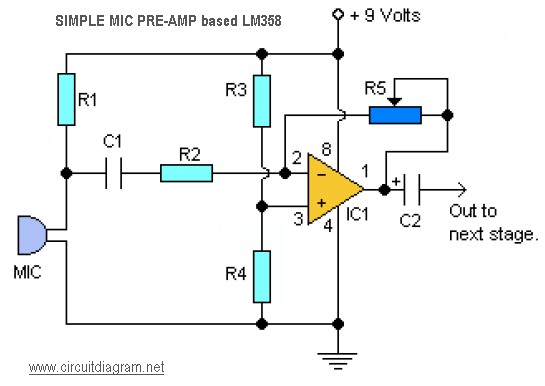
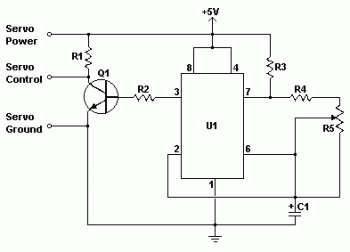
Simple aircraft radio circuitWorking

The circuit diagram and detailed explanation of a simple aircraft radio circuit are provided below.
The simple aircraft radio circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to facilitate communication between the aircraft and ground stations or other aircraft. The primary components include an antenna, a radio frequency (RF) amplifier, a mixer, a local oscillator, and a demodulator.
The antenna captures radio waves transmitted from ground stations or other aircraft. The RF amplifier boosts the weak signals received by the antenna to a level suitable for further processing. The mixer combines the amplified RF signal with a signal from the local oscillator to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. This IF signal is easier to filter and demodulate than the original RF signal.
The demodulator extracts the audio information from the IF signal, allowing the pilot or crew to hear the transmitted voice communications. The output of the demodulator is typically fed into an audio amplifier, which drives a speaker or headset for clear audio output.
Power supply considerations are crucial in aircraft radio circuits. A stable and reliable power source is necessary to ensure consistent operation of all components. Additionally, proper shielding and grounding techniques are employed to minimize interference and enhance the overall performance of the radio system.
Overall, the design of a simple aircraft radio circuit emphasizes reliability, clarity of communication, and resistance to environmental factors such as vibration and temperature variations encountered during flight.The circuit diagram and detailed explanation of a simple aircraft radio circuit is given below.. 🔗 External reference
The simple aircraft radio circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to facilitate communication between the aircraft and ground stations or other aircraft. The primary components include an antenna, a radio frequency (RF) amplifier, a mixer, a local oscillator, and a demodulator.
The antenna captures radio waves transmitted from ground stations or other aircraft. The RF amplifier boosts the weak signals received by the antenna to a level suitable for further processing. The mixer combines the amplified RF signal with a signal from the local oscillator to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. This IF signal is easier to filter and demodulate than the original RF signal.
The demodulator extracts the audio information from the IF signal, allowing the pilot or crew to hear the transmitted voice communications. The output of the demodulator is typically fed into an audio amplifier, which drives a speaker or headset for clear audio output.
Power supply considerations are crucial in aircraft radio circuits. A stable and reliable power source is necessary to ensure consistent operation of all components. Additionally, proper shielding and grounding techniques are employed to minimize interference and enhance the overall performance of the radio system.
Overall, the design of a simple aircraft radio circuit emphasizes reliability, clarity of communication, and resistance to environmental factors such as vibration and temperature variations encountered during flight.The circuit diagram and detailed explanation of a simple aircraft radio circuit is given below.. 🔗 External reference