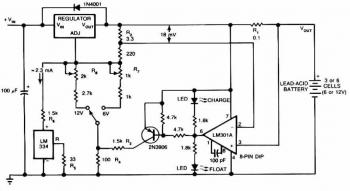
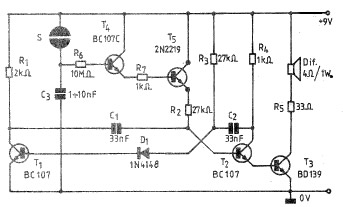
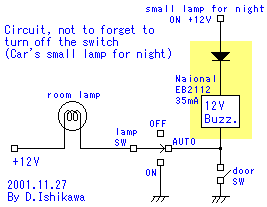
simple but reliable car battery tester
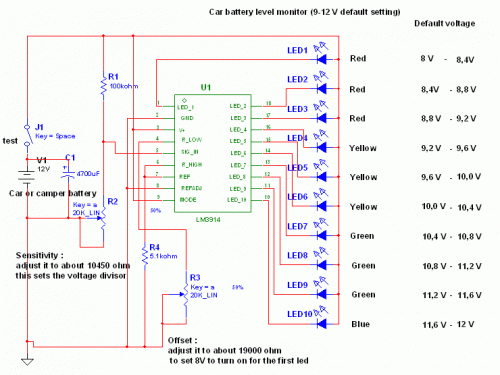
This circuit utilizes the well-known and easily accessible LM3914 integrated circuit (IC). The IC is straightforward to operate, requiring no external voltage regulators due to its built-in voltage regulation capability, and can be powered by a variety of sources. The operation of this circuit is simple: when the test button is pressed, the car battery voltage is fed into a high-impedance voltage divider. Its purpose is to reduce the 12V input to 1.25V (or lower values for lower inputs). This method is preferable to relying on the internal voltage regulator to set the 12V sample voltage for the internal voltage divider, as the regulator cannot effectively regulate 12V when the voltage drops below that level (linear regulators can only step down). The regulator provides a stable 1.25V, which is then fed into the precision internal resistor cascade to generate sample voltages for the internal comparators. The default configuration allows for measuring voltages between 8V and 12V; however, it is possible to measure from 0V to 12V by adjusting the offset trimmer to 0 (although it is noted that a car may not start under 9V). A smoothing capacitor (4700uF, 16V) is included to mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMF) noise generated by the ignition coil when measuring the battery voltage during engine operation. While diesel engines may not require this capacitor, uncertainty remains regarding its necessity. For those preferring a point graph display instead of a bar graph, pin 9 (MODE) on the IC can be disconnected from power. The calculations for this circuit are straightforward (default).
The LM3914 is a versatile LED bar graph/LED dot display driver that can be configured to display either a bar graph or a dot mode based on the connection of pin 9. In this circuit, the use of a high-impedance voltage divider is crucial, as it allows for accurate scaling of the car battery voltage to a level suitable for the LM3914’s internal comparators. The voltage divider typically consists of two resistors arranged in series, where the output voltage is taken from the junction of the two resistors. This configuration ensures that the voltage presented to the LM3914 does not exceed its maximum input rating while still providing a representative reading of the battery voltage.
The internal voltage regulation feature of the LM3914 simplifies the design by eliminating the need for an external regulator, thus reducing component count and potential points of failure. The stable output of 1.25V is critical for the accurate operation of the internal comparator network, which is responsible for determining the appropriate LED activation based on the input voltage.
The smoothing capacitor plays a significant role in stabilizing the voltage readings by filtering out transient spikes caused by the ignition system of the vehicle. This is particularly important in automotive applications, where electrical noise can lead to inaccurate voltage readings. The use of a 4700uF capacitor provides substantial filtering capability, ensuring that the circuit can deliver reliable performance even in the presence of electrical interference.
The ability to adjust the offset trimmer allows users to calibrate the circuit for different operational ranges. This flexibility is beneficial for users who may need to monitor battery voltages that fall below the typical operational range of 8V to 12V, enabling the circuit to function effectively across a broader spectrum of voltages.
Overall, this circuit design offers a practical solution for monitoring car battery voltage with an emphasis on simplicity, reliability, and adaptability to various automotive conditions.This circuit uses the popular and easy to find LM3914 IC. This IC is very simple to drive, needs no voltage regulators (it has a built in voltage regulator) and can be powered from almost every source. This circuit is very easy to explain: When the test button is pressed, the Car battery voltage is feed into a high impedance voltage divider.
His p urpose is to divide 12V to 1, 25V (or lower values to lower values). This solution is better than letting the internal voltage regulator set the 12V sample voltage to be feed into the internal voltage divider simply because it cannot regulate 12V when the voltage drops lower (linear regulators only step down). Simply wiring with no adjust, the regulator provides stable 1, 25V which is fed into the precision internal resistor cascade to generate sample voltages for the internal comparators.
Anyway the default setting let you to measure voltages between 8 and 12V but you can measure even from 0V to 12V setting the offset trimmer to 0 (but i think that under 9 volt your car would not start). There is a smoothing capacitor (4700uF 16V) it is used to adsorb EMF noise produced from the ignition coil if you are measuring the battery during the engine working.
Diesel engines would not need it, but I`m not sure. If you like more a point graph rather than a bar graph simply disconnect pin 9 on the IC (MODE) from power. The calculations are simple (default) 🔗 External reference
The LM3914 is a versatile LED bar graph/LED dot display driver that can be configured to display either a bar graph or a dot mode based on the connection of pin 9. In this circuit, the use of a high-impedance voltage divider is crucial, as it allows for accurate scaling of the car battery voltage to a level suitable for the LM3914’s internal comparators. The voltage divider typically consists of two resistors arranged in series, where the output voltage is taken from the junction of the two resistors. This configuration ensures that the voltage presented to the LM3914 does not exceed its maximum input rating while still providing a representative reading of the battery voltage.
The internal voltage regulation feature of the LM3914 simplifies the design by eliminating the need for an external regulator, thus reducing component count and potential points of failure. The stable output of 1.25V is critical for the accurate operation of the internal comparator network, which is responsible for determining the appropriate LED activation based on the input voltage.
The smoothing capacitor plays a significant role in stabilizing the voltage readings by filtering out transient spikes caused by the ignition system of the vehicle. This is particularly important in automotive applications, where electrical noise can lead to inaccurate voltage readings. The use of a 4700uF capacitor provides substantial filtering capability, ensuring that the circuit can deliver reliable performance even in the presence of electrical interference.
The ability to adjust the offset trimmer allows users to calibrate the circuit for different operational ranges. This flexibility is beneficial for users who may need to monitor battery voltages that fall below the typical operational range of 8V to 12V, enabling the circuit to function effectively across a broader spectrum of voltages.
Overall, this circuit design offers a practical solution for monitoring car battery voltage with an emphasis on simplicity, reliability, and adaptability to various automotive conditions.This circuit uses the popular and easy to find LM3914 IC. This IC is very simple to drive, needs no voltage regulators (it has a built in voltage regulator) and can be powered from almost every source. This circuit is very easy to explain: When the test button is pressed, the Car battery voltage is feed into a high impedance voltage divider.
His p urpose is to divide 12V to 1, 25V (or lower values to lower values). This solution is better than letting the internal voltage regulator set the 12V sample voltage to be feed into the internal voltage divider simply because it cannot regulate 12V when the voltage drops lower (linear regulators only step down). Simply wiring with no adjust, the regulator provides stable 1, 25V which is fed into the precision internal resistor cascade to generate sample voltages for the internal comparators.
Anyway the default setting let you to measure voltages between 8 and 12V but you can measure even from 0V to 12V setting the offset trimmer to 0 (but i think that under 9 volt your car would not start). There is a smoothing capacitor (4700uF 16V) it is used to adsorb EMF noise produced from the ignition coil if you are measuring the battery during the engine working.
Diesel engines would not need it, but I`m not sure. If you like more a point graph rather than a bar graph simply disconnect pin 9 on the IC (MODE) from power. The calculations are simple (default) 🔗 External reference