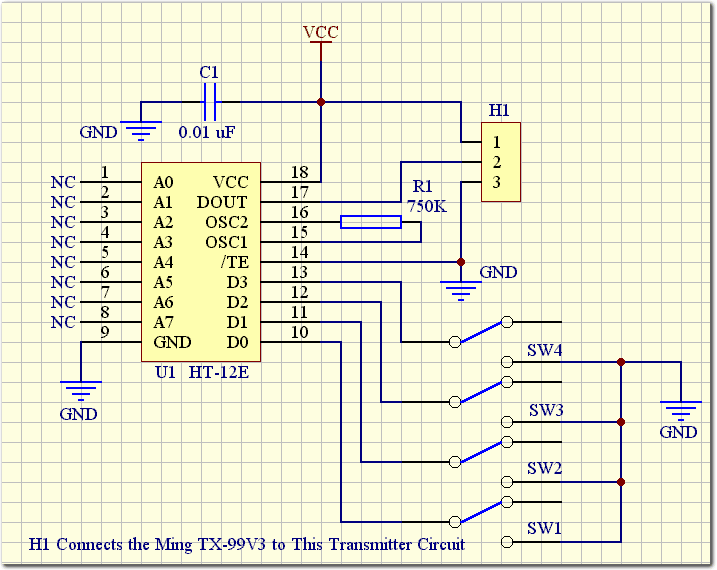
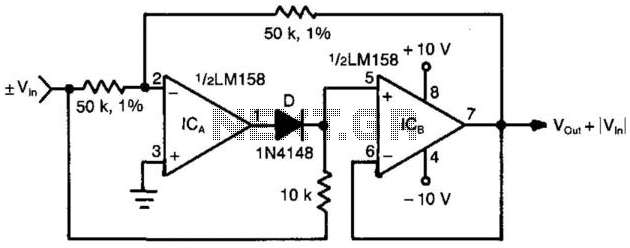
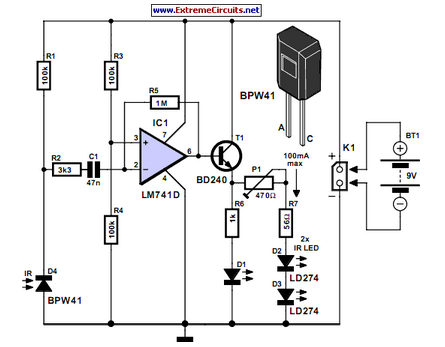
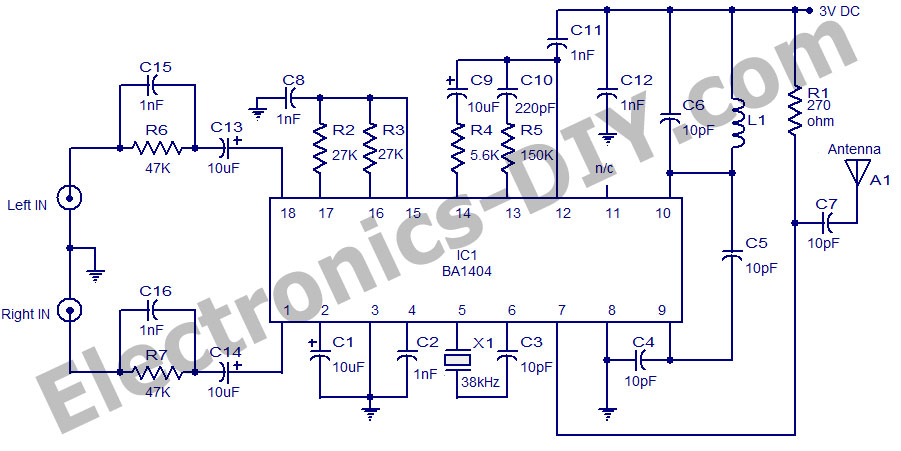
Simple Buzzer Using Only Passive Components
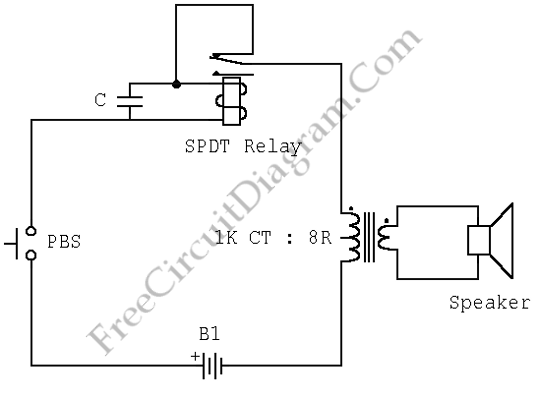
This circuit is a simple buzzer circuit known as a novel buzzer. It utilizes a relay in series with a small audio transformer and a speaker. The relay will activate the circuit.
The novel buzzer circuit operates by employing a relay to control the flow of current to a small audio transformer, which in turn drives a speaker to produce sound. The relay serves as an electromechanical switch that opens and closes the circuit, allowing for the modulation of audio signals.
The circuit can be described as follows: When a control voltage is applied to the relay's coil, it energizes the relay, closing its normally open contacts. This action allows current to flow through the audio transformer. The transformer steps up or modifies the audio signal, which is then delivered to the speaker. The speaker converts the electrical energy into sound waves, producing the desired buzzing noise.
Key components of the circuit include the relay, which should be selected based on the required voltage and current ratings, ensuring it can handle the load of the audio transformer and speaker. The audio transformer should be chosen to match the impedance of the speaker for optimal sound quality. The speaker itself should have an appropriate power rating to handle the output from the transformer without distortion or damage.
In summary, this simple buzzer circuit effectively demonstrates the use of a relay in conjunction with an audio transformer and speaker to generate sound, making it suitable for various applications such as alarms, notifications, or simple sound effects in electronic projects. Proper selection of components and attention to circuit design will ensure reliable operation and sound performance.This circuit is a simple buzzer circuit and it called novel buzzer. It only uses a relay in series with a small audio transformer and speaker. The relay will. 🔗 External reference
The novel buzzer circuit operates by employing a relay to control the flow of current to a small audio transformer, which in turn drives a speaker to produce sound. The relay serves as an electromechanical switch that opens and closes the circuit, allowing for the modulation of audio signals.
The circuit can be described as follows: When a control voltage is applied to the relay's coil, it energizes the relay, closing its normally open contacts. This action allows current to flow through the audio transformer. The transformer steps up or modifies the audio signal, which is then delivered to the speaker. The speaker converts the electrical energy into sound waves, producing the desired buzzing noise.
Key components of the circuit include the relay, which should be selected based on the required voltage and current ratings, ensuring it can handle the load of the audio transformer and speaker. The audio transformer should be chosen to match the impedance of the speaker for optimal sound quality. The speaker itself should have an appropriate power rating to handle the output from the transformer without distortion or damage.
In summary, this simple buzzer circuit effectively demonstrates the use of a relay in conjunction with an audio transformer and speaker to generate sound, making it suitable for various applications such as alarms, notifications, or simple sound effects in electronic projects. Proper selection of components and attention to circuit design will ensure reliable operation and sound performance.This circuit is a simple buzzer circuit and it called novel buzzer. It only uses a relay in series with a small audio transformer and speaker. The relay will. 🔗 External reference