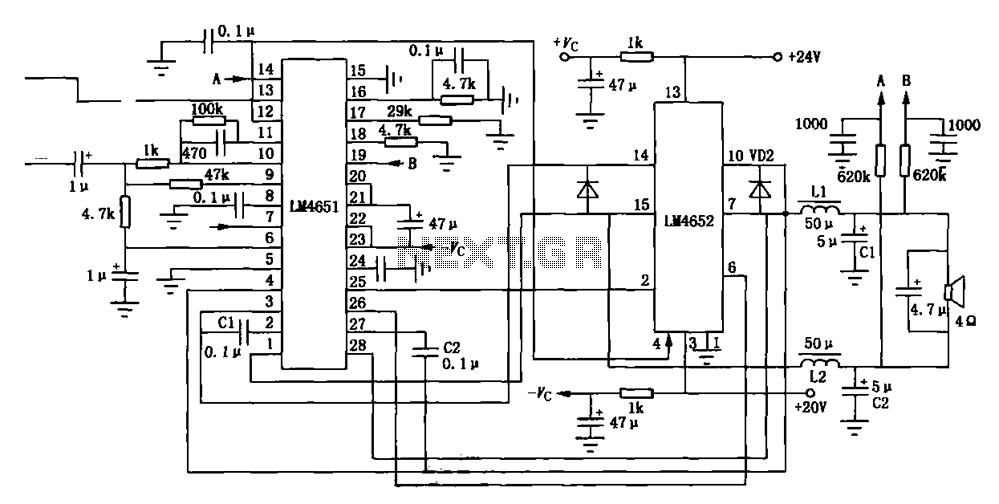
simple fluid level sensor circuit
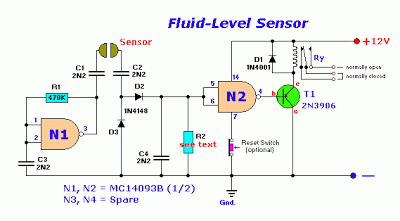
This compact single-chip circuit is designed for measuring the level of electrically conductive fluids or liquids. It functions as a voltage level sensor and employs an AC bias supply to prevent electrolysis of the probes, thereby enhancing their lifespan. This circuit is applicable for a variety of water or liquid level measurement and control scenarios, including heat registers, vending machines, washing machines, water softeners, irrigation systems, reservoirs, tanks, aquariums, and pumps. It can accurately track many types of electrically conductive liquids, such as city and groundwater, seawater, chopper solutions, weak acids, weak bases, household ammonia, and mixtures of water and glycol, as well as wet soil, coffee, and juices. It is important to note that most fuels are not electrically conductive; therefore, this circuit can also serve as a fuel level sensor assembly or detector. Other non-conductive liquids include pure water, gasoline, oil, brake fluid, alcohol, ethylene glycol, paraffin, dry soil, and whiskey. The schematic of the circuit is depicted in the accompanying figure.
This single-chip circuit utilizes a voltage level sensing mechanism that is particularly effective for measuring the levels of conductive liquids. The design incorporates an AC bias supply which mitigates the issue of electrolysis that can occur at the sensor probes when using direct current. By applying an alternating current, the longevity of the probes is significantly increased, making the sensor more reliable over time.
The circuit is versatile, suitable for a wide range of applications in both residential and industrial settings. In washing machines, for instance, it can monitor water levels to optimize water usage and prevent overflow. In irrigation systems, it ensures that water levels are maintained for optimal plant health. The ability to measure various conductive liquids makes this circuit invaluable in environments where different types of fluids are present.
The sensor can detect a range of liquids based on their electrical conductivity. For example, city water, seawater, and various household solutions can be effectively monitored. However, it is essential to recognize that non-conductive liquids such as pure water, gasoline, and oils will not yield accurate readings with this sensor. Therefore, while the circuit is adept at measuring many common liquids, care should be taken when considering its application for fuels or other non-conductive substances.
In terms of implementation, the schematic diagram provides a clear representation of the circuit layout, including key components such as the AC power supply, sensor probes, and any additional circuitry required for signal processing. Proper attention to the design will ensure optimal performance and reliability in liquid level measurement applications.For all electrically conductive Fluid or liquid level measurement, this single-chip circuit is very compact and simple. This circuit is a voltage level sensor encouraged the AC bias supply for the sensor to prevent the electrolysis of the probes used.
This AC excitation, the sensor has a longer life. This circuit is useful for a wide range of wate r or liquid level measurement and control, heat registers, vending machines, washing machines, water softener, irrigation, reservoir, tank, aquarium or pumps. Many types of liquids are electrically conductive and can track by using this level sensor: City / groundwater, seawater, Chopper solution, weak acid, weak base, household ammonia, water and glycol mixture, wet soil, coffee and juices.
Remember that most of the fuel is not electrically conductive, so that this circuit can be used as a fuel level sensor assembly / detector. Some other non-conductive liquid are: pure water, gasoline, oil, brake fluid, alcohol, ethylene glycol, paraffin, dry soil, and whiskey.
The following figure shows the schematic of the circuit. 🔗 External reference
This single-chip circuit utilizes a voltage level sensing mechanism that is particularly effective for measuring the levels of conductive liquids. The design incorporates an AC bias supply which mitigates the issue of electrolysis that can occur at the sensor probes when using direct current. By applying an alternating current, the longevity of the probes is significantly increased, making the sensor more reliable over time.
The circuit is versatile, suitable for a wide range of applications in both residential and industrial settings. In washing machines, for instance, it can monitor water levels to optimize water usage and prevent overflow. In irrigation systems, it ensures that water levels are maintained for optimal plant health. The ability to measure various conductive liquids makes this circuit invaluable in environments where different types of fluids are present.
The sensor can detect a range of liquids based on their electrical conductivity. For example, city water, seawater, and various household solutions can be effectively monitored. However, it is essential to recognize that non-conductive liquids such as pure water, gasoline, and oils will not yield accurate readings with this sensor. Therefore, while the circuit is adept at measuring many common liquids, care should be taken when considering its application for fuels or other non-conductive substances.
In terms of implementation, the schematic diagram provides a clear representation of the circuit layout, including key components such as the AC power supply, sensor probes, and any additional circuitry required for signal processing. Proper attention to the design will ensure optimal performance and reliability in liquid level measurement applications.For all electrically conductive Fluid or liquid level measurement, this single-chip circuit is very compact and simple. This circuit is a voltage level sensor encouraged the AC bias supply for the sensor to prevent the electrolysis of the probes used.
This AC excitation, the sensor has a longer life. This circuit is useful for a wide range of wate r or liquid level measurement and control, heat registers, vending machines, washing machines, water softener, irrigation, reservoir, tank, aquarium or pumps. Many types of liquids are electrically conductive and can track by using this level sensor: City / groundwater, seawater, Chopper solution, weak acid, weak base, household ammonia, water and glycol mixture, wet soil, coffee and juices.
Remember that most of the fuel is not electrically conductive, so that this circuit can be used as a fuel level sensor assembly / detector. Some other non-conductive liquid are: pure water, gasoline, oil, brake fluid, alcohol, ethylene glycol, paraffin, dry soil, and whiskey.
The following figure shows the schematic of the circuit. 🔗 External reference