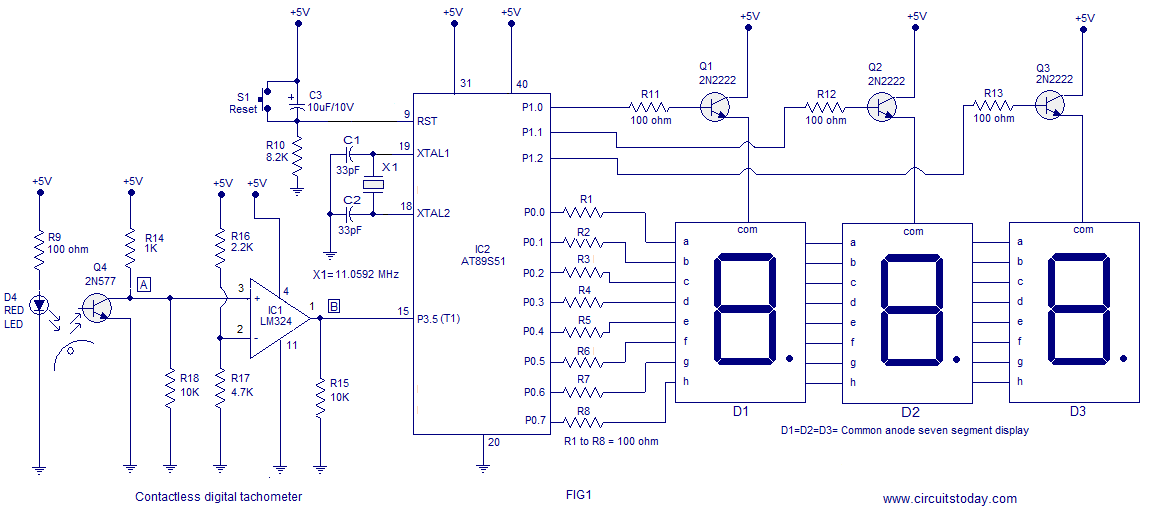
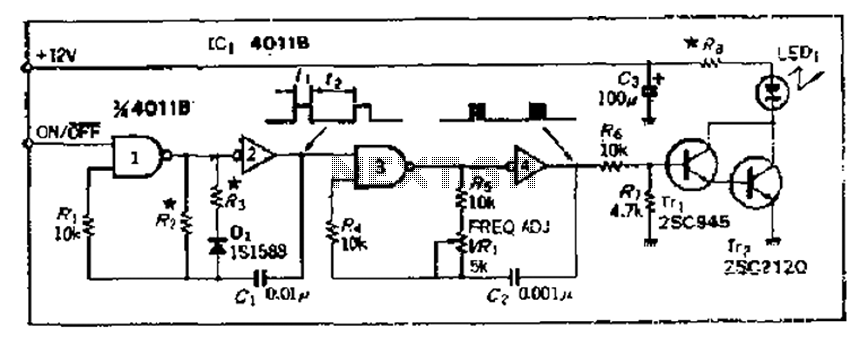
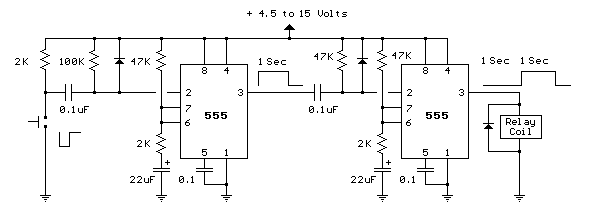
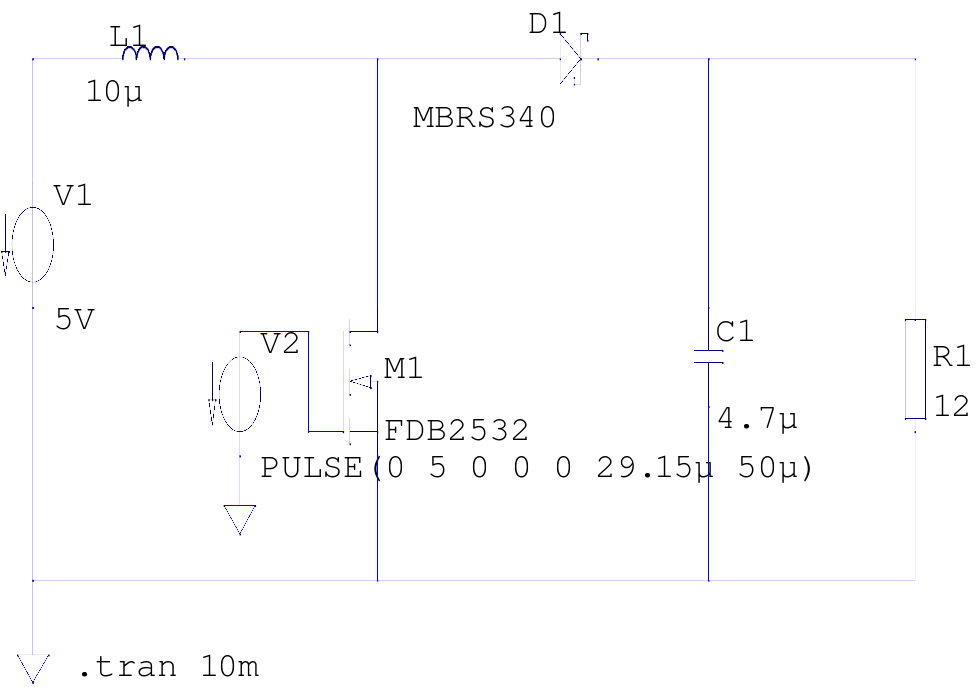
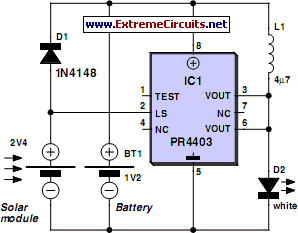
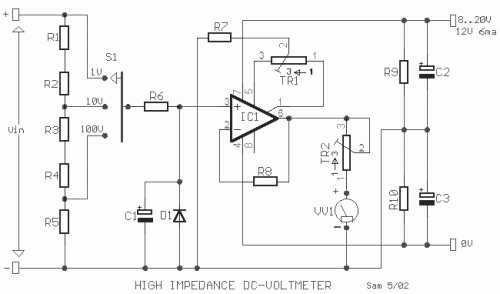
Simple Transistor Tester Using 555 IC
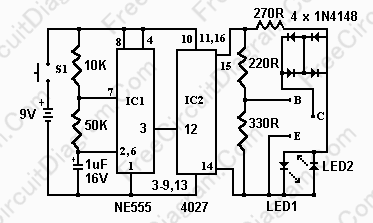
Testing whether a transistor is shorted or open is typically performed using an ohmmeter. The test involves checking if current can flow between the base and emitter or the collector.
To effectively test a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) for shorted or open conditions, an ohmmeter is utilized to measure the resistance across various junctions of the transistor. A BJT has three terminals: the emitter, base, and collector. The two primary junctions to test are the base-emitter (BE) and base-collector (BC) junctions.
1. **Base-Emitter Junction Test**:
- Set the ohmmeter to the resistance measurement mode.
- Connect the positive lead to the base and the negative lead to the emitter. A typical reading should show a low resistance (usually in the range of a few hundred ohms) in one direction (forward bias) and a very high resistance (open circuit) in the opposite direction (reverse bias).
- If the reading is low in both directions, the base-emitter junction is shorted. Conversely, if the resistance is high in both directions, the junction may be open.
2. **Base-Collector Junction Test**:
- Similarly, connect the positive lead to the base and the negative lead to the collector. The expected behavior is identical to that of the base-emitter junction. A low resistance reading in one direction indicates a functional junction, while a high resistance reading in both directions suggests an open or faulty junction.
- A shorted base-collector junction will show low resistance in both directions.
3. **Emitter-Collector Junction Test**:
- It is also beneficial to check the emitter-collector junction directly. Connect the positive lead to the emitter and the negative lead to the collector. The resistance should be high in both directions if the transistor is functioning correctly. A low reading in either direction indicates a short circuit.
In summary, the ohmmeter testing method provides a straightforward approach to determining the operational status of a transistor. By assessing the resistance across the critical junctions, one can ascertain if the transistor is shorted, open, or functioning normally. Proper testing is essential for ensuring reliable operation in electronic circuits where transistors are employed.Testing whether a transistor is shorted or open usually done by ohm meter. You test if the base to emitter? or collector permit a current flow in one. 🔗 External reference
To effectively test a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) for shorted or open conditions, an ohmmeter is utilized to measure the resistance across various junctions of the transistor. A BJT has three terminals: the emitter, base, and collector. The two primary junctions to test are the base-emitter (BE) and base-collector (BC) junctions.
1. **Base-Emitter Junction Test**:
- Set the ohmmeter to the resistance measurement mode.
- Connect the positive lead to the base and the negative lead to the emitter. A typical reading should show a low resistance (usually in the range of a few hundred ohms) in one direction (forward bias) and a very high resistance (open circuit) in the opposite direction (reverse bias).
- If the reading is low in both directions, the base-emitter junction is shorted. Conversely, if the resistance is high in both directions, the junction may be open.
2. **Base-Collector Junction Test**:
- Similarly, connect the positive lead to the base and the negative lead to the collector. The expected behavior is identical to that of the base-emitter junction. A low resistance reading in one direction indicates a functional junction, while a high resistance reading in both directions suggests an open or faulty junction.
- A shorted base-collector junction will show low resistance in both directions.
3. **Emitter-Collector Junction Test**:
- It is also beneficial to check the emitter-collector junction directly. Connect the positive lead to the emitter and the negative lead to the collector. The resistance should be high in both directions if the transistor is functioning correctly. A low reading in either direction indicates a short circuit.
In summary, the ohmmeter testing method provides a straightforward approach to determining the operational status of a transistor. By assessing the resistance across the critical junctions, one can ascertain if the transistor is shorted, open, or functioning normally. Proper testing is essential for ensuring reliable operation in electronic circuits where transistors are employed.Testing whether a transistor is shorted or open usually done by ohm meter. You test if the base to emitter? or collector permit a current flow in one. 🔗 External reference