Simple water detector circuits

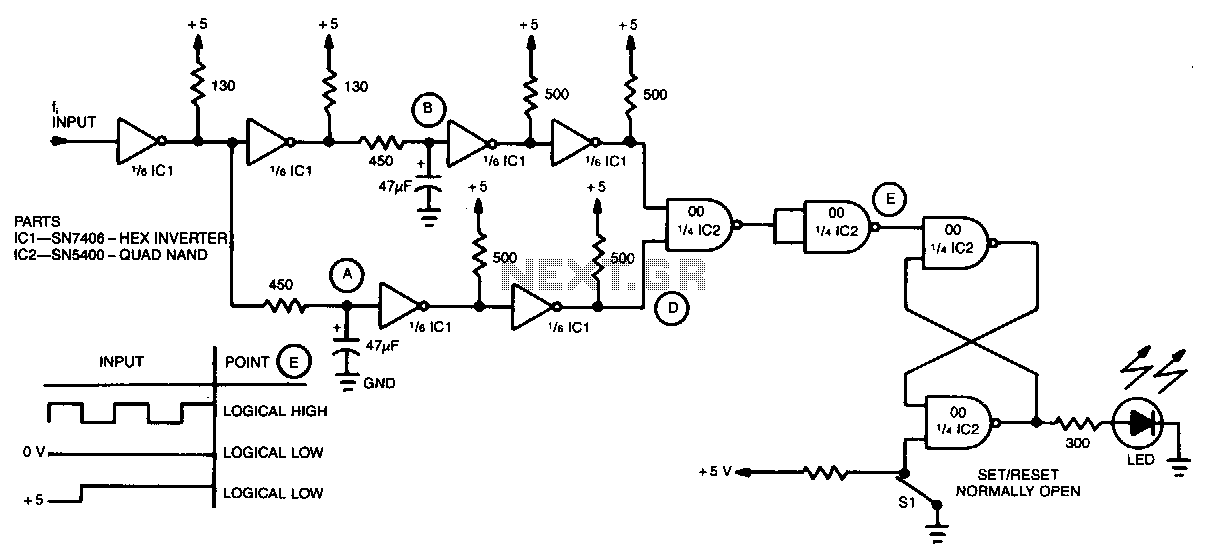
This simple water detector circuit utilizes alternating voltage to prevent electrode corrosion. It is easy to construct and employs N1 as a trigger Schmitt gate to generate the AC signal. When a conductive substance, such as an aqueous solution, is present between the electrodes, the rectifying action of diodes D1 and D2 charges capacitor C4.
The water detector circuit is designed to monitor the presence of water or other conductive liquids. The use of alternating voltage is crucial as it minimizes the risk of corrosion on the electrodes, enhancing the longevity and reliability of the sensor. The Schmitt trigger (N1) serves as a signal conditioning component, generating a stable AC signal that is essential for the operation of the circuit.
When moisture is detected between the electrodes, the conductive path allows current to flow, which is rectified by diodes D1 and D2. This rectification process converts the AC signal into a DC voltage, which is then used to charge capacitor C4. The charge on C4 can be monitored to determine the presence of water. If the voltage across C4 exceeds a certain threshold, it can trigger additional circuitry, such as an alarm or a relay, to indicate water presence.
The design of the circuit should also include appropriate values for the resistors and capacitors to ensure sensitivity and stability. The choice of diodes is important; they should have a low forward voltage drop to ensure efficient rectification. Additionally, the layout of the circuit should minimize noise and interference, which can affect the performance of the water detection system.
Overall, this water detector circuit serves as an effective solution for applications requiring moisture detection, such as leak detection systems, agricultural monitoring, and various industrial processes. The simplicity of the design allows for easy implementation and customization based on specific requirements.This simple water detector circuit uses alternative voltage in order to prevent the corrosion of the electrodes. It is easy to build and uses N1 as a trigger Schmitt gate which generate the AC. If between the electrodes is a electricity conductor, for example an aqueous solution, then because of the rectification action of D1 and D2, the C4 capacitor is char..
🔗 External reference
The water detector circuit is designed to monitor the presence of water or other conductive liquids. The use of alternating voltage is crucial as it minimizes the risk of corrosion on the electrodes, enhancing the longevity and reliability of the sensor. The Schmitt trigger (N1) serves as a signal conditioning component, generating a stable AC signal that is essential for the operation of the circuit.
When moisture is detected between the electrodes, the conductive path allows current to flow, which is rectified by diodes D1 and D2. This rectification process converts the AC signal into a DC voltage, which is then used to charge capacitor C4. The charge on C4 can be monitored to determine the presence of water. If the voltage across C4 exceeds a certain threshold, it can trigger additional circuitry, such as an alarm or a relay, to indicate water presence.
The design of the circuit should also include appropriate values for the resistors and capacitors to ensure sensitivity and stability. The choice of diodes is important; they should have a low forward voltage drop to ensure efficient rectification. Additionally, the layout of the circuit should minimize noise and interference, which can affect the performance of the water detection system.
Overall, this water detector circuit serves as an effective solution for applications requiring moisture detection, such as leak detection systems, agricultural monitoring, and various industrial processes. The simplicity of the design allows for easy implementation and customization based on specific requirements.This simple water detector circuit uses alternative voltage in order to prevent the corrosion of the electrodes. It is easy to build and uses N1 as a trigger Schmitt gate which generate the AC. If between the electrodes is a electricity conductor, for example an aqueous solution, then because of the rectification action of D1 and D2, the C4 capacitor is char..
🔗 External reference