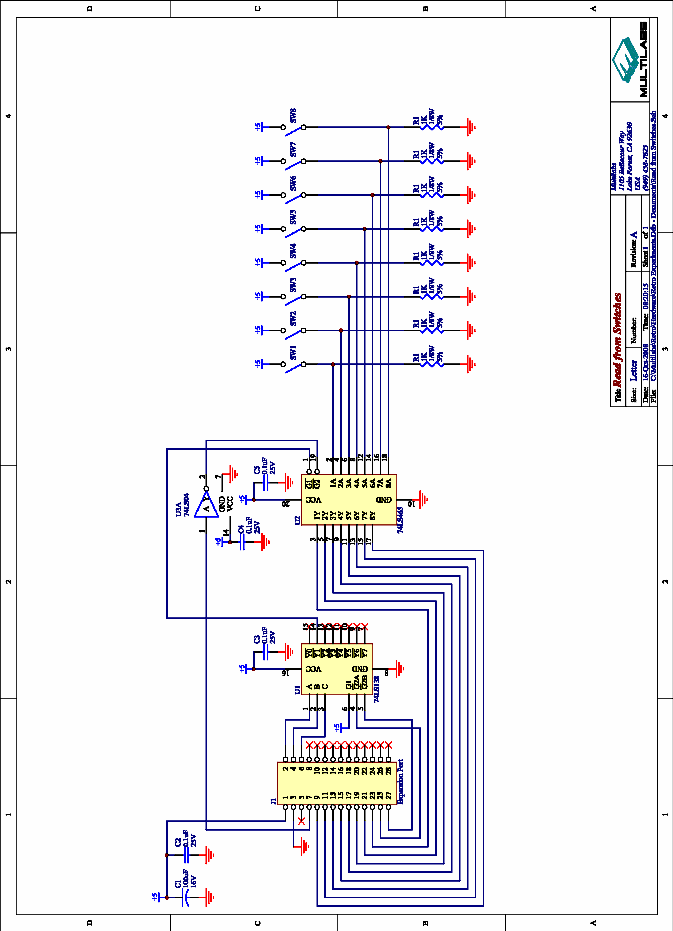
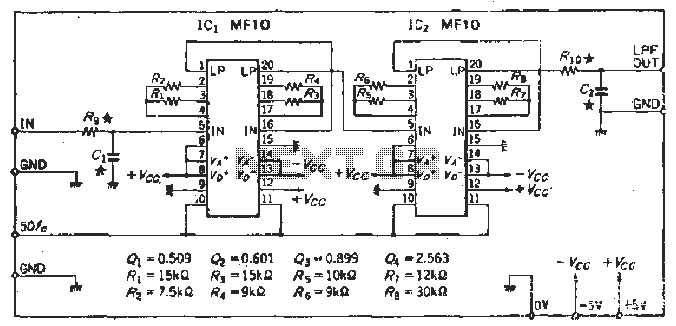
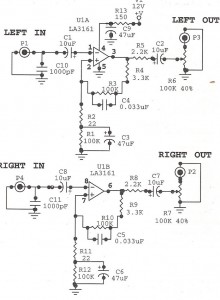
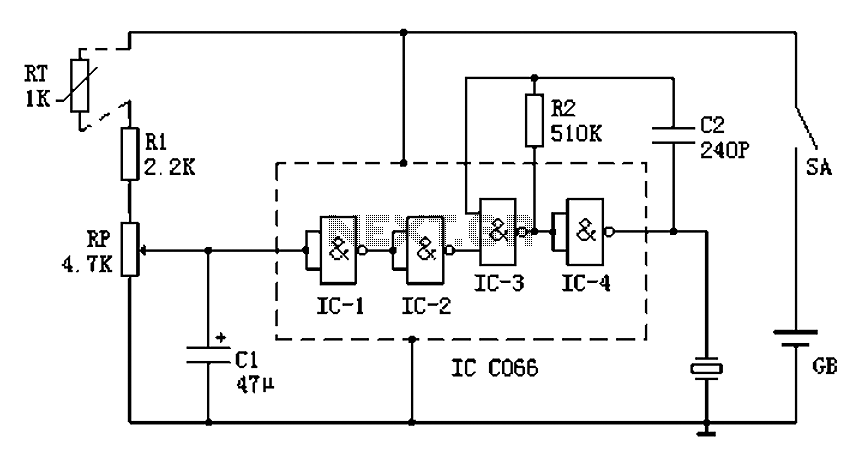
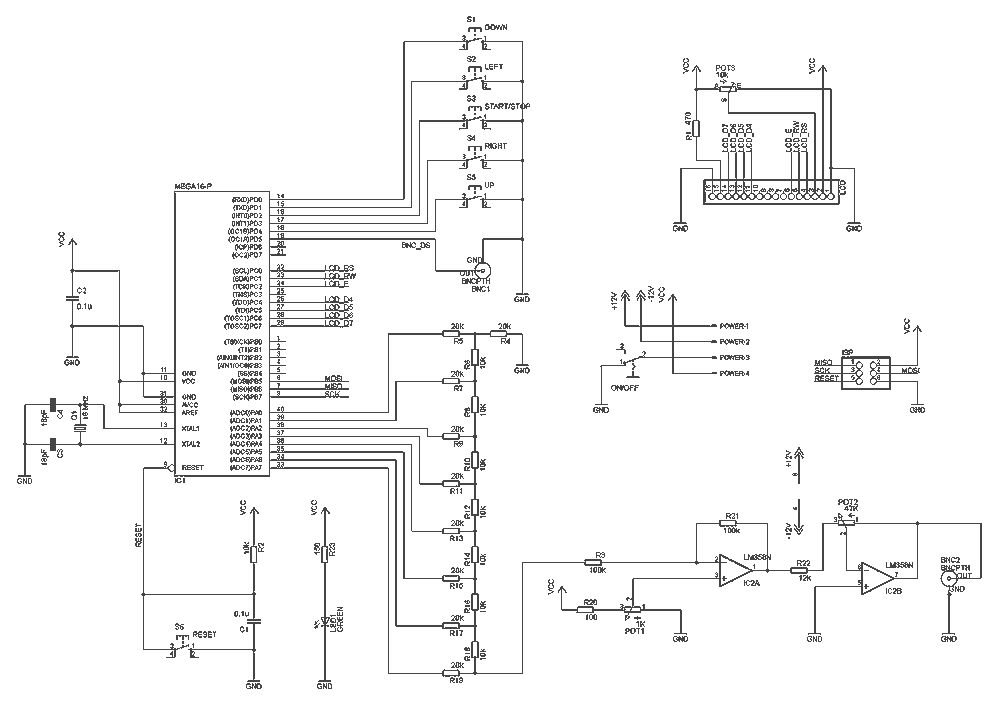
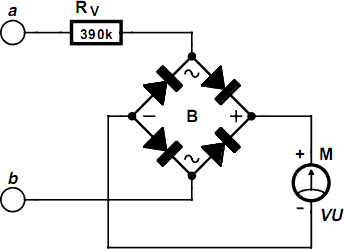
sine wave generator circuit
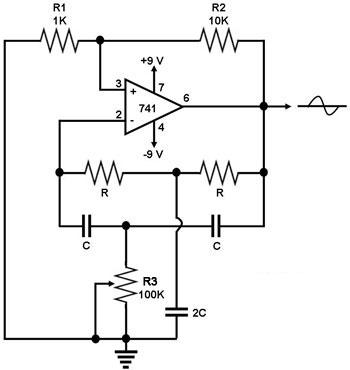
This circuit generates a sine wave using a single operational amplifier (741). The feedback loop of the op-amp includes a twin-T filter connected between its output and inverting input. Positive feedback for oscillation is provided by resistor R2. The twin-T filter is a passive notch filter consisting of two T-networks, with maximum attenuation occurring at the notch frequency fn = 1/(2πRC). One T-network comprises one resistor and two capacitors, while the other includes two resistors and one capacitor. At the notch frequency fn of the twin-T filter, the total phase shift around the loop gain of this op-amp circuit is zero, fulfilling the oscillation condition. Consequently, the circuit produces a sine wave with a frequency equal to fn = 1/(2πRC).
The sine wave generator circuit utilizing a single operational amplifier (741) is an effective design for generating sinusoidal waveforms. The operational amplifier is configured in a negative feedback arrangement with a twin-T notch filter, which is critical for achieving the desired oscillation. The twin-T filter is characterized by its unique configuration of resistors and capacitors, allowing it to create a notch in the frequency response at the specified frequency fn = 1/(2πRC).
In this configuration, one T-network consists of a resistor and two capacitors, while the second T-network is composed of two resistors and one capacitor. This arrangement ensures that at the notch frequency, the phase shift around the feedback loop is precisely zero degrees, which is a necessary condition for sustained oscillation. The resistor R2 is essential in providing the necessary positive feedback to enable the op-amp to oscillate.
The operational amplifier's output, which is a sine wave, can be adjusted for amplitude and frequency by modifying the values of the resistors and capacitors in the twin-T filter. This flexibility makes the circuit suitable for various applications, including signal generation, waveform shaping, and testing of audio equipment. The design is straightforward and cost-effective, leveraging the characteristics of passive components to achieve stable oscillations.
Overall, this sine wave generator circuit is a practical example of using operational amplifiers in waveform generation, demonstrating the fundamental principles of feedback and frequency response in electronic circuit design.This is a circuit for generating a sine wave from a single operational amplifier. The feedback loop of the op amp in this circuit (741) consists of a twin-T filter connected between its output and its inverting input. Positive feedback for oscillation is provided by R2. The twin-T filter (see Figure 2) is a passive notch filter composed of two T-n etworks, with maximum attenuation occurring at fn = 1/(2pRC). One of these T networks has one resistor and two capacitors, while the other has two resistors and one capacitor. At the notch frequency fn of the twin-T filter, the total phase shift around the loop gain of this op amp circuit is zero, which satisfies the requirement for oscillation.
This is why the circuit generates a sine wave with a frequency equal to fn = 1/(2pRC). 🔗 External reference
The sine wave generator circuit utilizing a single operational amplifier (741) is an effective design for generating sinusoidal waveforms. The operational amplifier is configured in a negative feedback arrangement with a twin-T notch filter, which is critical for achieving the desired oscillation. The twin-T filter is characterized by its unique configuration of resistors and capacitors, allowing it to create a notch in the frequency response at the specified frequency fn = 1/(2πRC).
In this configuration, one T-network consists of a resistor and two capacitors, while the second T-network is composed of two resistors and one capacitor. This arrangement ensures that at the notch frequency, the phase shift around the feedback loop is precisely zero degrees, which is a necessary condition for sustained oscillation. The resistor R2 is essential in providing the necessary positive feedback to enable the op-amp to oscillate.
The operational amplifier's output, which is a sine wave, can be adjusted for amplitude and frequency by modifying the values of the resistors and capacitors in the twin-T filter. This flexibility makes the circuit suitable for various applications, including signal generation, waveform shaping, and testing of audio equipment. The design is straightforward and cost-effective, leveraging the characteristics of passive components to achieve stable oscillations.
Overall, this sine wave generator circuit is a practical example of using operational amplifiers in waveform generation, demonstrating the fundamental principles of feedback and frequency response in electronic circuit design.This is a circuit for generating a sine wave from a single operational amplifier. The feedback loop of the op amp in this circuit (741) consists of a twin-T filter connected between its output and its inverting input. Positive feedback for oscillation is provided by R2. The twin-T filter (see Figure 2) is a passive notch filter composed of two T-n etworks, with maximum attenuation occurring at fn = 1/(2pRC). One of these T networks has one resistor and two capacitors, while the other has two resistors and one capacitor. At the notch frequency fn of the twin-T filter, the total phase shift around the loop gain of this op amp circuit is zero, which satisfies the requirement for oscillation.
This is why the circuit generates a sine wave with a frequency equal to fn = 1/(2pRC). 🔗 External reference