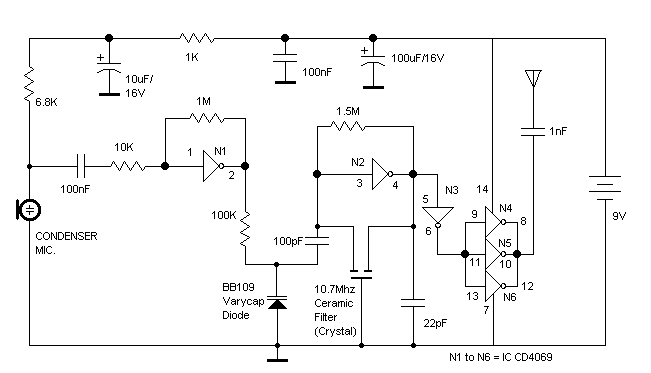
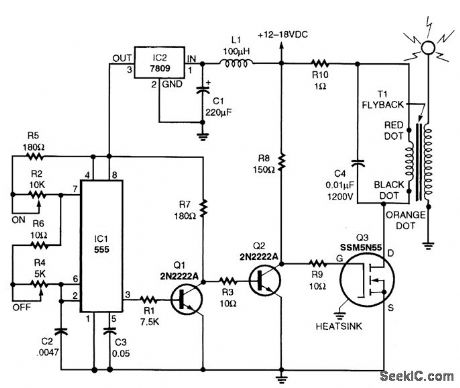
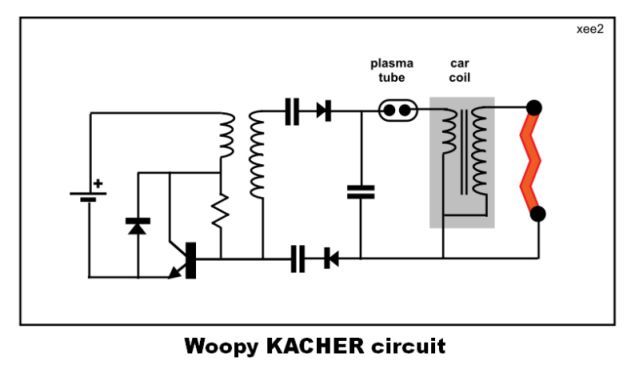
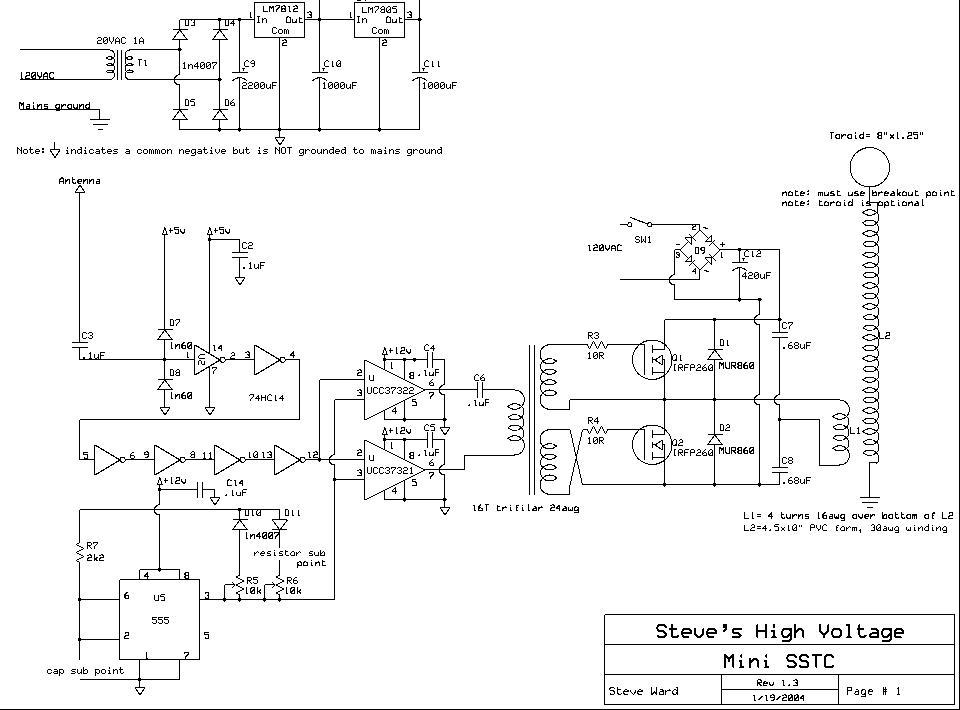
Singing Tesla Coil
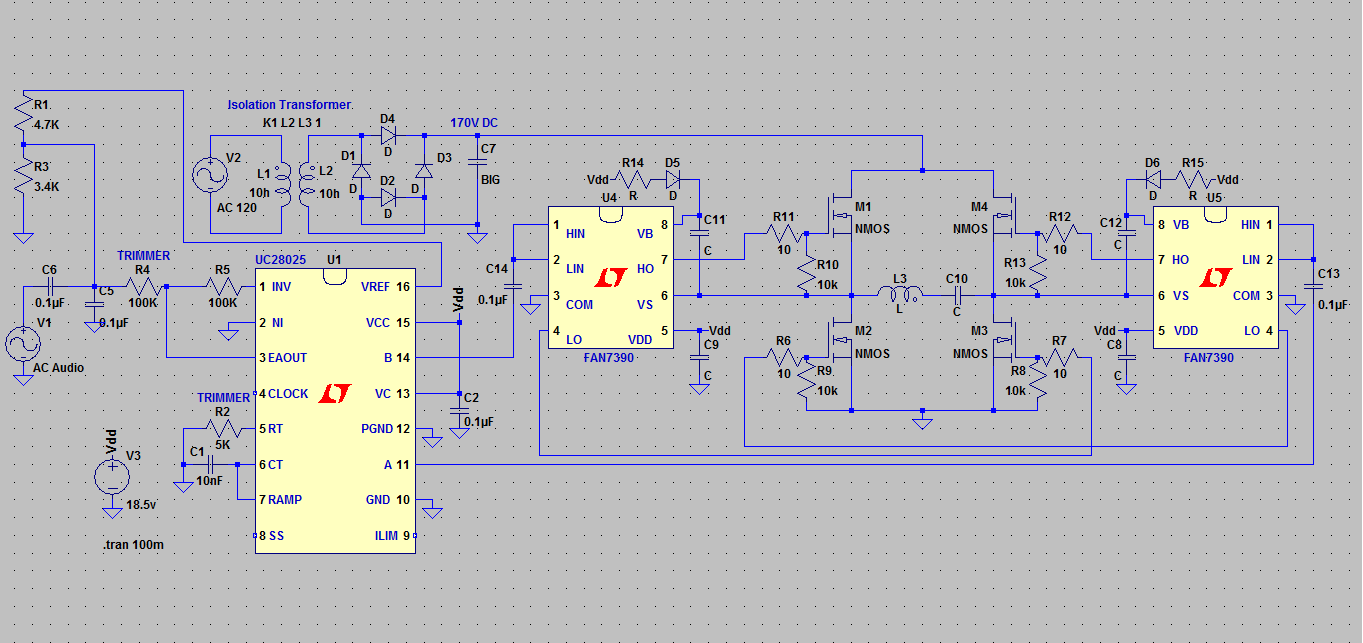
It is a beneficial approach to utilize the chip's internal reference along with some resistors to achieve the appropriate biasing for audio applications, as this method can significantly decrease the component count.
The implementation of an internal reference within an integrated circuit (IC) for audio biasing presents several advantages. By leveraging the chip's built-in voltage reference, one can establish a stable bias point for audio signals, which is crucial for maintaining audio fidelity and minimizing distortion. This method not only simplifies the design but also enhances reliability by reducing the number of external components required.
In typical audio circuit designs, biasing is essential for ensuring that the audio signal operates within the optimal range of the amplifier or processing stage. The use of resistors in conjunction with the internal reference allows for precise voltage division, enabling the designer to set the desired bias level effectively. The choice of resistor values will directly influence the bias voltage, and careful selection is necessary to achieve the intended performance characteristics.
Additionally, minimizing the parts count contributes to a more compact and cost-effective design, which is particularly important in consumer electronics where space and cost constraints are prevalent. This approach can lead to improved manufacturability and reduced assembly time, further enhancing the overall efficiency of the product development process.
Overall, utilizing the chip's internal reference in combination with resistors for audio biasing is a strategic design choice that optimizes performance while simplifying the circuit architecture. This method is particularly advantageous in applications where space, cost, and reliability are critical factors.That`s a great idea to use the chips internal reference and some resistance to get the right bias on the audio; it would really reduce the parts count 🔗 External reference
The implementation of an internal reference within an integrated circuit (IC) for audio biasing presents several advantages. By leveraging the chip's built-in voltage reference, one can establish a stable bias point for audio signals, which is crucial for maintaining audio fidelity and minimizing distortion. This method not only simplifies the design but also enhances reliability by reducing the number of external components required.
In typical audio circuit designs, biasing is essential for ensuring that the audio signal operates within the optimal range of the amplifier or processing stage. The use of resistors in conjunction with the internal reference allows for precise voltage division, enabling the designer to set the desired bias level effectively. The choice of resistor values will directly influence the bias voltage, and careful selection is necessary to achieve the intended performance characteristics.
Additionally, minimizing the parts count contributes to a more compact and cost-effective design, which is particularly important in consumer electronics where space and cost constraints are prevalent. This approach can lead to improved manufacturability and reduced assembly time, further enhancing the overall efficiency of the product development process.
Overall, utilizing the chip's internal reference in combination with resistors for audio biasing is a strategic design choice that optimizes performance while simplifying the circuit architecture. This method is particularly advantageous in applications where space, cost, and reliability are critical factors.That`s a great idea to use the chips internal reference and some resistance to get the right bias on the audio; it would really reduce the parts count 🔗 External reference