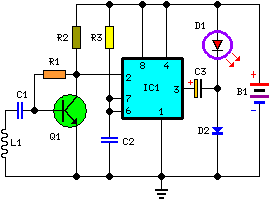
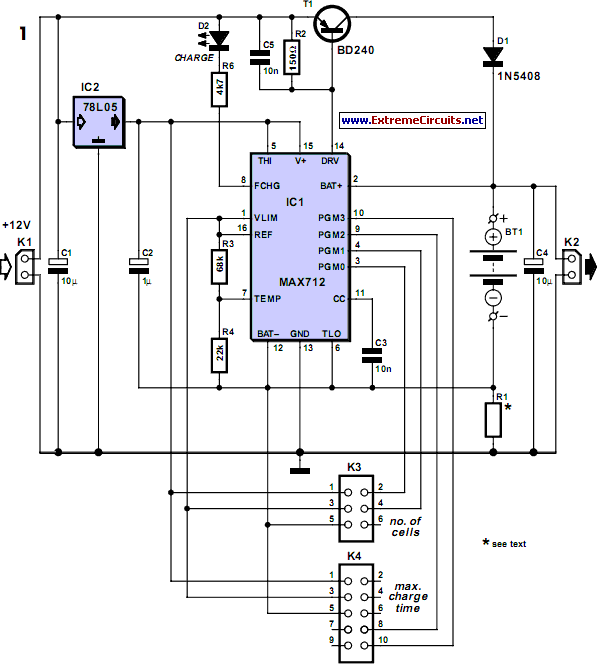
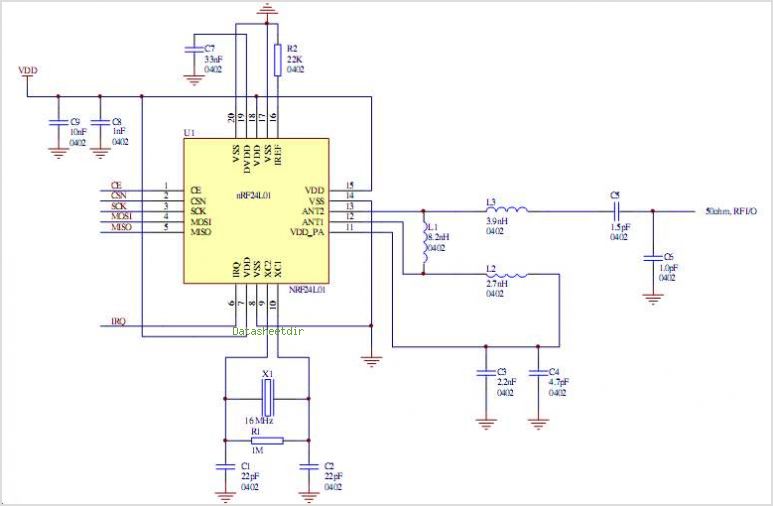
Single Cell 1.5V Hearing Aid
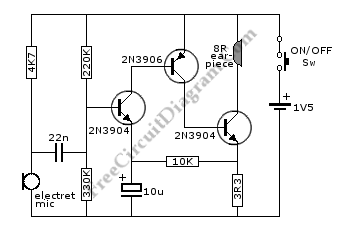
This is a hearing aid circuit powered by a 1.5V supply. It is designed to detect very faint sounds and deliver these sounds to an 8-ohm earpiece.
The hearing aid circuit operates by amplifying low-level audio signals to make them audible for individuals with hearing impairments. The primary components typically include a microphone, an amplifier, and a speaker (earpiece).
The microphone captures ambient sounds, converting them into electrical signals. These signals are often very weak, necessitating amplification for proper hearing. The amplifier, which can be implemented using operational amplifiers (op-amps) or dedicated audio amplifier ICs, increases the signal strength. The gain of the amplifier must be carefully selected to ensure that it enhances the sound without introducing excessive noise or distortion.
The output of the amplifier is then fed to an 8-ohm earpiece, which converts the amplified electrical signals back into sound waves. The earpiece is designed to match the output impedance of the amplifier, ensuring efficient power transfer and optimal sound quality.
Power management is crucial in hearing aid circuits, especially since they are often battery-operated. The 1.5V supply is typically derived from standard batteries, such as AA or AAA cells. Circuit design considerations may include low-power components and techniques to extend battery life, such as automatic shut-off features when not in use.
Additional features may include volume control, tone adjustment, and noise filtering to enhance the listening experience. These can be achieved through the use of potentiometers and passive components, or more advanced digital signal processing techniques in modern designs.
Overall, the hearing aid circuit is a compact and efficient system tailored to improve sound detection and clarity for users with hearing difficulties.This is a hearing aid circuit with 1.5v supply. This circuit is used to detect very faint sounds, then deliver the sounds to an 8 ohm earpiece. This circuit. 🔗 External reference
The hearing aid circuit operates by amplifying low-level audio signals to make them audible for individuals with hearing impairments. The primary components typically include a microphone, an amplifier, and a speaker (earpiece).
The microphone captures ambient sounds, converting them into electrical signals. These signals are often very weak, necessitating amplification for proper hearing. The amplifier, which can be implemented using operational amplifiers (op-amps) or dedicated audio amplifier ICs, increases the signal strength. The gain of the amplifier must be carefully selected to ensure that it enhances the sound without introducing excessive noise or distortion.
The output of the amplifier is then fed to an 8-ohm earpiece, which converts the amplified electrical signals back into sound waves. The earpiece is designed to match the output impedance of the amplifier, ensuring efficient power transfer and optimal sound quality.
Power management is crucial in hearing aid circuits, especially since they are often battery-operated. The 1.5V supply is typically derived from standard batteries, such as AA or AAA cells. Circuit design considerations may include low-power components and techniques to extend battery life, such as automatic shut-off features when not in use.
Additional features may include volume control, tone adjustment, and noise filtering to enhance the listening experience. These can be achieved through the use of potentiometers and passive components, or more advanced digital signal processing techniques in modern designs.
Overall, the hearing aid circuit is a compact and efficient system tailored to improve sound detection and clarity for users with hearing difficulties.This is a hearing aid circuit with 1.5v supply. This circuit is used to detect very faint sounds, then deliver the sounds to an 8 ohm earpiece. This circuit. 🔗 External reference