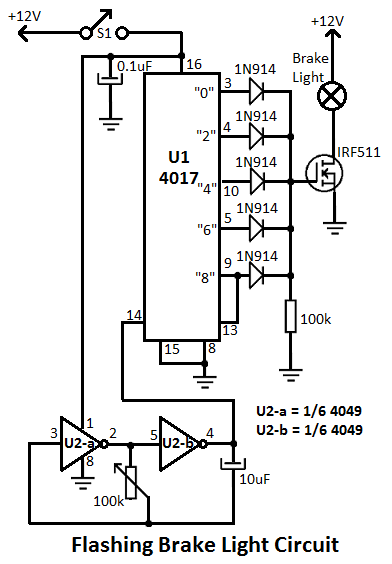
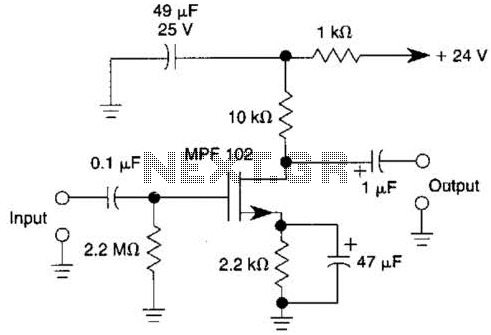
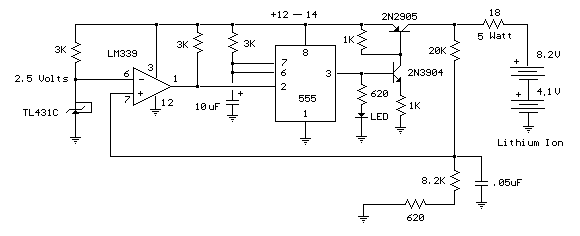
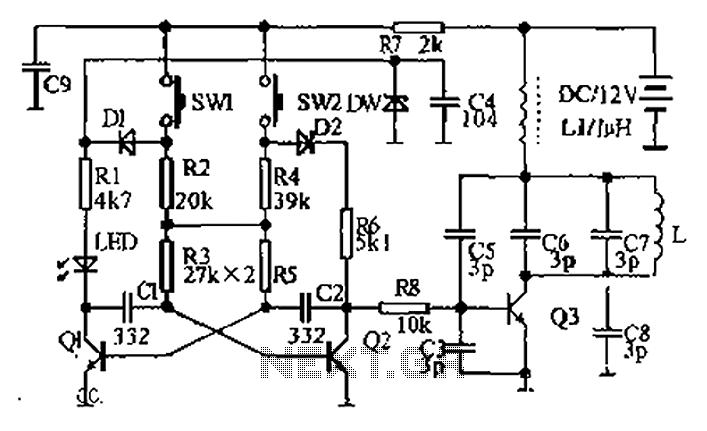
mobile cellphone battery charger circuit
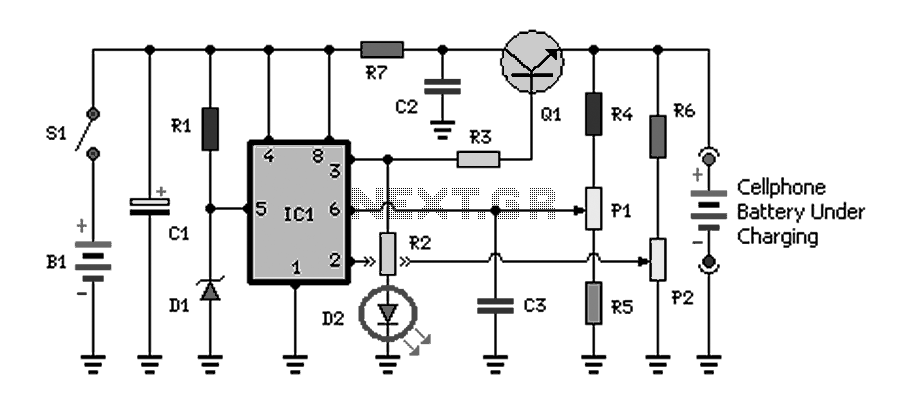
Charging a mobile phone or cellphone battery presents a significant challenge while traveling, as a power supply source is often not readily available. If the cellphone remains switched on continuously, its battery can deplete within five to six hours, rendering the device inoperable.
The issue of mobile phone battery depletion during travel necessitates the design of effective charging solutions. A typical mobile phone battery, often a lithium-ion type, has a limited capacity that can be quickly consumed by continuous use. To address this challenge, various portable charging solutions can be employed, including power banks, solar chargers, and vehicle chargers.
A power bank is a compact, portable device that stores electrical energy and can recharge a mobile phone when a power outlet is unavailable. The design of a power bank typically includes a lithium-ion battery, a charging circuit, and multiple output ports to accommodate different devices. The charging circuit regulates the input and output voltage to ensure safe and efficient charging.
Solar chargers represent another innovative solution, utilizing photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electrical energy. The design of a solar charger includes solar panels, a rechargeable battery, and a circuit to manage power distribution. This type of charger is particularly useful for outdoor activities, allowing users to harness renewable energy while on the go.
Vehicle chargers provide yet another option, enabling users to charge their devices using the car's power supply. This design involves a car adapter that converts the vehicle's 12V output to the appropriate voltage for mobile devices, often including safety features to prevent overcharging.
In summary, to mitigate the issue of mobile phone battery depletion during travel, various charging solutions can be implemented, each with its own design considerations and applications. These solutions enhance the usability of mobile devices, ensuring that users remain connected even in the absence of traditional power sources.Charging of the mobile phone, cellphone battery is a big problem while traveling as power supply source is not generally accessible. If you keep your cellphone switched on continuously, its battery will go flat within five to six hours, making the cellphone useless..
🔗 External reference
The issue of mobile phone battery depletion during travel necessitates the design of effective charging solutions. A typical mobile phone battery, often a lithium-ion type, has a limited capacity that can be quickly consumed by continuous use. To address this challenge, various portable charging solutions can be employed, including power banks, solar chargers, and vehicle chargers.
A power bank is a compact, portable device that stores electrical energy and can recharge a mobile phone when a power outlet is unavailable. The design of a power bank typically includes a lithium-ion battery, a charging circuit, and multiple output ports to accommodate different devices. The charging circuit regulates the input and output voltage to ensure safe and efficient charging.
Solar chargers represent another innovative solution, utilizing photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electrical energy. The design of a solar charger includes solar panels, a rechargeable battery, and a circuit to manage power distribution. This type of charger is particularly useful for outdoor activities, allowing users to harness renewable energy while on the go.
Vehicle chargers provide yet another option, enabling users to charge their devices using the car's power supply. This design involves a car adapter that converts the vehicle's 12V output to the appropriate voltage for mobile devices, often including safety features to prevent overcharging.
In summary, to mitigate the issue of mobile phone battery depletion during travel, various charging solutions can be implemented, each with its own design considerations and applications. These solutions enhance the usability of mobile devices, ensuring that users remain connected even in the absence of traditional power sources.Charging of the mobile phone, cellphone battery is a big problem while traveling as power supply source is not generally accessible. If you keep your cellphone switched on continuously, its battery will go flat within five to six hours, making the cellphone useless..
🔗 External reference