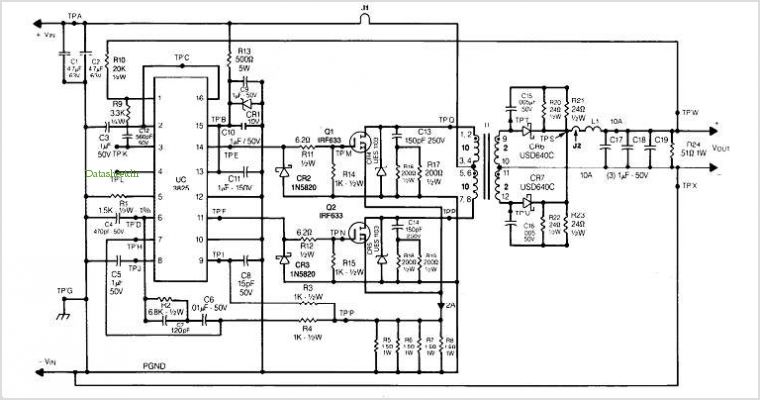
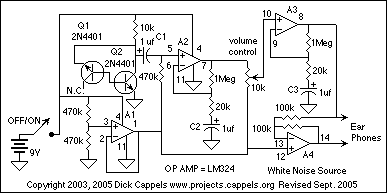
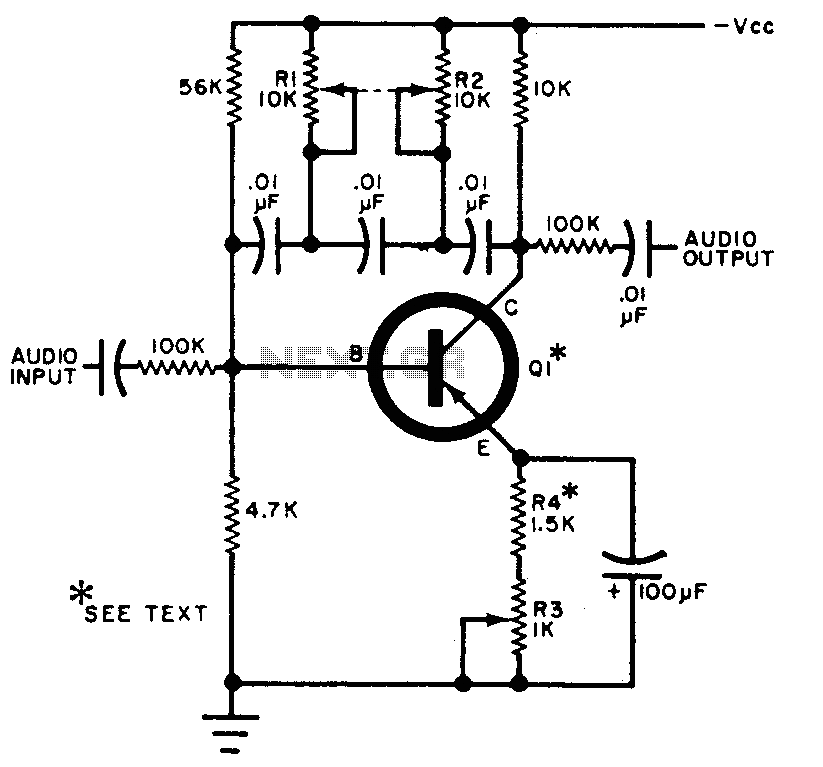
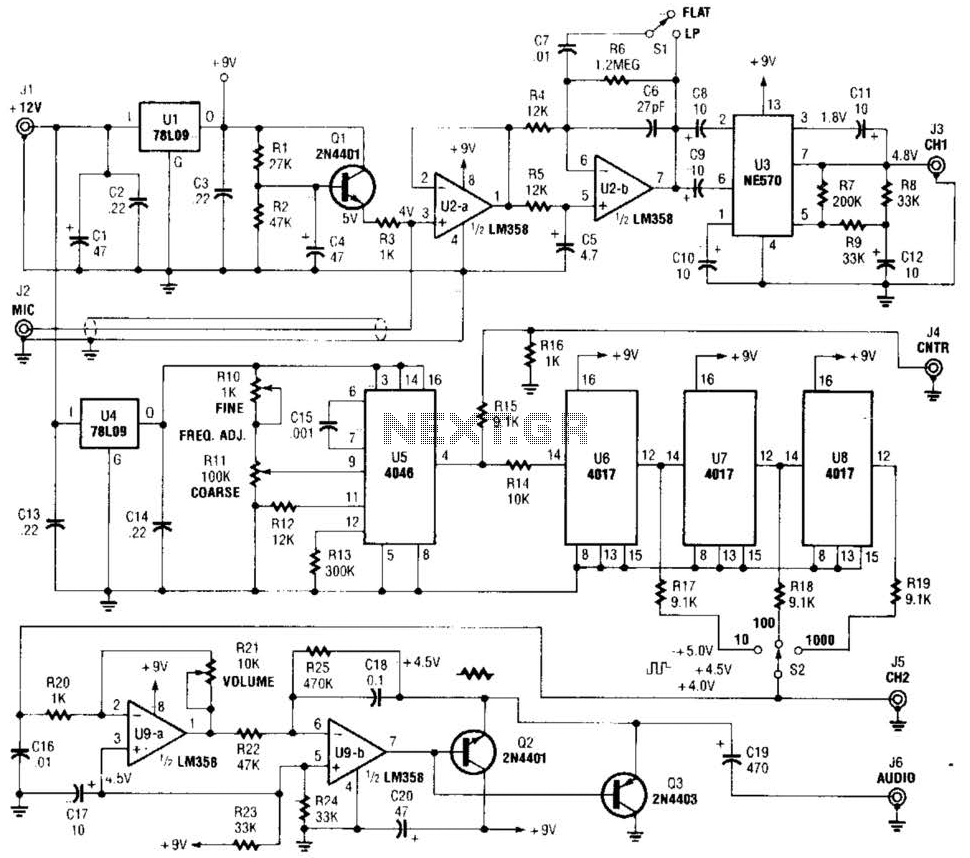
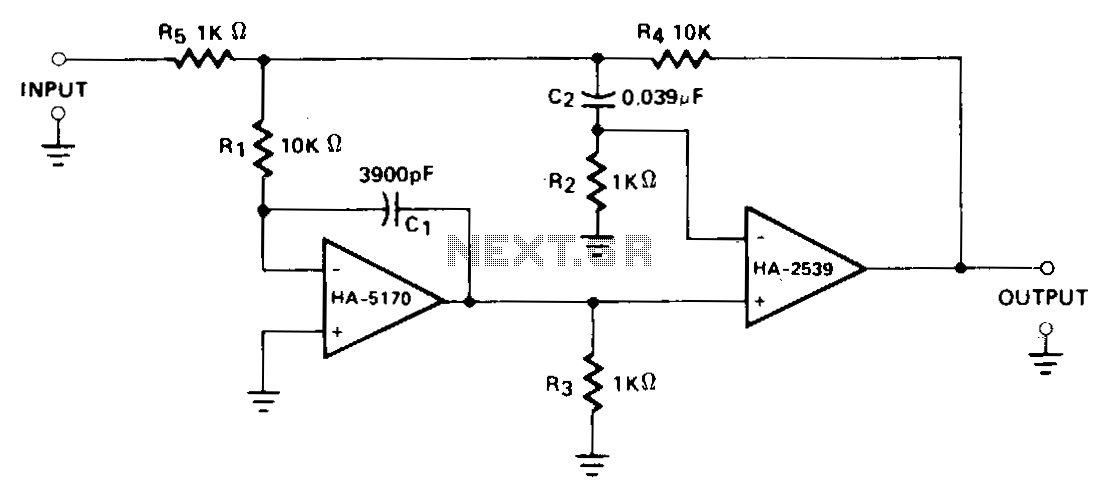
Single Supply Summing Amplifier for Audio Mixer
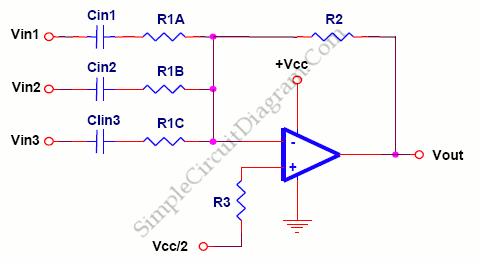
The foundation of an audio mixer is an inverting summing circuit. In practical audio mixers, a single-supply voltage is rarely utilized. To enhance dynamic range, ...
The inverting summing circuit serves as a fundamental building block in audio mixing applications, allowing multiple audio signals to be combined into a single output. This circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in an inverting mode. The inputs to the op-amp are connected through resistors, which determine the weighting of each input signal in the final mix.
In a typical setup, the op-amp is powered by dual supply voltages, which provide a greater dynamic range than a single-supply configuration. This dual supply allows the op-amp to handle both positive and negative signal excursions, thereby accommodating the full waveform of audio signals without distortion. The resistors connected to the inputs not only serve to scale the input signals but also ensure that the input impedance of the circuit remains high, minimizing loading effects on the preceding stages of the audio chain.
The feedback resistor connected from the output of the op-amp back to its inverting input sets the gain of the circuit. By adjusting the values of the input and feedback resistors, the designer can control the overall gain and mixing characteristics of the circuit. Additionally, the circuit can be designed to include features such as level adjustment and pan control, further enhancing its functionality in a mixer.
In summary, the inverting summing circuit is a crucial element in audio mixers, facilitating the combination of multiple audio sources while maximizing dynamic range and minimizing distortion through careful design and component selection.The basis of an audio mixer is an inverting summing circuit below. For real audio mixers, a single-supply voltage is seldom used. To increase dynamic range,.. 🔗 External reference
The inverting summing circuit serves as a fundamental building block in audio mixing applications, allowing multiple audio signals to be combined into a single output. This circuit typically employs operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured in an inverting mode. The inputs to the op-amp are connected through resistors, which determine the weighting of each input signal in the final mix.
In a typical setup, the op-amp is powered by dual supply voltages, which provide a greater dynamic range than a single-supply configuration. This dual supply allows the op-amp to handle both positive and negative signal excursions, thereby accommodating the full waveform of audio signals without distortion. The resistors connected to the inputs not only serve to scale the input signals but also ensure that the input impedance of the circuit remains high, minimizing loading effects on the preceding stages of the audio chain.
The feedback resistor connected from the output of the op-amp back to its inverting input sets the gain of the circuit. By adjusting the values of the input and feedback resistors, the designer can control the overall gain and mixing characteristics of the circuit. Additionally, the circuit can be designed to include features such as level adjustment and pan control, further enhancing its functionality in a mixer.
In summary, the inverting summing circuit is a crucial element in audio mixers, facilitating the combination of multiple audio sources while maximizing dynamic range and minimizing distortion through careful design and component selection.The basis of an audio mixer is an inverting summing circuit below. For real audio mixers, a single-supply voltage is seldom used. To increase dynamic range,.. 🔗 External reference