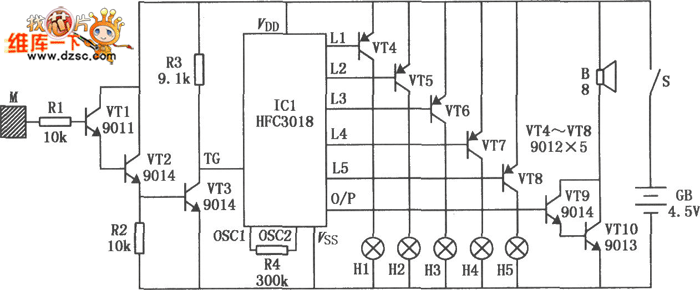
Sound level monitor

A loudness detector is composed of a 555 integrated circuit (IC) configured as a Schmitt trigger. The output transitions from high to low when the input voltage exceeds a specified threshold. This threshold voltage is determined by the resistance value of R4.
The loudness detector circuit utilizes the 555 timer IC, which is a versatile and widely used component in various electronic applications. When configured as a Schmitt trigger, the 555 IC provides hysteresis in the output, which helps to eliminate noise from the input signal and ensures stable switching behavior.
In this configuration, the input voltage is continuously monitored. When the input voltage rises above the threshold set by the resistor R4, the output of the 555 IC switches from a high state (logic level '1') to a low state (logic level '0'). This transition can be used to trigger other circuits or devices, such as an LED indicator or a sound alert, indicating that a certain loudness level has been detected.
The threshold voltage is critical for the operation of the loudness detector. It is determined by the resistor R4, which is part of a voltage divider network. By adjusting the resistance of R4, the sensitivity of the detector can be modified, allowing it to respond to different levels of input voltage. This feature makes the circuit adaptable for various applications, such as audio processing, sound level monitoring, or automatic gain control systems.
In summary, the loudness detector circuit employing a 555 IC as a Schmitt trigger provides a reliable means of detecting loudness levels by utilizing a threshold voltage established by the resistor R4, thereby facilitating various audio-related applications.Loudness detector consists of a 555 IC wired as a Schmitt trigger. The output changes state—from high to low—whenever the input crosses a certain voltage That threshold voltage is established by the setting of R4.
The loudness detector circuit utilizes the 555 timer IC, which is a versatile and widely used component in various electronic applications. When configured as a Schmitt trigger, the 555 IC provides hysteresis in the output, which helps to eliminate noise from the input signal and ensures stable switching behavior.
In this configuration, the input voltage is continuously monitored. When the input voltage rises above the threshold set by the resistor R4, the output of the 555 IC switches from a high state (logic level '1') to a low state (logic level '0'). This transition can be used to trigger other circuits or devices, such as an LED indicator or a sound alert, indicating that a certain loudness level has been detected.
The threshold voltage is critical for the operation of the loudness detector. It is determined by the resistor R4, which is part of a voltage divider network. By adjusting the resistance of R4, the sensitivity of the detector can be modified, allowing it to respond to different levels of input voltage. This feature makes the circuit adaptable for various applications, such as audio processing, sound level monitoring, or automatic gain control systems.
In summary, the loudness detector circuit employing a 555 IC as a Schmitt trigger provides a reliable means of detecting loudness levels by utilizing a threshold voltage established by the resistor R4, thereby facilitating various audio-related applications.Loudness detector consists of a 555 IC wired as a Schmitt trigger. The output changes state—from high to low—whenever the input crosses a certain voltage That threshold voltage is established by the setting of R4.