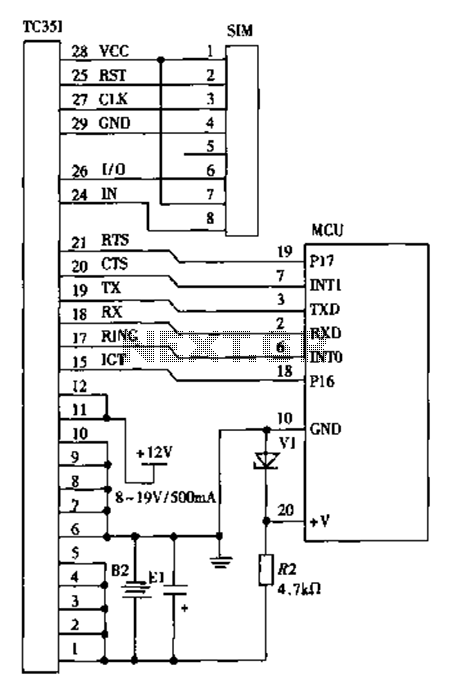
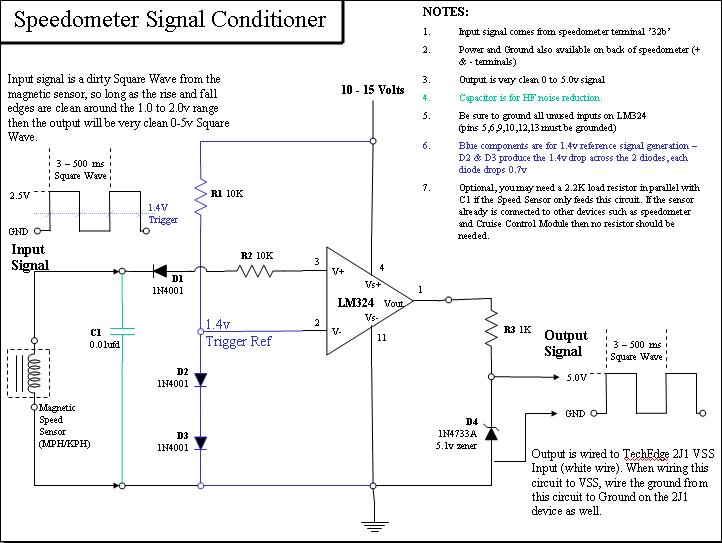
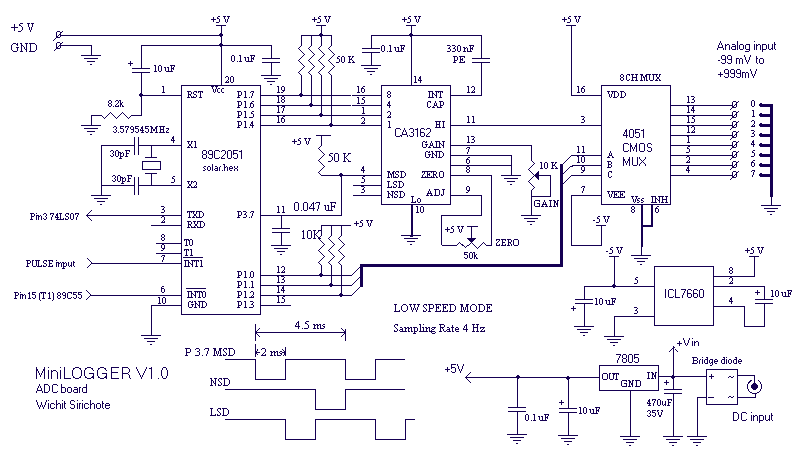
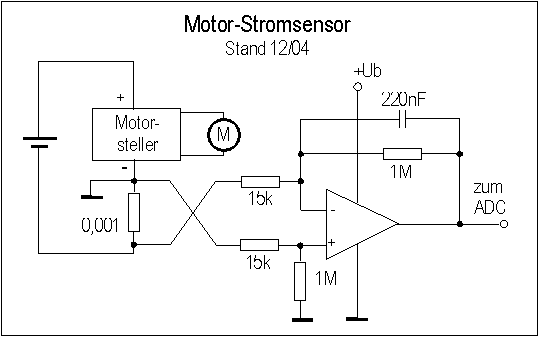
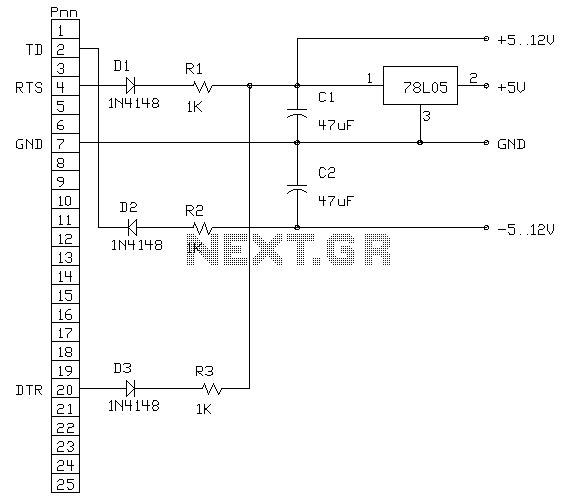
Split-Phase Data Synchronization and Decoding
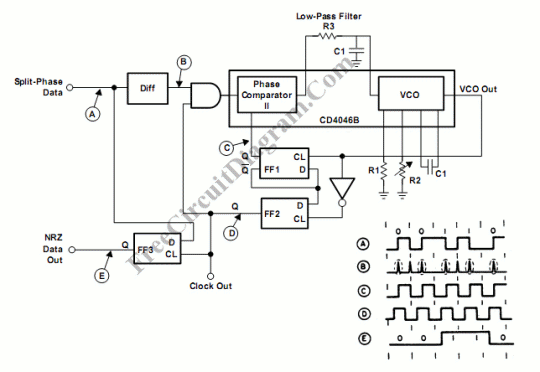
A split-phase data signal comprises a sequence of binary digits that are transmitted at a regular interval, as illustrated in waveform A of the timing chart. The significance of each digit is determined by its position in the sequence.
A split-phase data signal is characterized by its method of transmission, which typically involves two distinct phases: a positive phase and a negative phase. In this configuration, the binary digits are represented by changes in voltage levels, with a transition occurring at the midpoint of each bit period. This allows for a more robust signal, as the transitions can be used to synchronize the receiving equipment with the timing of the signal.
In a practical implementation, the split-phase signal can be generated using a combination of digital logic circuits and oscillators. The timing chart indicates the precise moments when the signal transitions from high to low and vice versa, ensuring that the data can be accurately interpreted by the receiving system. The use of split-phase signaling is particularly advantageous in environments where noise may affect signal integrity, as the clear transitions help maintain data accuracy.
The design of a split-phase data signal circuit may include components such as flip-flops for data storage, clock generators for timing control, and buffers to drive the signal over longer distances. Each binary digit's weight is critical, as it influences the overall data representation. For instance, in a binary system, the least significant bit (LSB) represents the smallest value, while the most significant bit (MSB) contributes the most to the overall value.
In summary, a split-phase data signal is an efficient method of transmitting binary information that leverages the timing of voltage transitions to enhance data integrity and synchronization. The careful design of the associated circuitry is essential for ensuring reliable communication in digital systems.A split-phase data signal consists of a series of binary digits that occur at a periodic rate, as shown in waveform A in the timing chart. The weight of each. 🔗 External reference
A split-phase data signal is characterized by its method of transmission, which typically involves two distinct phases: a positive phase and a negative phase. In this configuration, the binary digits are represented by changes in voltage levels, with a transition occurring at the midpoint of each bit period. This allows for a more robust signal, as the transitions can be used to synchronize the receiving equipment with the timing of the signal.
In a practical implementation, the split-phase signal can be generated using a combination of digital logic circuits and oscillators. The timing chart indicates the precise moments when the signal transitions from high to low and vice versa, ensuring that the data can be accurately interpreted by the receiving system. The use of split-phase signaling is particularly advantageous in environments where noise may affect signal integrity, as the clear transitions help maintain data accuracy.
The design of a split-phase data signal circuit may include components such as flip-flops for data storage, clock generators for timing control, and buffers to drive the signal over longer distances. Each binary digit's weight is critical, as it influences the overall data representation. For instance, in a binary system, the least significant bit (LSB) represents the smallest value, while the most significant bit (MSB) contributes the most to the overall value.
In summary, a split-phase data signal is an efficient method of transmitting binary information that leverages the timing of voltage transitions to enhance data integrity and synchronization. The careful design of the associated circuitry is essential for ensuring reliable communication in digital systems.A split-phase data signal consists of a series of binary digits that occur at a periodic rate, as shown in waveform A in the timing chart. The weight of each. 🔗 External reference