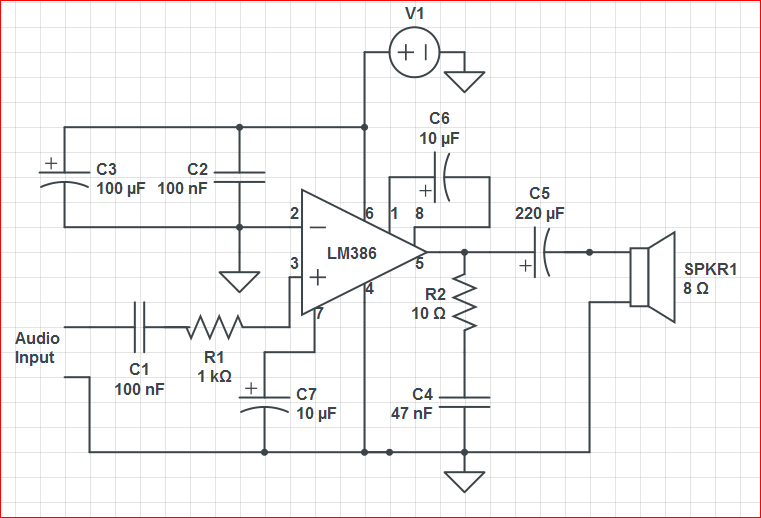
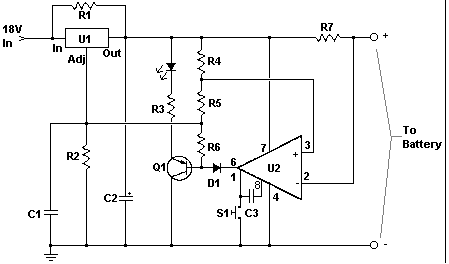
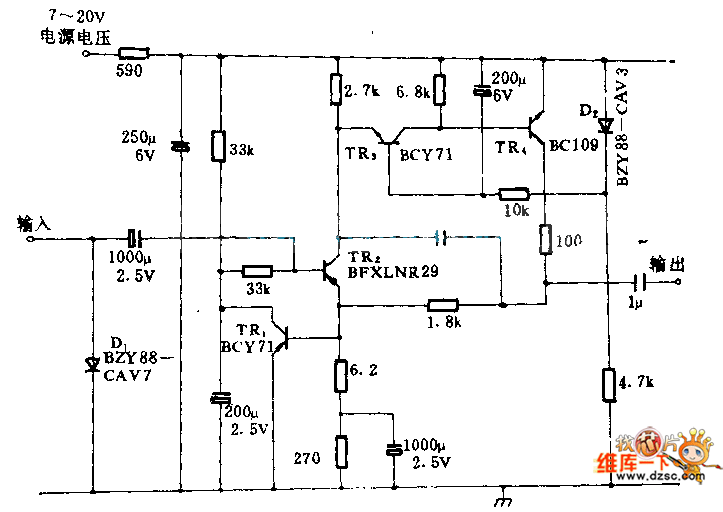
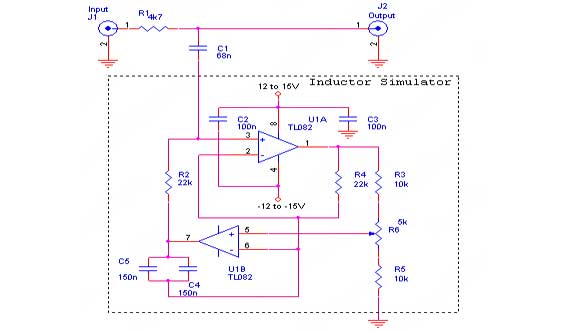
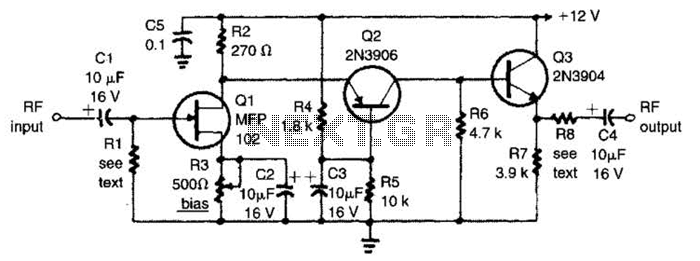
Stabilised amplifier schematic

It uses the LT1052 and LT1028. The power supply should be dual with ±15V at 500mA. This is an ideal stabilized amplifier.
The circuit utilizes the LT1052 and LT1028 operational amplifiers, which are known for their precision and stability. The LT1052 is a low-noise, high-speed operational amplifier, while the LT1028 is a precision, low-drift op-amp designed for applications requiring high accuracy.
The power supply requirements specify a dual ±15V output with a current capacity of 500mA. This configuration is essential for providing the necessary headroom for the amplifiers, ensuring that they operate efficiently within their specified voltage range. The dual supply configuration allows for both positive and negative signal swings, which is critical for amplifying AC signals or processing differential inputs.
In terms of circuit design, the ideal stabilized amplifier configuration would likely include feedback components to set the gain and bandwidth of the amplifier. Resistors and capacitors would be selected based on the desired frequency response and stability criteria. Proper bypass capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out noise and ensure stable operation.
Thermal management is also a consideration, as the LT1028 can generate heat under high load conditions. Adequate heat sinking or thermal relief techniques may be necessary to maintain performance and reliability.
Overall, this circuit design provides a robust solution for applications requiring high-performance amplification, such as audio processing, instrumentation, or signal conditioning, leveraging the strengths of the LT1052 and LT1028 op-amps.It use the LT1052 and LT1028. Power supply should be double with +-15V 500mA. This is a ideal stabilised amplifier.
The circuit utilizes the LT1052 and LT1028 operational amplifiers, which are known for their precision and stability. The LT1052 is a low-noise, high-speed operational amplifier, while the LT1028 is a precision, low-drift op-amp designed for applications requiring high accuracy.
The power supply requirements specify a dual ±15V output with a current capacity of 500mA. This configuration is essential for providing the necessary headroom for the amplifiers, ensuring that they operate efficiently within their specified voltage range. The dual supply configuration allows for both positive and negative signal swings, which is critical for amplifying AC signals or processing differential inputs.
In terms of circuit design, the ideal stabilized amplifier configuration would likely include feedback components to set the gain and bandwidth of the amplifier. Resistors and capacitors would be selected based on the desired frequency response and stability criteria. Proper bypass capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the op-amps to filter out noise and ensure stable operation.
Thermal management is also a consideration, as the LT1028 can generate heat under high load conditions. Adequate heat sinking or thermal relief techniques may be necessary to maintain performance and reliability.
Overall, this circuit design provides a robust solution for applications requiring high-performance amplification, such as audio processing, instrumentation, or signal conditioning, leveraging the strengths of the LT1052 and LT1028 op-amps.It use the LT1052 and LT1028. Power supply should be double with +-15V 500mA. This is a ideal stabilised amplifier.