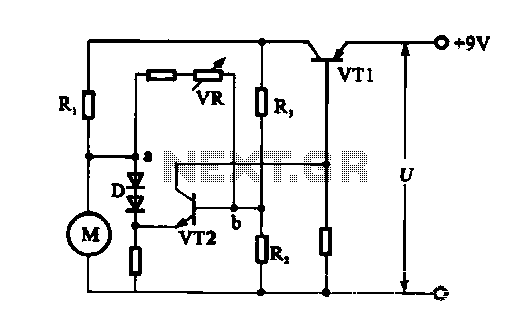
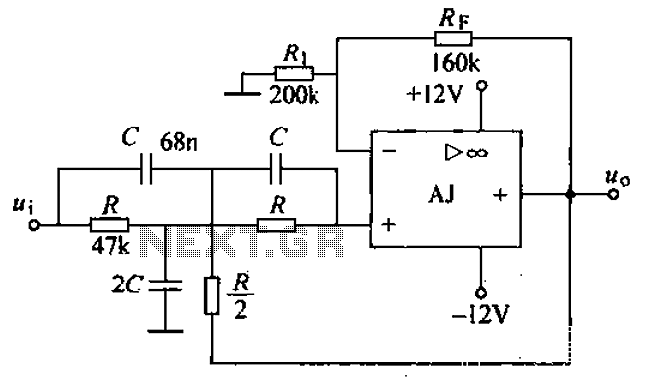
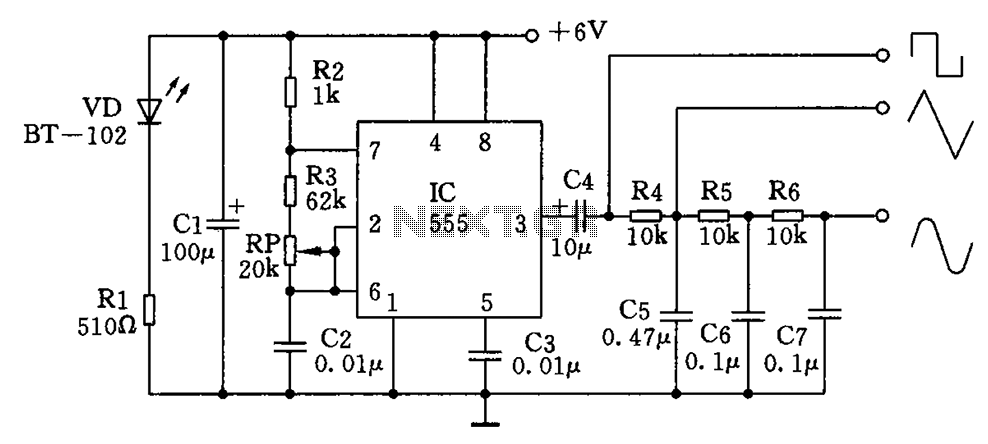
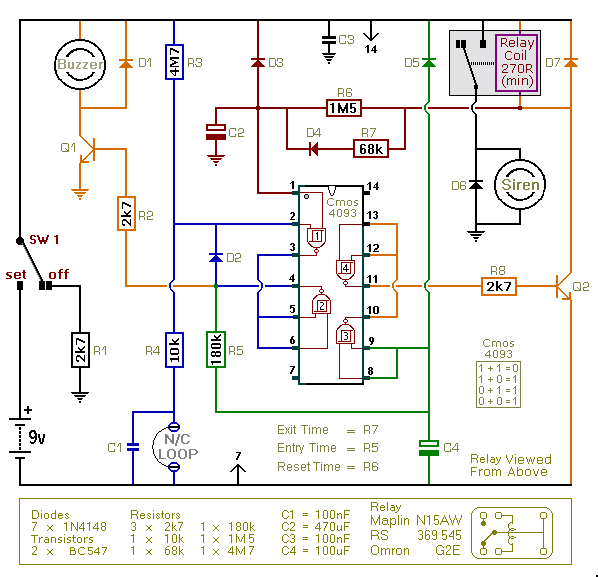
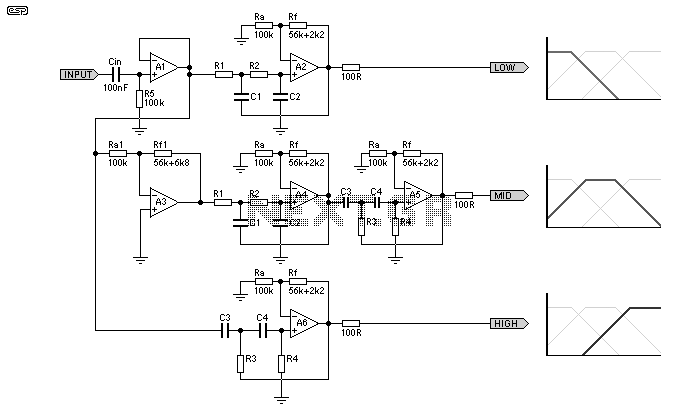
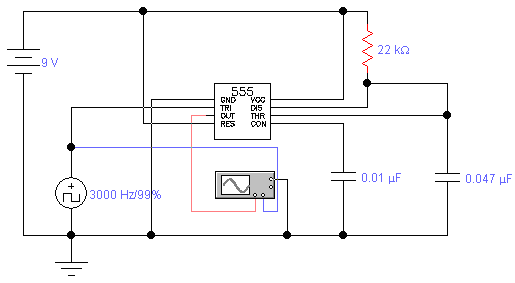
Strong excitation DC electromagnet rapid pull-ter a circuit

Both resistive and capacitive types of capacitor discharge circuits utilize strong excitation methods. The capacity of capacitor C influences the duration of strong excitation.
The operation of a capacitor discharge circuit involves the release of stored electrical energy from a capacitor through a load, which can be resistive, capacitive, or a combination of both. In a resistive discharge circuit, the capacitor discharges through a resistor, resulting in a predictable exponential decay of voltage over time, governed by the time constant τ (tau), which is the product of resistance (R) and capacitance (C). The voltage across the capacitor can be described by the equation V(t) = V0 * e^(-t/τ), where V0 is the initial voltage and t is the time elapsed since discharge began.
In a capacitive discharge circuit, the capacitor may discharge through another capacitor, leading to a more complex interaction. The discharge profile will depend on the capacitance values and the configuration of the circuit. The strong excitation method refers to the rapid application of voltage or current to the circuit, which can enhance the discharge rate and efficiency. The longer the strong excitation time is maintained, the more significant the energy transfer can be, allowing for a more substantial impact on the circuit's performance.
The design considerations for such circuits include selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values to achieve the desired discharge characteristics, ensuring that components can handle the energy levels involved, and incorporating safety mechanisms to prevent damage from excessive current or voltage spikes. Proper simulation and testing are essential to validate the circuit's performance before implementation in practical applications. Both resistive and capacitive type capacitor discharge circuit is the use of the method of strong excitation. Capacitor C capacity, the longer the strong excitation time.
The operation of a capacitor discharge circuit involves the release of stored electrical energy from a capacitor through a load, which can be resistive, capacitive, or a combination of both. In a resistive discharge circuit, the capacitor discharges through a resistor, resulting in a predictable exponential decay of voltage over time, governed by the time constant τ (tau), which is the product of resistance (R) and capacitance (C). The voltage across the capacitor can be described by the equation V(t) = V0 * e^(-t/τ), where V0 is the initial voltage and t is the time elapsed since discharge began.
In a capacitive discharge circuit, the capacitor may discharge through another capacitor, leading to a more complex interaction. The discharge profile will depend on the capacitance values and the configuration of the circuit. The strong excitation method refers to the rapid application of voltage or current to the circuit, which can enhance the discharge rate and efficiency. The longer the strong excitation time is maintained, the more significant the energy transfer can be, allowing for a more substantial impact on the circuit's performance.
The design considerations for such circuits include selecting appropriate resistor and capacitor values to achieve the desired discharge characteristics, ensuring that components can handle the energy levels involved, and incorporating safety mechanisms to prevent damage from excessive current or voltage spikes. Proper simulation and testing are essential to validate the circuit's performance before implementation in practical applications. Both resistive and capacitive type capacitor discharge circuit is the use of the method of strong excitation. Capacitor C capacity, the longer the strong excitation time.