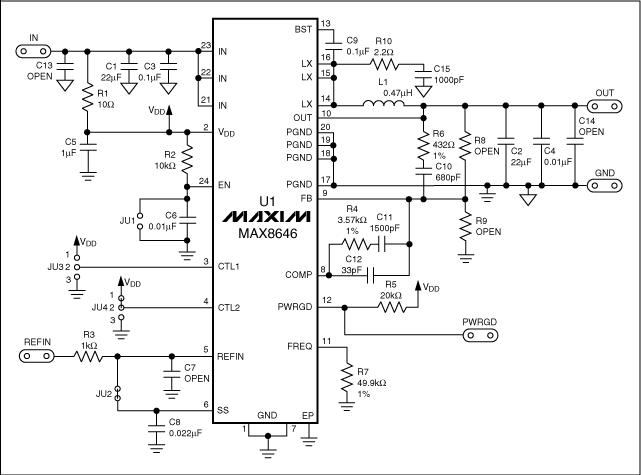
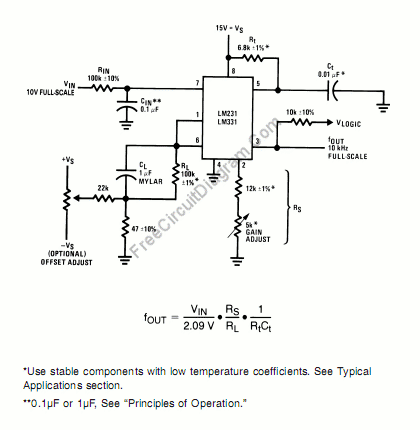
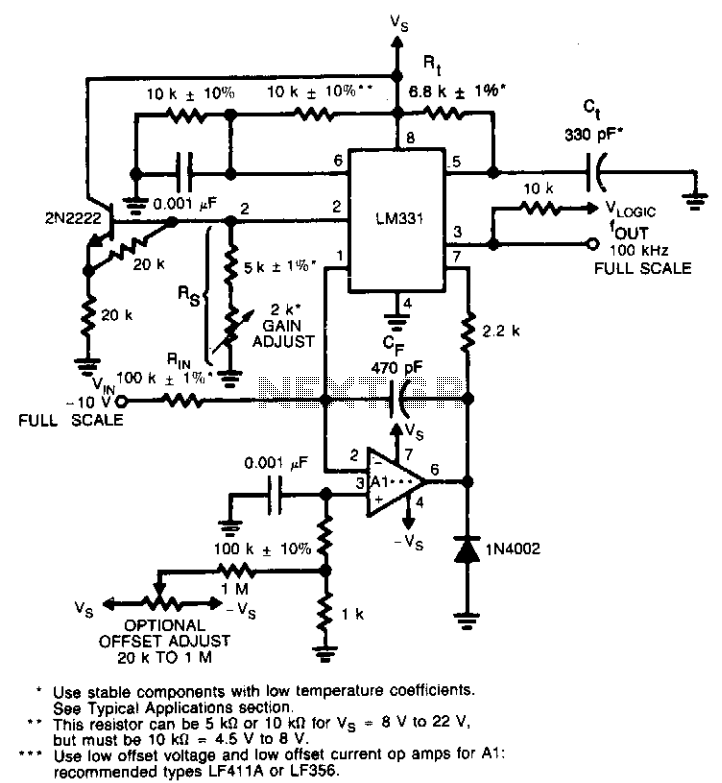
TC1043C Voltage-to-Frequency / Frequency-to-Voltage Converters
The TC9400, TC9401, and TC9402 are low-cost voltage-to-frequency (V/F) converters that utilize low-power CMOS technology. These converters accept a variable analog input signal and generate an output pulse train, with a frequency that is linearly proportional to the input voltage. Additionally, these devices can function as highly accurate frequency-to-voltage (F/V) converters, capable of accepting virtually any input frequency waveform and providing a linearly proportional voltage output. To create a complete V/F or F/V system, only two capacitors, three resistors, and a reference voltage are required. This technology is provided by Microchip Technology Inc.
The TC9400 series of converters are designed to transform an analog voltage into a corresponding frequency output, which is particularly useful in applications where signal transmission over long distances is required without degradation. The output frequency can be easily measured using standard frequency counters or microcontroller input capture features, allowing for precise monitoring and control.
The primary operational principle of the TC9400 series is based on the conversion of an analog input voltage into a digital pulse frequency. This is achieved through the internal circuitry, which includes a voltage comparator and a timing circuit that generates a pulse train. The frequency of this pulse train is directly proportional to the input voltage applied to the converter, allowing for linear operation over a specified range.
For applications requiring frequency-to-voltage conversion, the TC9400 series can be configured to accept various frequency waveforms, including square, sine, and triangle waves. The output voltage produced is also linear, making it suitable for feedback control systems and analog signal processing.
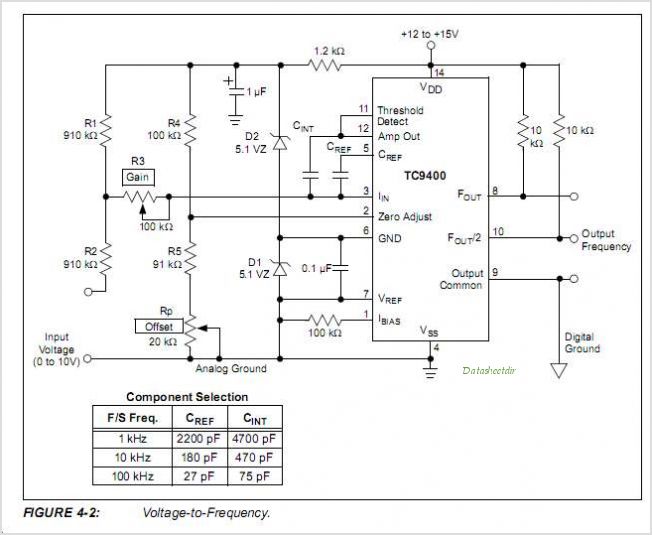
To implement a complete voltage-to-frequency or frequency-to-voltage conversion system, the addition of two capacitors and three resistors is necessary. These passive components help to stabilize the operation of the converter and set the desired gain and frequency response characteristics. A reference voltage is also required to establish the baseline for the input signal.
Overall, the TC9400 series offers a versatile and cost-effective solution for converting analog signals to frequency or vice versa, making it an excellent choice for a wide range of electronic applications, including sensor interfacing, data acquisition, and signal conditioning.TC9402 The TC9400 TC9401 TC9402 are low-cost Voltage-to-Fre- quency (V/F) converters, utilizing low-power CMOS technology. The converters accept a variable Analog input signal and generate an output pulse train, whose frequency is linearly proportional to the input voltage.
The devices CAN also be used as highly accurate Frequency-to-Voltage (F/V) converters, accepting virtually any input frequency waveform and providing a linearly proportional voltage output. A complete V/F or F/V system only requires the addition of two capacitors, three resistors, and refer- ence voltage.
By Microchip Technology Inc. 🔗 External reference
The TC9400 series of converters are designed to transform an analog voltage into a corresponding frequency output, which is particularly useful in applications where signal transmission over long distances is required without degradation. The output frequency can be easily measured using standard frequency counters or microcontroller input capture features, allowing for precise monitoring and control.
The primary operational principle of the TC9400 series is based on the conversion of an analog input voltage into a digital pulse frequency. This is achieved through the internal circuitry, which includes a voltage comparator and a timing circuit that generates a pulse train. The frequency of this pulse train is directly proportional to the input voltage applied to the converter, allowing for linear operation over a specified range.
For applications requiring frequency-to-voltage conversion, the TC9400 series can be configured to accept various frequency waveforms, including square, sine, and triangle waves. The output voltage produced is also linear, making it suitable for feedback control systems and analog signal processing.
To implement a complete voltage-to-frequency or frequency-to-voltage conversion system, the addition of two capacitors and three resistors is necessary. These passive components help to stabilize the operation of the converter and set the desired gain and frequency response characteristics. A reference voltage is also required to establish the baseline for the input signal.
Overall, the TC9400 series offers a versatile and cost-effective solution for converting analog signals to frequency or vice versa, making it an excellent choice for a wide range of electronic applications, including sensor interfacing, data acquisition, and signal conditioning.TC9402 The TC9400 TC9401 TC9402 are low-cost Voltage-to-Fre- quency (V/F) converters, utilizing low-power CMOS technology. The converters accept a variable Analog input signal and generate an output pulse train, whose frequency is linearly proportional to the input voltage.
The devices CAN also be used as highly accurate Frequency-to-Voltage (F/V) converters, accepting virtually any input frequency waveform and providing a linearly proportional voltage output. A complete V/F or F/V system only requires the addition of two capacitors, three resistors, and refer- ence voltage.
By Microchip Technology Inc. 🔗 External reference