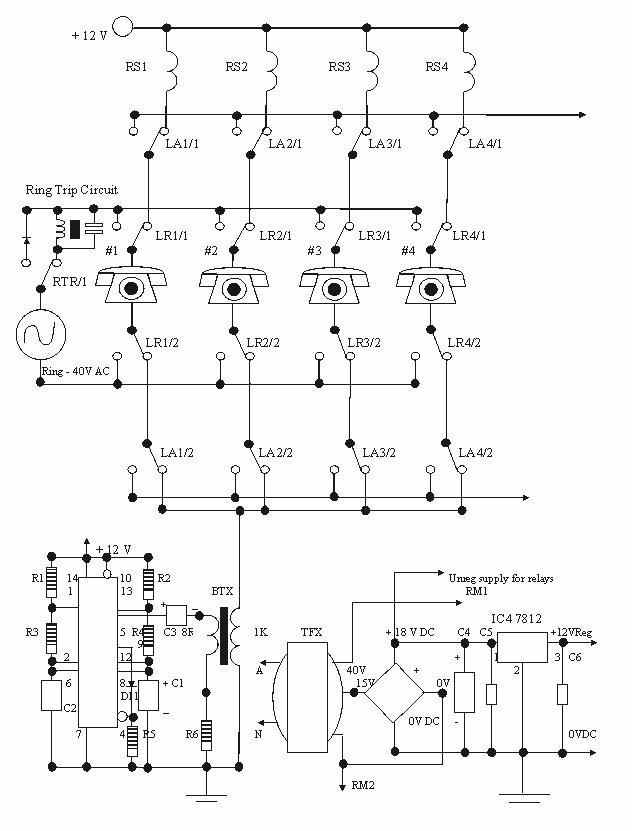
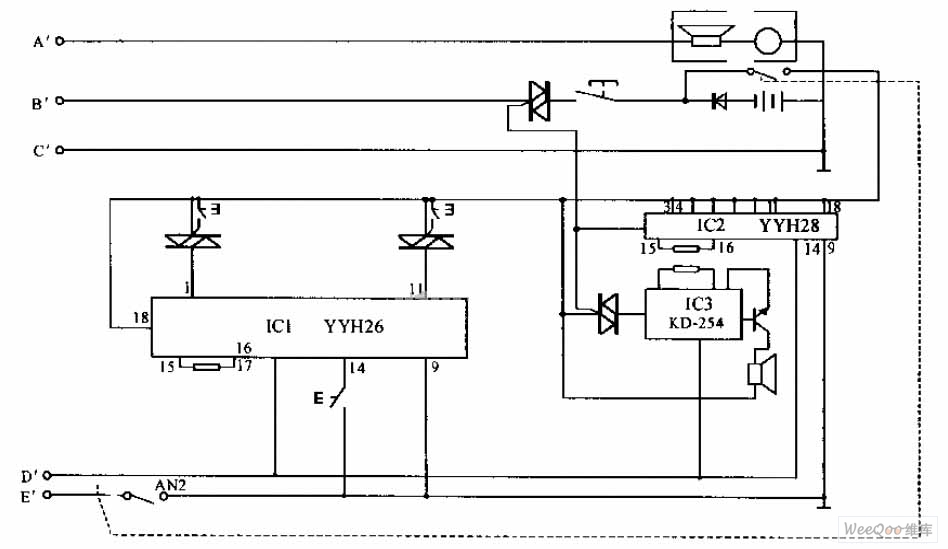
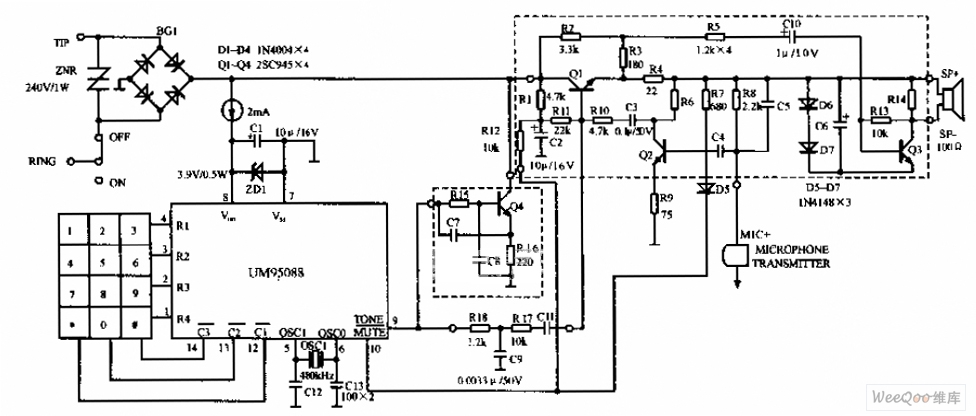
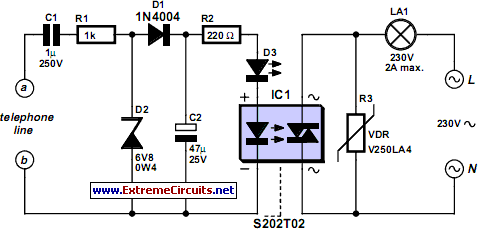
Telephone Headgear

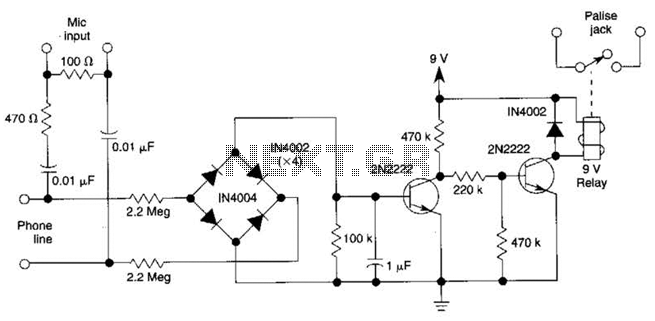
Telephone headgear. A compact, inexpensive, and low component count telecom headset can be constructed using two readily available transistors and a few other electronic components.
The design of a compact and cost-effective telephone headset can be achieved using a minimal number of components, specifically two transistors along with additional electronic parts. The primary function of the headset is to facilitate clear audio communication, which is essential in various applications, including telephony and audio monitoring.
The schematic typically includes two key transistors configured as an amplifier circuit. These transistors serve to boost the audio signals received from the microphone and ensure that the output to the speaker is at a sufficient level for clear sound reproduction. The choice of transistors should consider parameters such as gain, frequency response, and power handling capabilities to ensure optimal performance.
Additional components may include resistors and capacitors that are used to set the biasing conditions for the transistors, filter unwanted noise, and stabilize the circuit. A power supply circuit, possibly using a small battery or a USB power source, will be necessary to provide the required voltage for the operation of the transistors.
The microphone, which can be an electret type for its sensitivity and compact size, is connected to the input of the amplifier circuit. The output from the transistors is then routed to the speaker, which converts the amplified electrical signals back into audible sound.
Overall, the design emphasizes simplicity and efficiency, making it suitable for various applications where a reliable and economical headset solution is required. Proper layout considerations and component selection will further enhance the performance and durability of the headset.Telephone Headgear. Acompact, inexpensive and low component count telecom head- set can be constructed using two readily available transistors and a few other electronic. 🔗 External reference
The design of a compact and cost-effective telephone headset can be achieved using a minimal number of components, specifically two transistors along with additional electronic parts. The primary function of the headset is to facilitate clear audio communication, which is essential in various applications, including telephony and audio monitoring.
The schematic typically includes two key transistors configured as an amplifier circuit. These transistors serve to boost the audio signals received from the microphone and ensure that the output to the speaker is at a sufficient level for clear sound reproduction. The choice of transistors should consider parameters such as gain, frequency response, and power handling capabilities to ensure optimal performance.
Additional components may include resistors and capacitors that are used to set the biasing conditions for the transistors, filter unwanted noise, and stabilize the circuit. A power supply circuit, possibly using a small battery or a USB power source, will be necessary to provide the required voltage for the operation of the transistors.
The microphone, which can be an electret type for its sensitivity and compact size, is connected to the input of the amplifier circuit. The output from the transistors is then routed to the speaker, which converts the amplified electrical signals back into audible sound.
Overall, the design emphasizes simplicity and efficiency, making it suitable for various applications where a reliable and economical headset solution is required. Proper layout considerations and component selection will further enhance the performance and durability of the headset.Telephone Headgear. Acompact, inexpensive and low component count telecom head- set can be constructed using two readily available transistors and a few other electronic. 🔗 External reference