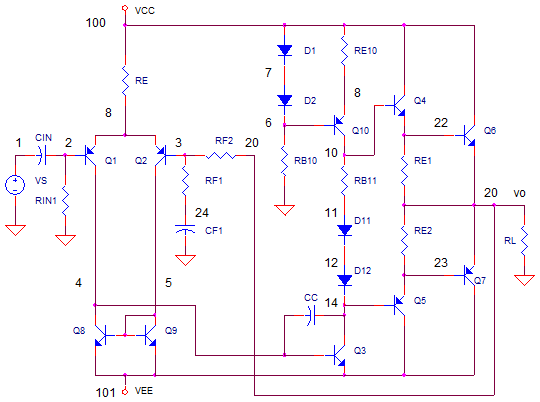
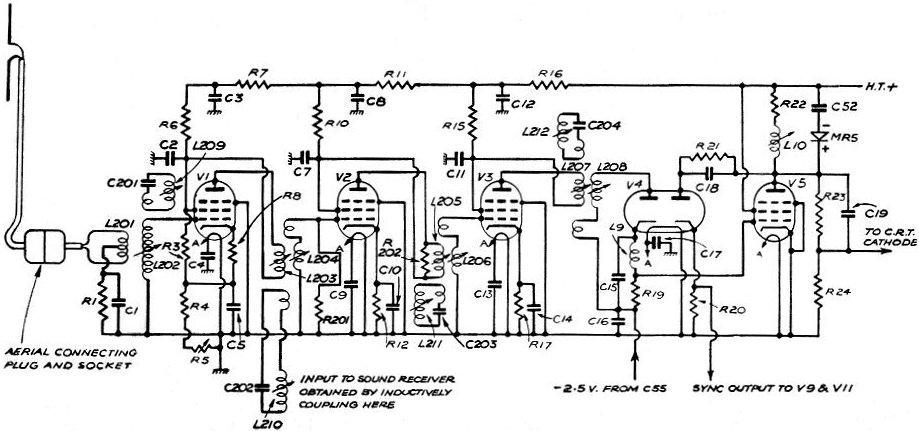
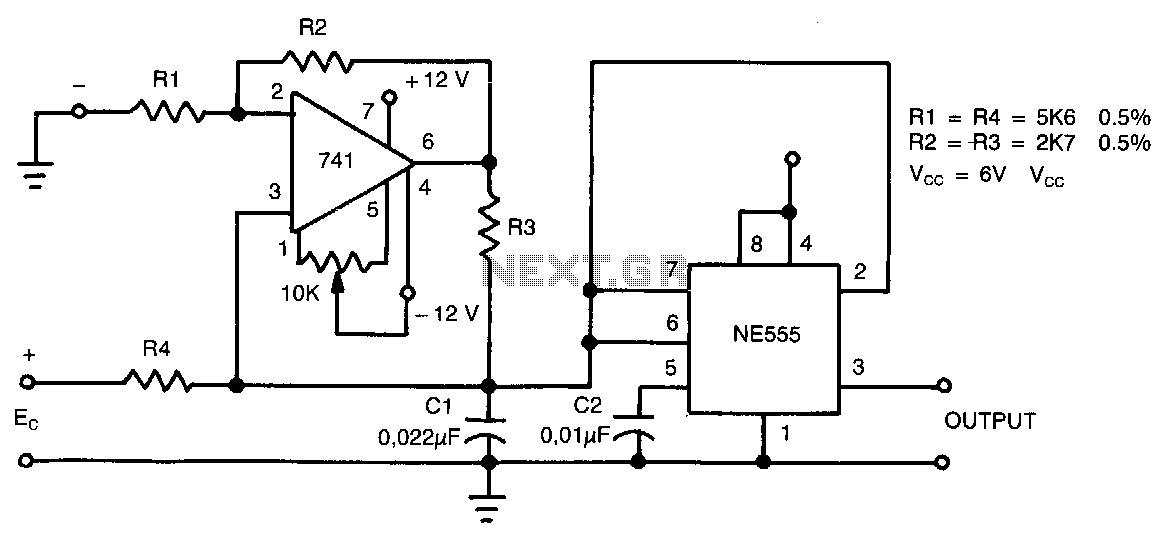
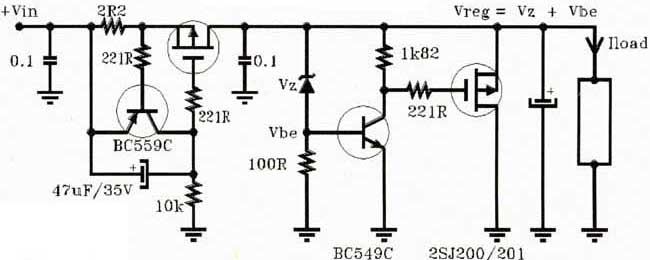
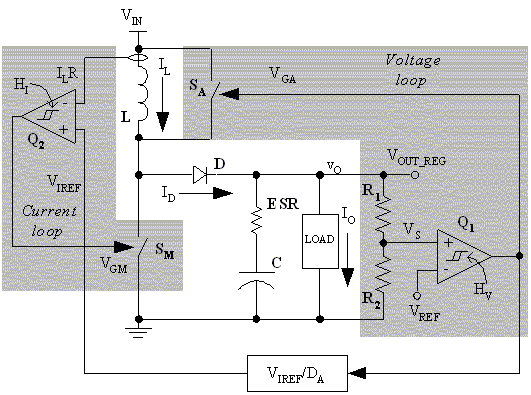
The basic structure of the DA converter
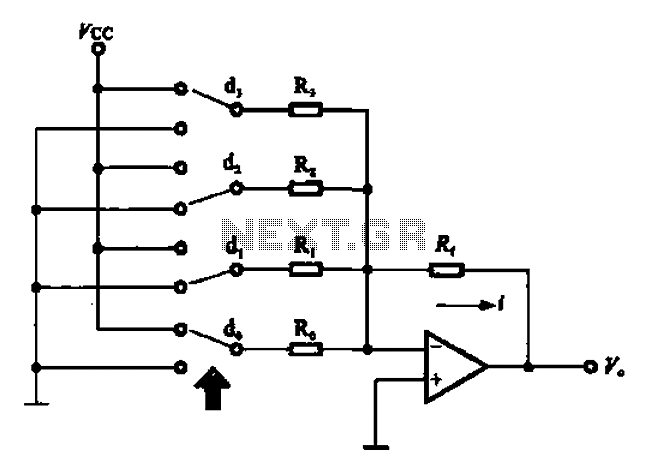
An A/D converter circuit can be represented by a simplified schematic, which illustrates a parallel type A/D converter. The term "median" refers to the number of bits in the digital signal output. The figure displays four A/D converters utilizing five voltage comparators, with quantization levels of 24 and 16, corresponding to 16 quantization levels.
The parallel type A/D converter circuit operates by converting an analog signal into a digital representation through simultaneous comparisons. In this configuration, the circuit employs multiple voltage comparators to assess the input signal against predefined reference voltages. The number of bits determines the resolution of the output digital signal, where each bit corresponds to a quantization level.
In this specific design, four A/D converters are integrated, each contributing to the overall conversion process. The use of five voltage comparators allows for effective discrimination between the quantization levels, enhancing the accuracy of the conversion. The quantization levels mentioned, 24 and 16, indicate the potential output states that the analog input can be mapped to, with 16 distinct levels being a common standard for many applications.
This circuit design is particularly useful in applications requiring high-speed data acquisition and processing, where rapid conversion of analog signals to digital form is essential. The parallel nature of the circuit allows for simultaneous processing of multiple signals, significantly improving the throughput of data in systems such as digital oscilloscopes, data loggers, and various measurement instruments. The careful selection of voltage comparators and quantization levels plays a critical role in optimizing the performance and accuracy of the A/D conversion process.A/D converter circuit can be represented by a simplified circuit shown in Figure 4 is a (bit) parallel type A/D converter circuit, the so-called median is the number of bits in a digital signal output means. From the figure shows, four A/D converters use I5 voltage comparators. 4 quantization, namely 24 16, press l6 quantization levels.
The parallel type A/D converter circuit operates by converting an analog signal into a digital representation through simultaneous comparisons. In this configuration, the circuit employs multiple voltage comparators to assess the input signal against predefined reference voltages. The number of bits determines the resolution of the output digital signal, where each bit corresponds to a quantization level.
In this specific design, four A/D converters are integrated, each contributing to the overall conversion process. The use of five voltage comparators allows for effective discrimination between the quantization levels, enhancing the accuracy of the conversion. The quantization levels mentioned, 24 and 16, indicate the potential output states that the analog input can be mapped to, with 16 distinct levels being a common standard for many applications.
This circuit design is particularly useful in applications requiring high-speed data acquisition and processing, where rapid conversion of analog signals to digital form is essential. The parallel nature of the circuit allows for simultaneous processing of multiple signals, significantly improving the throughput of data in systems such as digital oscilloscopes, data loggers, and various measurement instruments. The careful selection of voltage comparators and quantization levels plays a critical role in optimizing the performance and accuracy of the A/D conversion process.A/D converter circuit can be represented by a simplified circuit shown in Figure 4 is a (bit) parallel type A/D converter circuit, the so-called median is the number of bits in a digital signal output means. From the figure shows, four A/D converters use I5 voltage comparators. 4 quantization, namely 24 16, press l6 quantization levels.