Frequency converter circuit
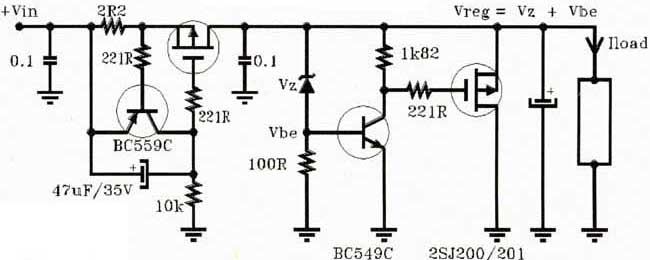
Frequency converter schematic, frequency to voltage converter schematic, frequency to voltage converter using TR, voltage to frequency converter application.
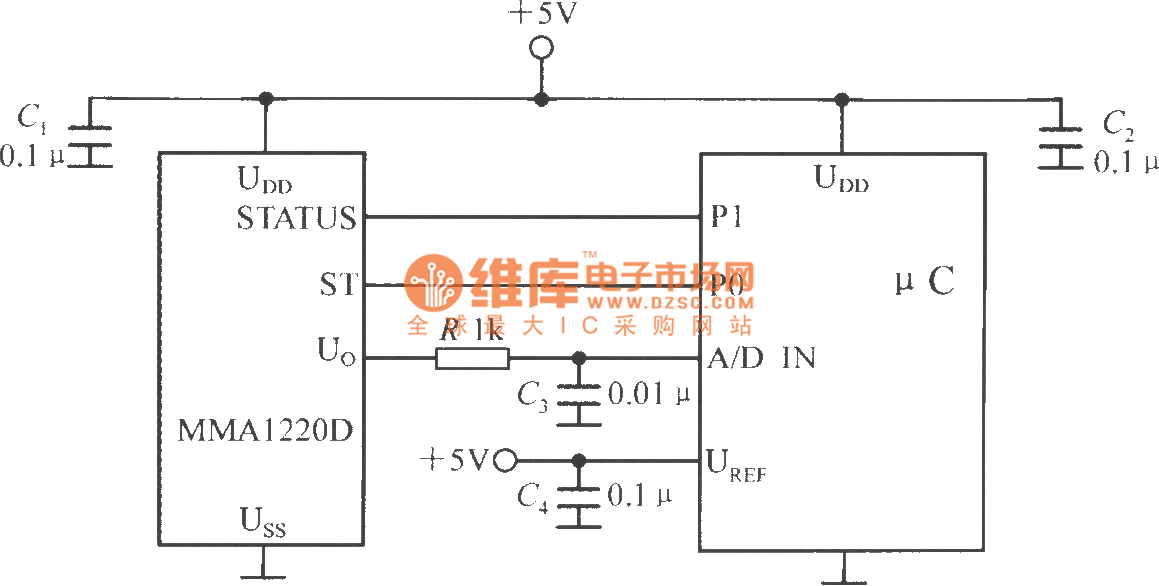
A frequency converter is an essential electronic circuit that transforms frequency signals into corresponding voltage levels or vice versa. The frequency to voltage converter schematic is designed to provide a linear output voltage that is proportional to the input frequency. This is particularly useful in applications where frequency signals need to be monitored or processed, such as in signal processing or control systems.
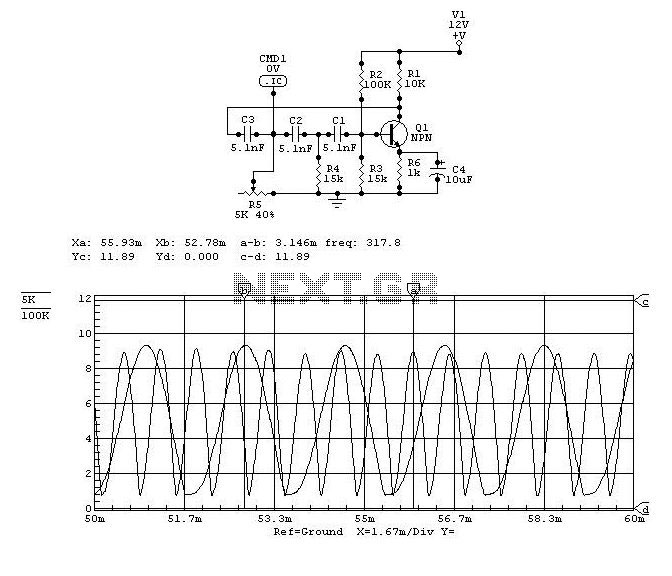
The frequency to voltage converter using a transistor (TR) typically employs a configuration where the input frequency signal is fed into a transistor circuit. The transistor operates in a switching mode, converting the frequency variations into a varying voltage output. The output voltage can then be further processed or displayed, providing a clear representation of the input frequency.
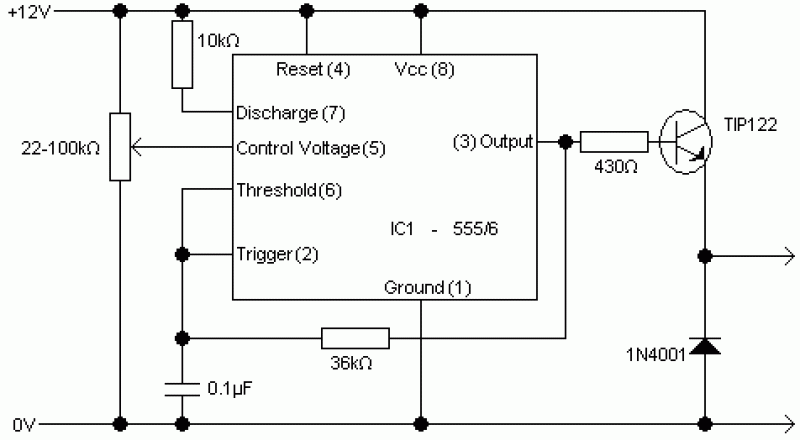
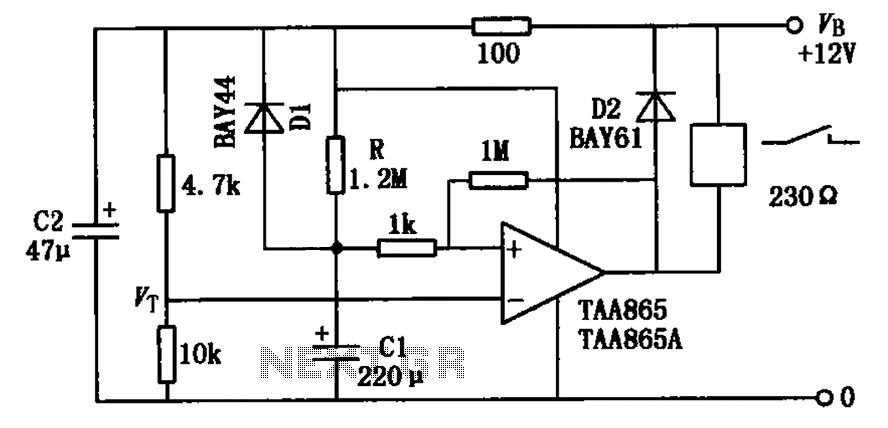
On the other hand, the voltage to frequency converter application is designed to achieve the opposite function, where an input voltage signal is converted into a frequency output. This type of converter is useful in telemetry systems and for generating frequency-modulated signals. The circuit generally utilizes operational amplifiers and other components to ensure that the output frequency is accurately proportional to the input voltage.
Both types of converters can be integrated into various electronic systems, enabling effective communication, control, and monitoring of frequency-based signals. Proper design considerations include component selection, circuit stability, and the linearity of the conversion process, which are crucial for achieving desired performance in practical applications.Frequency converter schematic, frequency to voltage converter schematic, Frequency to Voltage Converter Using TR, Voltage to Frequency Converter Application 🔗 External reference
A frequency converter is an essential electronic circuit that transforms frequency signals into corresponding voltage levels or vice versa. The frequency to voltage converter schematic is designed to provide a linear output voltage that is proportional to the input frequency. This is particularly useful in applications where frequency signals need to be monitored or processed, such as in signal processing or control systems.
The frequency to voltage converter using a transistor (TR) typically employs a configuration where the input frequency signal is fed into a transistor circuit. The transistor operates in a switching mode, converting the frequency variations into a varying voltage output. The output voltage can then be further processed or displayed, providing a clear representation of the input frequency.
On the other hand, the voltage to frequency converter application is designed to achieve the opposite function, where an input voltage signal is converted into a frequency output. This type of converter is useful in telemetry systems and for generating frequency-modulated signals. The circuit generally utilizes operational amplifiers and other components to ensure that the output frequency is accurately proportional to the input voltage.
Both types of converters can be integrated into various electronic systems, enabling effective communication, control, and monitoring of frequency-based signals. Proper design considerations include component selection, circuit stability, and the linearity of the conversion process, which are crucial for achieving desired performance in practical applications.Frequency converter schematic, frequency to voltage converter schematic, Frequency to Voltage Converter Using TR, Voltage to Frequency Converter Application 🔗 External reference