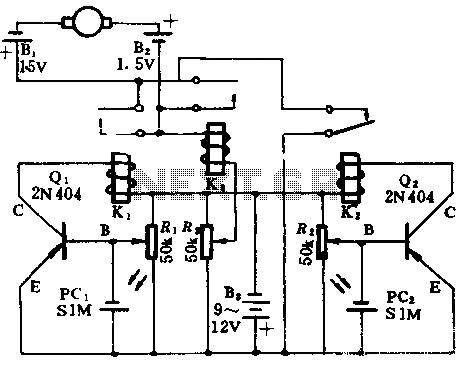
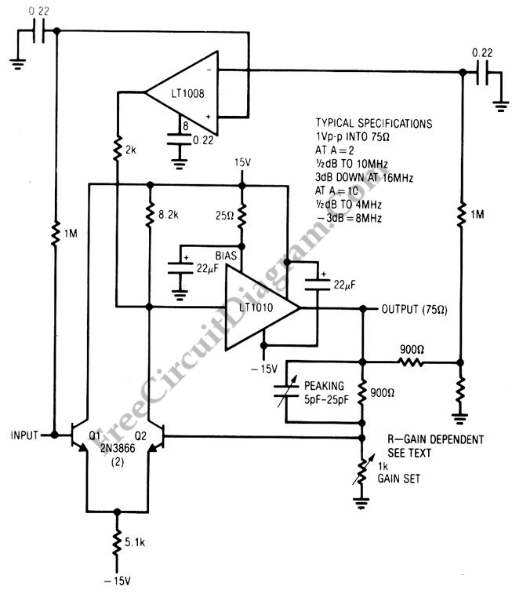
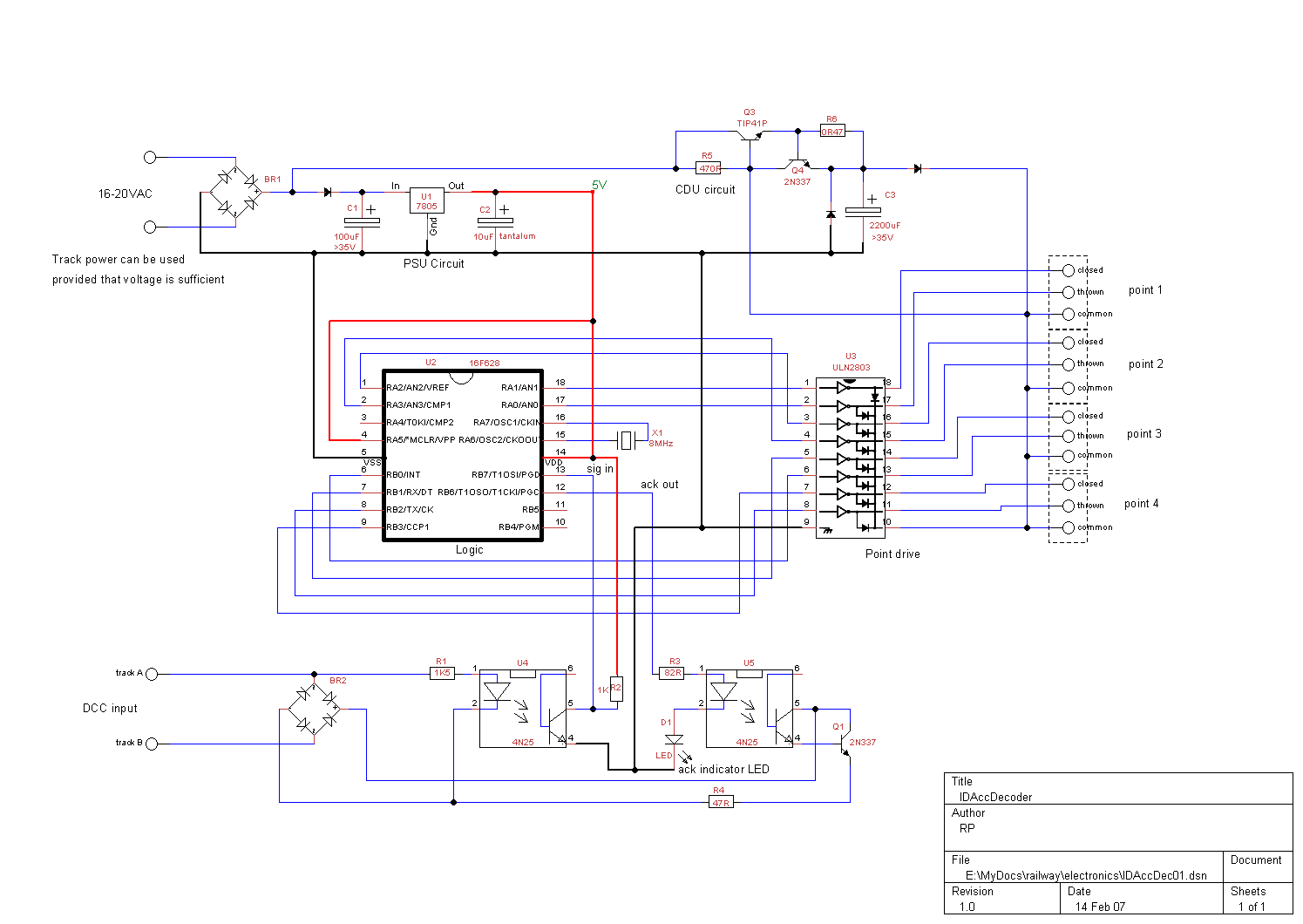
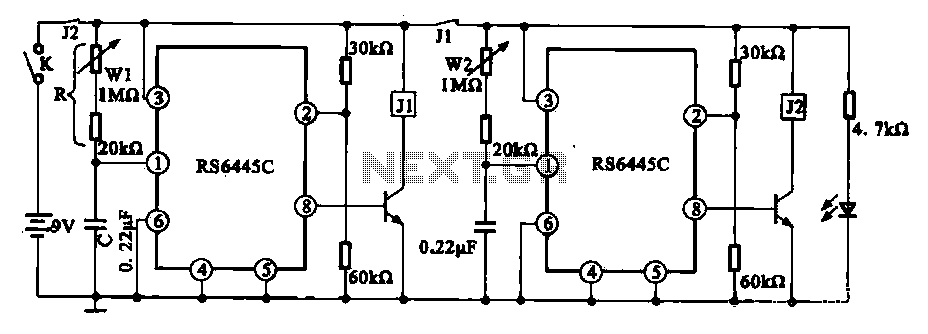
The PLL FM demodulator (4046) circuit
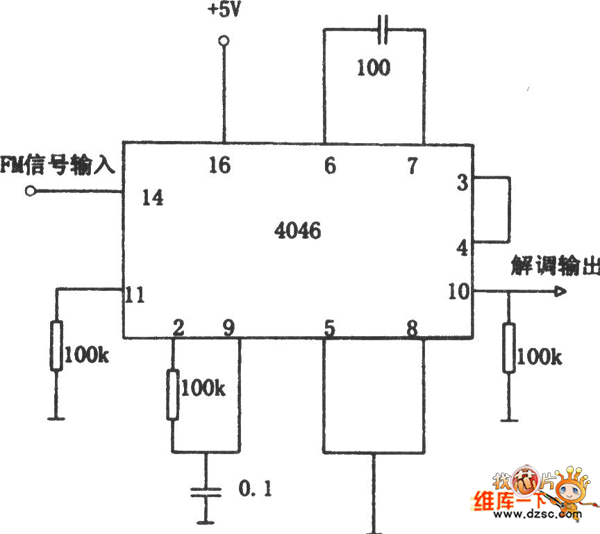
The FM demodulator circuit, as illustrated in the figure, utilizes a 4046 Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) integrated circuit to convert the intermediate frequency FM input signal into a lower frequency output.
The FM demodulator circuit based on the 4046 PLL IC operates by employing phase-locked loop techniques to achieve demodulation of frequency-modulated signals. The 4046 IC includes a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) and a phase comparator, which are integral to the demodulation process.
In this configuration, the FM input signal is fed into the phase comparator, which compares the phase of the incoming signal with the output of the VCO. Any phase difference detected results in an adjustment of the VCO frequency, effectively tracking the frequency variations of the FM signal. This tracking action allows the circuit to convert the frequency variations into corresponding voltage changes, which represent the original audio or data signal.
The output of the VCO is then filtered to remove high-frequency components, resulting in a low-frequency output that is a replica of the original modulating signal. Additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be included in the circuit to set the bandwidth and stability of the PLL, ensuring optimal performance for the specific FM signals being demodulated.
Overall, the 4046 PLL-based FM demodulator circuit is a robust solution for demodulating FM signals, suitable for various applications in communication systems where reliable and accurate signal processing is essential.See as the figure, the FM demodulator circuit consists of 4046 PLL particles, the intermediate FM input signal is demodulated into the low frequency by the circuit.. 🔗 External reference
The FM demodulator circuit based on the 4046 PLL IC operates by employing phase-locked loop techniques to achieve demodulation of frequency-modulated signals. The 4046 IC includes a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) and a phase comparator, which are integral to the demodulation process.
In this configuration, the FM input signal is fed into the phase comparator, which compares the phase of the incoming signal with the output of the VCO. Any phase difference detected results in an adjustment of the VCO frequency, effectively tracking the frequency variations of the FM signal. This tracking action allows the circuit to convert the frequency variations into corresponding voltage changes, which represent the original audio or data signal.
The output of the VCO is then filtered to remove high-frequency components, resulting in a low-frequency output that is a replica of the original modulating signal. Additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be included in the circuit to set the bandwidth and stability of the PLL, ensuring optimal performance for the specific FM signals being demodulated.
Overall, the 4046 PLL-based FM demodulator circuit is a robust solution for demodulating FM signals, suitable for various applications in communication systems where reliable and accurate signal processing is essential.See as the figure, the FM demodulator circuit consists of 4046 PLL particles, the intermediate FM input signal is demodulated into the low frequency by the circuit.. 🔗 External reference