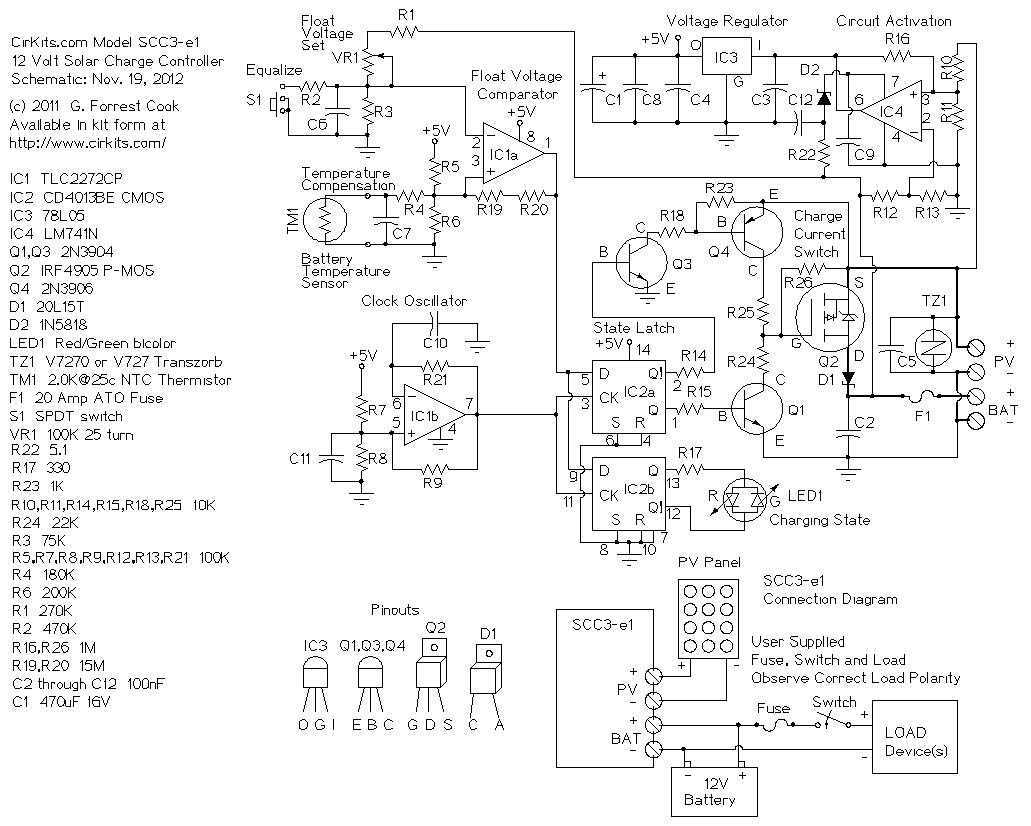
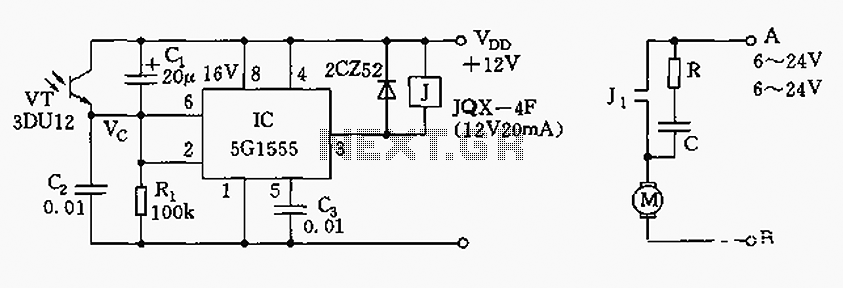
The Zener-based solar engine
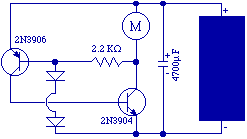
The capacitor charges until the PNP transistor (here shown as a 2N3906, but you could also use a BC327) receives base current through the Zener and turns on. Then the NPN transistor (here shown as a 2N3904, but you could also use a BC337) turns on and the capacitor is discharged through the motor. As the NPN turns on the 2.2K resistor starts to supply base current to the PNP and the circuit snaps on.
The described circuit operates as a simple motor control mechanism utilizing a PNP and an NPN transistor configuration. The PNP transistor (2N3906 or BC327) is responsible for initial activation, while the NPN transistor (2N3904 or BC337) handles the power delivery to the motor.
Initially, the capacitor charges through a resistor until the voltage across it reaches a level sufficient to forward-bias the base-emitter junction of the PNP transistor. The Zener diode in the circuit serves to regulate the voltage applied to the base of the PNP transistor, ensuring that it turns on at a specific threshold voltage. Once the PNP transistor is activated, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, which in turn provides base current to the NPN transistor through the 2.2K resistor.
As the NPN transistor turns on, it creates a low-resistance path from the collector to the emitter, enabling the capacitor to discharge rapidly through the motor connected to the NPN's collector. This discharge provides the necessary current to drive the motor, effectively turning it on. The action of the NPN transistor also reinforces the PNP transistor's conduction, creating a regenerative feedback loop that keeps the circuit in an 'on' state until the capacitor discharges below a certain threshold.
Overall, this configuration allows for a controlled and efficient method to activate a motor using capacitive discharge, leveraging the properties of both transistor types to achieve reliable operation.The capacitor charges until the PNP transistor (here shown as a 2N3906, but you could also use a BC327) receives base current through the Zener and turns on. Then the NPN transistor (here shown as a 2N3904, but you could also use a BC337) turns on and the capacitor is discharged through the motor.
As the NPN turns on the 2.2K resistor starts to supply base current to the PNP and the circuit snaps on. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a simple motor control mechanism utilizing a PNP and an NPN transistor configuration. The PNP transistor (2N3906 or BC327) is responsible for initial activation, while the NPN transistor (2N3904 or BC337) handles the power delivery to the motor.
Initially, the capacitor charges through a resistor until the voltage across it reaches a level sufficient to forward-bias the base-emitter junction of the PNP transistor. The Zener diode in the circuit serves to regulate the voltage applied to the base of the PNP transistor, ensuring that it turns on at a specific threshold voltage. Once the PNP transistor is activated, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, which in turn provides base current to the NPN transistor through the 2.2K resistor.
As the NPN transistor turns on, it creates a low-resistance path from the collector to the emitter, enabling the capacitor to discharge rapidly through the motor connected to the NPN's collector. This discharge provides the necessary current to drive the motor, effectively turning it on. The action of the NPN transistor also reinforces the PNP transistor's conduction, creating a regenerative feedback loop that keeps the circuit in an 'on' state until the capacitor discharges below a certain threshold.
Overall, this configuration allows for a controlled and efficient method to activate a motor using capacitive discharge, leveraging the properties of both transistor types to achieve reliable operation.The capacitor charges until the PNP transistor (here shown as a 2N3906, but you could also use a BC327) receives base current through the Zener and turns on. Then the NPN transistor (here shown as a 2N3904, but you could also use a BC337) turns on and the capacitor is discharged through the motor.
As the NPN turns on the 2.2K resistor starts to supply base current to the PNP and the circuit snaps on. 🔗 External reference