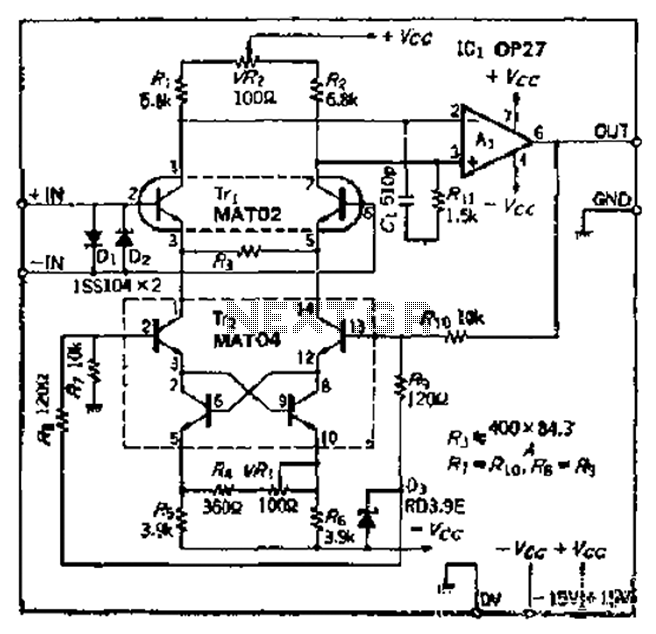
There are preamplifier with four inputs
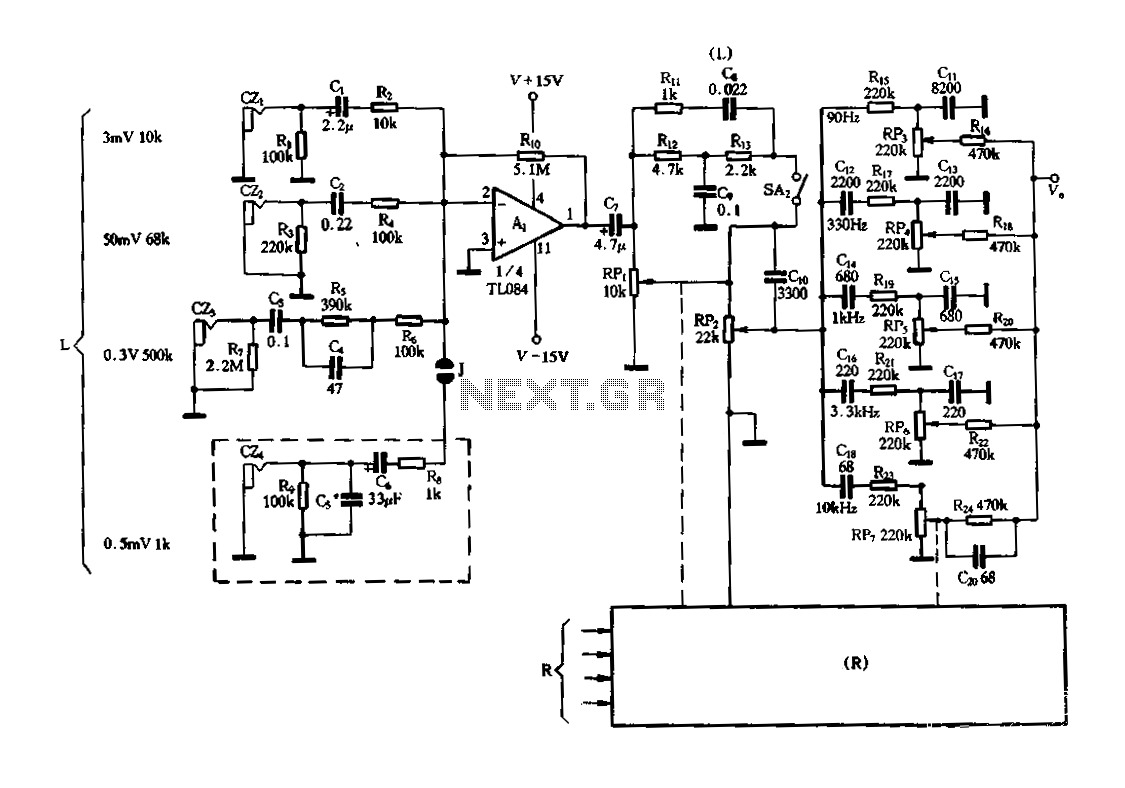
Figure 3-25 illustrates a hybrid circuit featuring four input preamplifiers. The components C1, C2, C3, and C4 can accept signals from a microphone, line, phono, and crystal head respectively. The configuration allows for the individual or simultaneous entry of four mixed inputs, facilitating program dubbing, commentary, and other editing tasks. The inputs do not interfere with each other. The preamplifier employs the principle of a proportional adder using an inverting operational amplifier. When multiple signals are input simultaneously, the output voltage corresponds to the sum of each input voltage. The inverting input of the operational amplifier acts as a virtual ground summing point, effectively isolating the respective input signals. When the input signal is at 0V, the voltage across the resistor is also zero, ensuring that the operation of other channels remains unaffected. Each input source can accommodate different input voltage levels, and the four input interfaces utilize various structures and component values, along with additional required inputs. The values of the input interface circuit components are detailed in the diagram, aligned with the sensitivity calculations of the input signals. The actual component values can be adjusted based on standard values using resistors R2, R3, and R6. When C4 is used as a head input, resistor Ra is set to 1 kΩ, which attenuates high-frequency signals, contributing to frequency equalization effects. The volume control potentiometers R1 and R11, along with C for treble compensation, form an automatic compensation circuit for treble frequencies. Similarly, R1, R12, C9, and R13 create a low-frequency automatic compensation circuit. Increasing the volume with R1 enhances the compensation amount, allowing for volume adjustments without resetting the pitch controller. The SA control switch regulates the compensation circuit. The RC network consists of five sections of the equalization circuit, allowing for a range adjustment of 12 dB. C3 and C4 are designed for high sensitivity, ensuring that large amplitude signals do not inadvertently overload the amplifier. If C4 is absent, point J should be disconnected during commissioning. To minimize hum and induced noise, the input elements, including C1 to C4, should be enclosed in a shielded metal cover with a solid ground connection. All input signal lines should be constructed using well-grounded metal shielded wire. The circuit employs the TL084 quad operational amplifier, known for its excellent frequency response, with a passband bandwidth of approximately 20 Hz to 20 kHz and a distortion level of 0.5%.
The hybrid circuit represented in Figure 3-25 is designed to accommodate a variety of audio input sources while maintaining signal integrity through isolation and compensation techniques. The use of an inverting operational amplifier as a proportional adder allows for the seamless summation of multiple audio signals, making it particularly useful in applications such as broadcasting, recording, and live sound reinforcement. The layout of the input stages ensures that each source can be independently adjusted without affecting the others, a critical feature in multi-source environments.
The automatic compensation circuits for both treble and bass frequencies enhance the overall audio quality by maintaining a balanced sound profile, regardless of the volume level. This feature is particularly beneficial in professional audio applications where consistent sound quality is paramount. The adjustable resistors and capacitors allow for fine-tuning of the circuit, enabling it to cater to various input sensitivities and signal characteristics.
Furthermore, the choice of the TL084 operational amplifier ensures that the circuit operates efficiently across a wide frequency range, making it suitable for high-fidelity audio applications. The design considerations, including the shielding of input elements and grounding practices, further contribute to the circuit's resilience against noise and interference, ensuring high-quality audio output.
In summary, the hybrid circuit in Figure 3-25 exemplifies a versatile solution for audio signal processing, integrating advanced features that enhance functionality, performance, and user control in professional audio environments.Figure 3-25 is a hybrid having four input preamplifier, in the circuit, cZ1, cz, C23 and cz4 respectively, can enter the microphone, line, phono and crystal head signal. Quad c an enter individually or simultaneously four mixed input, but also for dubbing the program needed chipped commentary and other editing. Enter either alone or in combination input, nothing happens to them between each other. The preamplifier input is applied the principle of proportional adder inverting operational amplifier, when several signals simultaneously input Pops, the output voltage is equal to the sum of each of the input voltage.
While at the inverting input of the operational amplifier summing point of virtual ground, and therefore between the respective input signal is isolated from each other when the input signal is a road 0:00, the input voltage across the resistor is also zero, so it does not affect the work of other separate ways o to accommodate each source input voltage is different, four input interface uses a different structure and number of circuit elements value, while also adding additional input required. The input interface circuit component values are shown in the diagram in accordance with the subject of the input signal sensitivity calculations.
If the actual figure depending on the input with the standard values can be properly adjusted R2, R, R6, or where the resistance can be. When C24 as head input, Ra take 1kfl, thus attenuating the treble, treble end of the play frequency equalization effect o volume control potentiometer RPi and Rl1, C treble consisting of automatic compensation circuit; RPi and Rt2, c9, Rl3 form a low tone automatic compensation circuit.
When RPl turn up the volume the more hours, the larger the amount of compensation Pak compensation circuit, therefore, adjust the sound volume when, without resetting the pitch controller.. SA control switch for the compensation circuit. RC network composed of five sections of the equalization circuit, adjust the range of 12dB. czJ and C24 high sensitivity, large-amplitude signal can not accidentally access lines, etc., so as not to damage the amplifier overload and bad.
No C24, the commissioning should point J disconnected. In order to reduce hum and induced noise, (: zl ~ C24 and an input element should be shielded metal cover, and good well grounded input signal line should be used in all metal shielded wire, and the end is well grounded. Circuit adoption of better performance quad op amp TL084, has good frequency response of the input line, the passband bandwidth of approximately 20Hz ~ 20kHz, distortion 0.5% o
The hybrid circuit represented in Figure 3-25 is designed to accommodate a variety of audio input sources while maintaining signal integrity through isolation and compensation techniques. The use of an inverting operational amplifier as a proportional adder allows for the seamless summation of multiple audio signals, making it particularly useful in applications such as broadcasting, recording, and live sound reinforcement. The layout of the input stages ensures that each source can be independently adjusted without affecting the others, a critical feature in multi-source environments.
The automatic compensation circuits for both treble and bass frequencies enhance the overall audio quality by maintaining a balanced sound profile, regardless of the volume level. This feature is particularly beneficial in professional audio applications where consistent sound quality is paramount. The adjustable resistors and capacitors allow for fine-tuning of the circuit, enabling it to cater to various input sensitivities and signal characteristics.
Furthermore, the choice of the TL084 operational amplifier ensures that the circuit operates efficiently across a wide frequency range, making it suitable for high-fidelity audio applications. The design considerations, including the shielding of input elements and grounding practices, further contribute to the circuit's resilience against noise and interference, ensuring high-quality audio output.
In summary, the hybrid circuit in Figure 3-25 exemplifies a versatile solution for audio signal processing, integrating advanced features that enhance functionality, performance, and user control in professional audio environments.Figure 3-25 is a hybrid having four input preamplifier, in the circuit, cZ1, cz, C23 and cz4 respectively, can enter the microphone, line, phono and crystal head signal. Quad c an enter individually or simultaneously four mixed input, but also for dubbing the program needed chipped commentary and other editing. Enter either alone or in combination input, nothing happens to them between each other. The preamplifier input is applied the principle of proportional adder inverting operational amplifier, when several signals simultaneously input Pops, the output voltage is equal to the sum of each of the input voltage.
While at the inverting input of the operational amplifier summing point of virtual ground, and therefore between the respective input signal is isolated from each other when the input signal is a road 0:00, the input voltage across the resistor is also zero, so it does not affect the work of other separate ways o to accommodate each source input voltage is different, four input interface uses a different structure and number of circuit elements value, while also adding additional input required. The input interface circuit component values are shown in the diagram in accordance with the subject of the input signal sensitivity calculations.
If the actual figure depending on the input with the standard values can be properly adjusted R2, R, R6, or where the resistance can be. When C24 as head input, Ra take 1kfl, thus attenuating the treble, treble end of the play frequency equalization effect o volume control potentiometer RPi and Rl1, C treble consisting of automatic compensation circuit; RPi and Rt2, c9, Rl3 form a low tone automatic compensation circuit.
When RPl turn up the volume the more hours, the larger the amount of compensation Pak compensation circuit, therefore, adjust the sound volume when, without resetting the pitch controller.. SA control switch for the compensation circuit. RC network composed of five sections of the equalization circuit, adjust the range of 12dB. czJ and C24 high sensitivity, large-amplitude signal can not accidentally access lines, etc., so as not to damage the amplifier overload and bad.
No C24, the commissioning should point J disconnected. In order to reduce hum and induced noise, (: zl ~ C24 and an input element should be shielded metal cover, and good well grounded input signal line should be used in all metal shielded wire, and the end is well grounded. Circuit adoption of better performance quad op amp TL084, has good frequency response of the input line, the passband bandwidth of approximately 20Hz ~ 20kHz, distortion 0.5% o