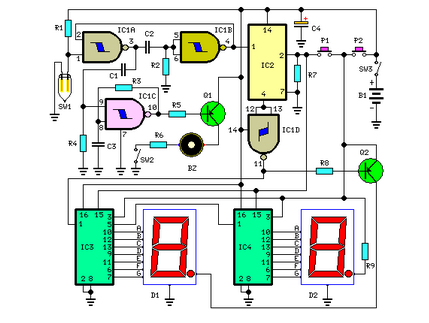
TRANSISTORIZED THYRATRON RING COUNTER

Each bistable circuit comprises two oppositely-symmetrical germanium transistors, two diodes, and four resistors. An additional transistor, Q, facilitates the transition of the conducting state to the next position when actuated by a transfer pulse. The absence of capacitors allows for high-speed operation, and no bias current is necessary from the ON stage to maintain the cutoff of other stages.
The described bistable circuit operates using a pair of germanium transistors configured in a complementary manner to achieve stability in two distinct states. The transistors are pivotal in defining the circuit's functionality, where one transistor is turned ON while the other remains OFF, thus creating a stable logic state. The two diodes serve to protect the circuit from reverse polarity and to ensure proper signal direction, contributing to the overall reliability of the circuit.
The four resistors are strategically placed to set the biasing and feedback conditions for the transistors, ensuring that the switching characteristics are optimized for rapid transitions between states. The additional transistor, labeled Q, plays a crucial role in the circuit's operation by receiving transfer pulses that prompt it to change the conducting state, effectively allowing the circuit to toggle between its two stable states.
The design choice to exclude capacitors is significant, as it enhances the circuit's speed of operation. Capacitors, while useful for filtering and timing applications, can introduce delays due to their charging and discharging times. By eliminating these components, the circuit can achieve faster response times, making it suitable for applications requiring quick switching.
Moreover, the absence of bias current from the ON stage to the other stages ensures that the circuit remains in a stable state without unnecessary power consumption. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in battery-operated devices or low-power applications, where efficiency is paramount.
In summary, the bistable circuit described is a robust and efficient design utilizing germanium transistors, diodes, and resistors to achieve high-speed operation and stable state retention without the need for bias currents or capacitors. This configuration is ideal for various electronic applications, including memory storage and digital logic systems.Each bistable circuit has two opposite-symmetry germanium transistors, two diodes, and four resistors. Additional transistor Q transfers conducting stage to next position when actuated by transfer pulse. Absence of capacitors gives high-speed operation. No bias current is required from ON stage to keep other stages cut off. -J. A. Pecar, Ring Count er Uses Transistors, Electronics, 34:4, p 49-51. 🔗 External reference
The described bistable circuit operates using a pair of germanium transistors configured in a complementary manner to achieve stability in two distinct states. The transistors are pivotal in defining the circuit's functionality, where one transistor is turned ON while the other remains OFF, thus creating a stable logic state. The two diodes serve to protect the circuit from reverse polarity and to ensure proper signal direction, contributing to the overall reliability of the circuit.
The four resistors are strategically placed to set the biasing and feedback conditions for the transistors, ensuring that the switching characteristics are optimized for rapid transitions between states. The additional transistor, labeled Q, plays a crucial role in the circuit's operation by receiving transfer pulses that prompt it to change the conducting state, effectively allowing the circuit to toggle between its two stable states.
The design choice to exclude capacitors is significant, as it enhances the circuit's speed of operation. Capacitors, while useful for filtering and timing applications, can introduce delays due to their charging and discharging times. By eliminating these components, the circuit can achieve faster response times, making it suitable for applications requiring quick switching.
Moreover, the absence of bias current from the ON stage to the other stages ensures that the circuit remains in a stable state without unnecessary power consumption. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in battery-operated devices or low-power applications, where efficiency is paramount.
In summary, the bistable circuit described is a robust and efficient design utilizing germanium transistors, diodes, and resistors to achieve high-speed operation and stable state retention without the need for bias currents or capacitors. This configuration is ideal for various electronic applications, including memory storage and digital logic systems.Each bistable circuit has two opposite-symmetry germanium transistors, two diodes, and four resistors. Additional transistor Q transfers conducting stage to next position when actuated by transfer pulse. Absence of capacitors gives high-speed operation. No bias current is required from ON stage to keep other stages cut off. -J. A. Pecar, Ring Count er Uses Transistors, Electronics, 34:4, p 49-51. 🔗 External reference