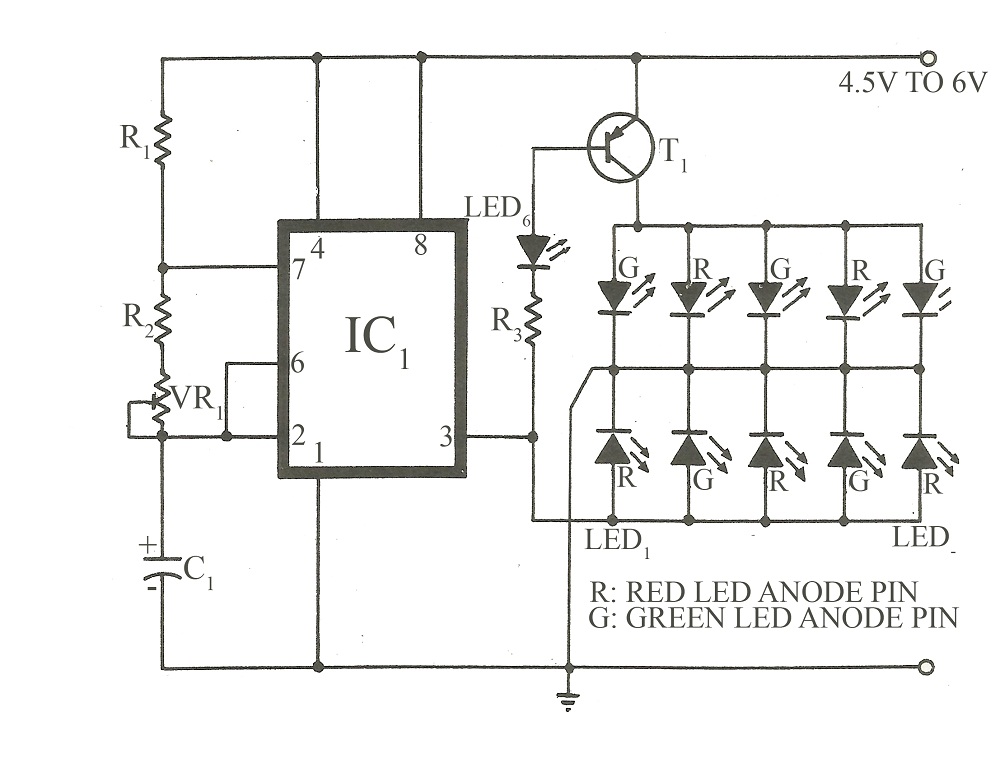
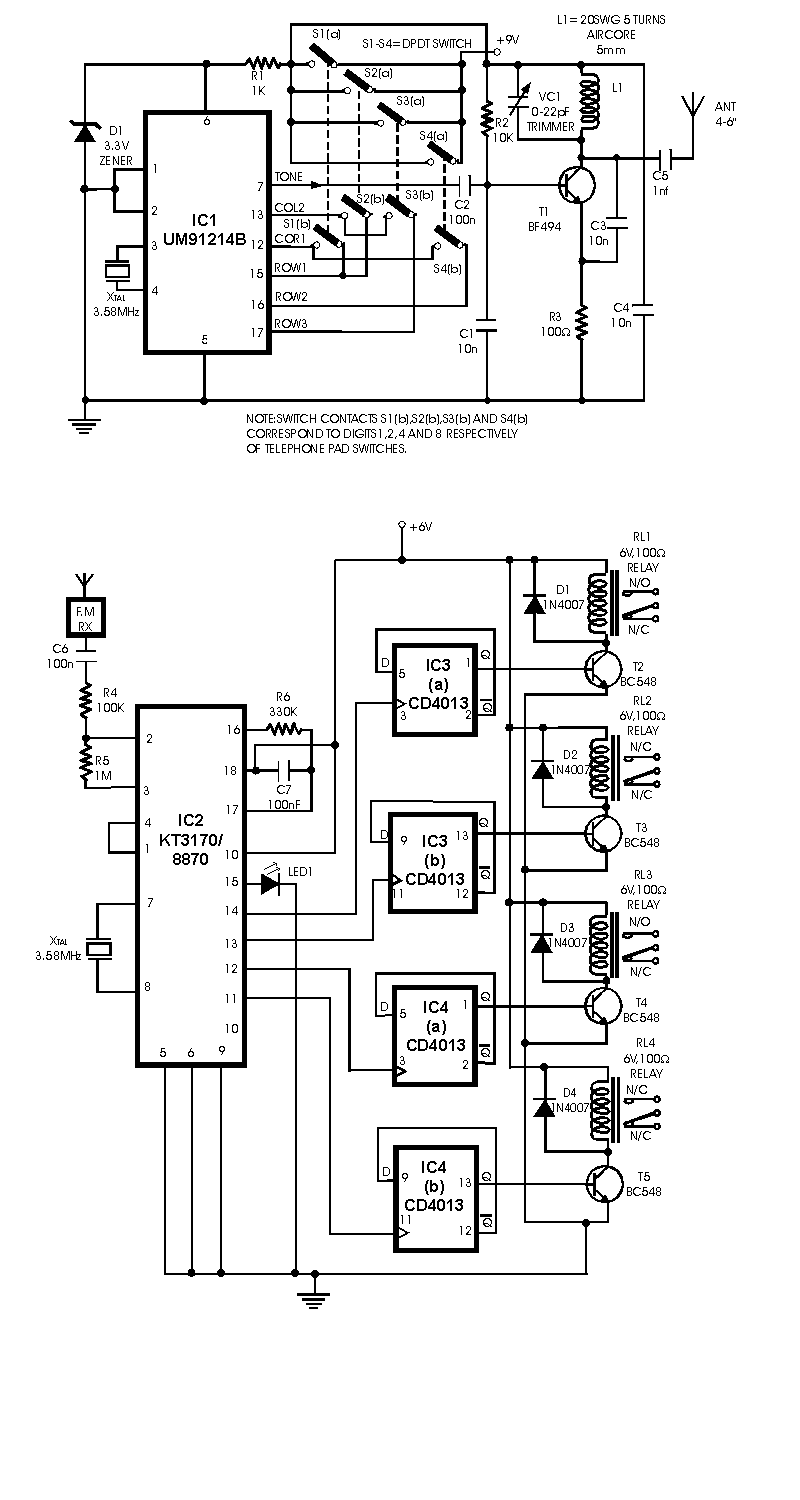
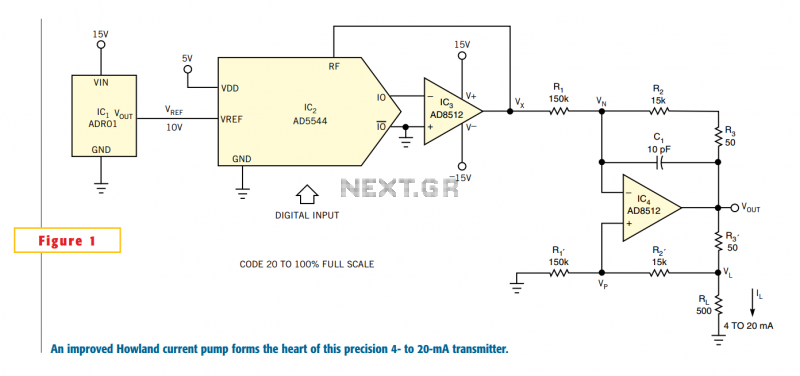
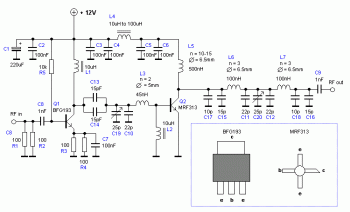
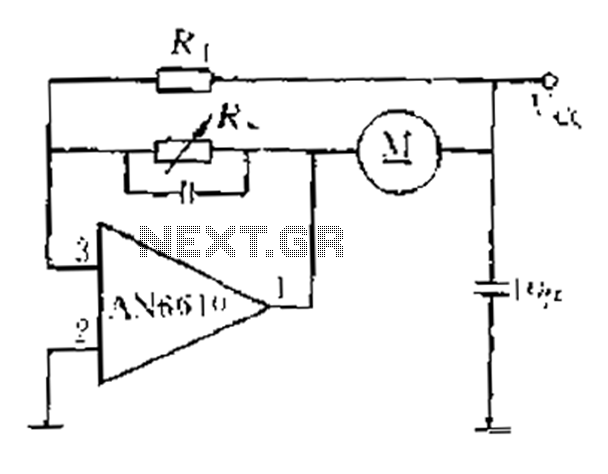
Triac motor drive circuit

The triac motor drive circuit depicted demonstrates the operation of a TRIAC, which is often referred to as a solid-state relay. Figure (a) illustrates the circuit configuration, while figure (b) presents the connections for the motor coils.
The triac motor drive circuit is designed to control the operation of AC motors using a TRIAC as the primary switching element. A TRIAC is a semiconductor device that can conduct current in both directions when triggered, making it suitable for controlling AC loads. The circuit typically includes components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes, which work together to manage the triggering and operation of the TRIAC.
In the configuration shown in figure (a), the main components are arranged to ensure that the TRIAC can be triggered at the appropriate phase angle of the AC waveform. This phase control allows for variable speed operation of the motor, as adjusting the triggering point alters the effective voltage and current supplied to the motor.
Figure (b) illustrates how the motor coils are connected to the circuit. The connections must be made carefully to ensure that the motor operates efficiently and safely. The design may also incorporate protective elements such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent damage from overcurrent conditions.
The overall design of the triac motor drive circuit emphasizes reliability and efficiency in motor control applications, making it ideal for various industrial and consumer applications. Proper thermal management is also essential, as TRIACs can generate heat during operation, necessitating the use of heat sinks or other cooling methods to maintain optimal performance.Triac motor drive circuit b Shows the motor drive circuit TRIAC TRIAC has been called solid state relays. Figure (a) shows a circuit configuration diagram (b) shows the connection of the motor coils.
The triac motor drive circuit is designed to control the operation of AC motors using a TRIAC as the primary switching element. A TRIAC is a semiconductor device that can conduct current in both directions when triggered, making it suitable for controlling AC loads. The circuit typically includes components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes, which work together to manage the triggering and operation of the TRIAC.
In the configuration shown in figure (a), the main components are arranged to ensure that the TRIAC can be triggered at the appropriate phase angle of the AC waveform. This phase control allows for variable speed operation of the motor, as adjusting the triggering point alters the effective voltage and current supplied to the motor.
Figure (b) illustrates how the motor coils are connected to the circuit. The connections must be made carefully to ensure that the motor operates efficiently and safely. The design may also incorporate protective elements such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent damage from overcurrent conditions.
The overall design of the triac motor drive circuit emphasizes reliability and efficiency in motor control applications, making it ideal for various industrial and consumer applications. Proper thermal management is also essential, as TRIACs can generate heat during operation, necessitating the use of heat sinks or other cooling methods to maintain optimal performance.Triac motor drive circuit b Shows the motor drive circuit TRIAC TRIAC has been called solid state relays. Figure (a) shows a circuit configuration diagram (b) shows the connection of the motor coils.