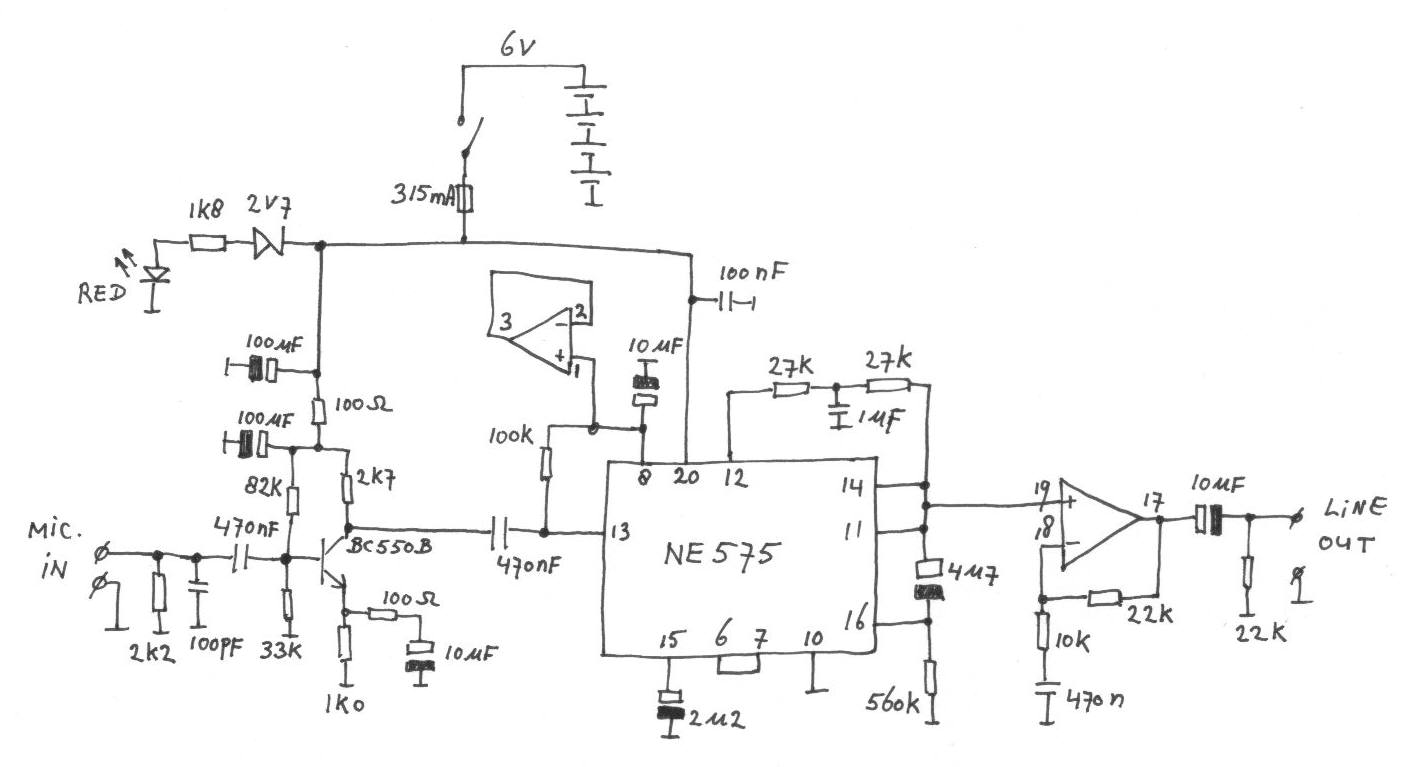
Tube Technology
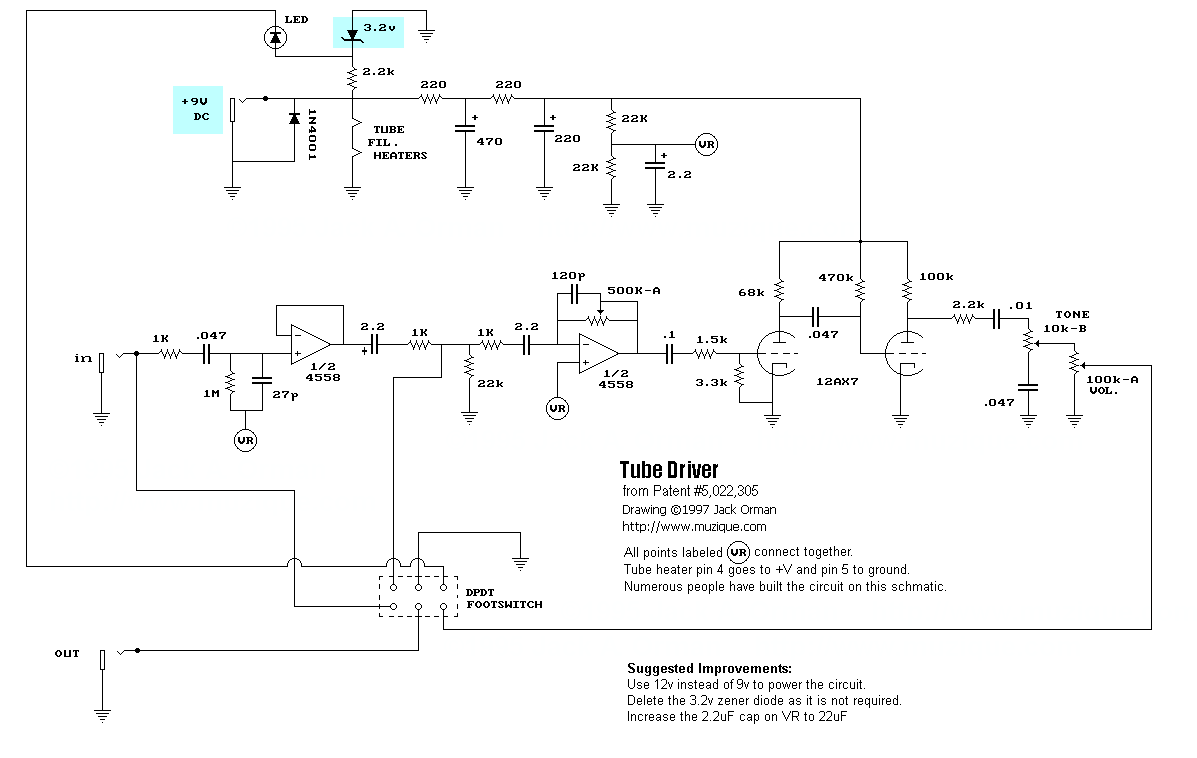
Electron tubes, their operation, early history, types including triodes, tetrodes, beam power tubes, pentodes, combination tubes, ionization (gas-filled) tubes, display tubes, and microwave tubes, as well as a comparison with semiconductors. This site is dedicated to all types of electron tubes, providing information on their construction and applications. Topics include electronic emission, diode tubes, grid bias operation, classifications of tube amplifiers, power amplifiers, planar tubes, gas-filled tubes, cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), electrostatic deflection, power supplies, rectifiers (full-wave, bridge, half-wave with LC choke-input filter), voltage regulation, basic VR tube regulator circuits, and current regulation. Additional content covers antique light bulbs and radio tubes, Crookes tubes, Geissler tubes, classic vacuum tube and incandescent lamp packaging, and LC oscillators (Armstrong, Hartley, Colpitts, Crystal, Electron-coupled). Power supplies utilizing tubes are also discussed, including diode operation, rectification methods, filters, voltage dividers, voltage regulators, and AC/DC power supplies.
Electron tubes, also known as vacuum tubes, are electronic devices that control the flow of electric current in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied. The fundamental operation of these tubes hinges on the principles of thermionic emission, where electrons are emitted from a heated cathode and travel towards an anode, creating a flow of current. Early historical developments in electron tubes paved the way for advancements in electronics, leading to the invention of various types of tubes, including triodes, which introduced the concept of amplification through grid control.
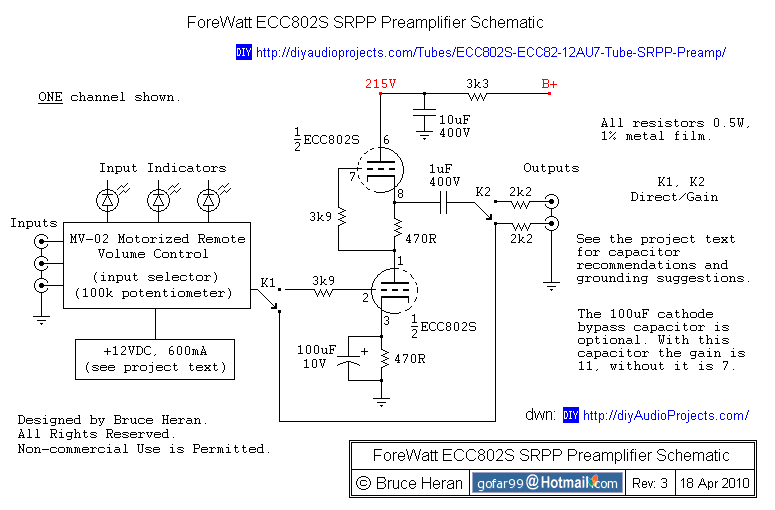
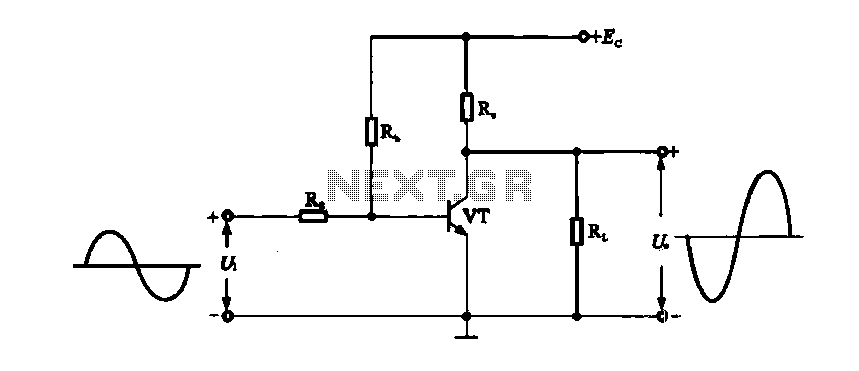
Triodes consist of three electrodes: the cathode, anode, and control grid. The grid allows for the modulation of the current flowing from the cathode to the anode, effectively amplifying the input signal. Tetrodes and pentodes further enhance this design by adding additional grids to improve performance and reduce unwanted capacitance, thus allowing for greater frequency response and power handling capabilities.
Beam power tubes are specialized pentodes designed to deliver high output power, making them suitable for audio amplification and radio frequency applications. Combination tubes integrate multiple functions, such as amplification and rectification, into a single package, optimizing space and performance in electronic circuits.
Ionization tubes, which include gas-filled tubes, utilize gas to create a conductive path for current when ionized. This principle is applied in various display technologies, such as neon lights and cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), where visual output is achieved through controlled electron beams striking phosphorescent surfaces.
The comparison between electron tubes and semiconductors highlights the evolution of electronic components, with semiconductors often offering greater efficiency and miniaturization. However, electron tubes are still valued in certain applications, particularly in high-power RF transmission and audio amplification, due to their unique characteristics.
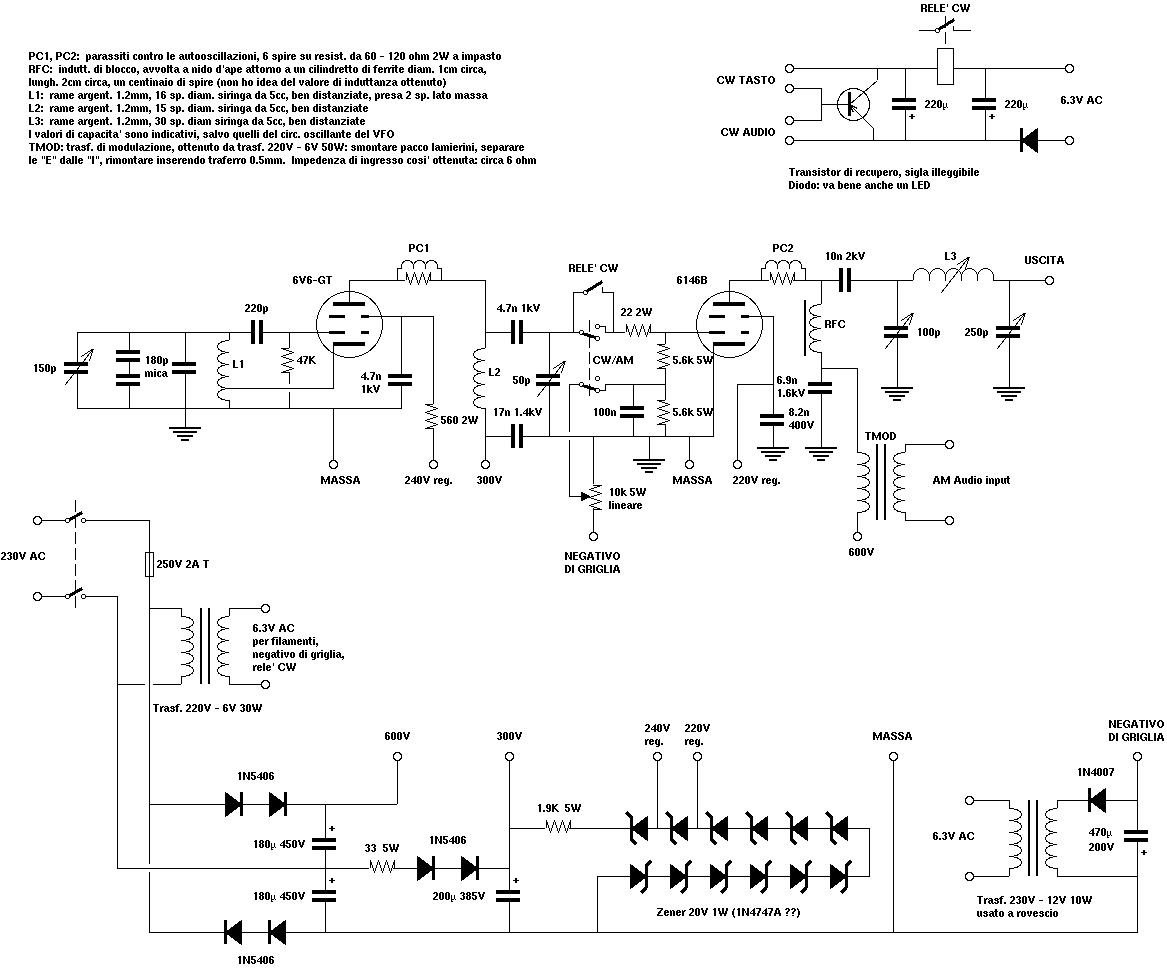
Power supply designs utilizing electron tubes encompass a variety of rectification methods, including half-wave and full-wave configurations. Filters are employed to smooth the output voltage, while voltage dividers and regulators ensure stable operation across varying loads. The integration of LC oscillators within tube circuits allows for the generation of oscillating signals, crucial for radio frequency applications.
Overall, electron tubes represent a significant chapter in the history of electronics, with ongoing relevance in niche applications despite the widespread adoption of semiconductor technology. The study of these devices continues to offer insights into the fundamentals of electronic signal control and amplification.Electron tubes How Electron tubes work, Early tube history, The triode, The tetrode, Beam power tubes, The pentode, Combination tubes, Tube parameters, Ionization (gas-filled) tubes, Display tubes, Microwave tubes, Tubes versus Semiconductors Electron tubes This site is dedicated to Electron Tubes of all kinds. Here you will find information about the construction of tubes and what some of them were used for, a tip Fun With Tubes Electronic emission, tubes, and power introduction to electron tubes, the diode tube, grid bias operating, classifications of tube amplifiers, the pentode, beam power and power pentode tues, power amplifier, planar tubes, gas-filled tubes, the cathode-ray tube (CRT), electrostatic deflection, power supplies, rectifiers, full wave rectifier, bridge rectifier, filters, half-wave rectifier with an LC choke-input filter, voltage regulation, basic VR tube regulator circuit, VR tubes Connected in parallel, current regulation Kilokat`s antique light bulb antique light bulbs, antique radio tubes, tube bulb box art, Crookes tubes, Geissler tubes, view classic vacuum tube and incandescent lamp packaging LC Oscillators with tubes The LC Oscillator, Armstrong Oscillator, Hartley Oscillator, Colpitts Oscillator, Crystal Oscillator, Electron-coupled Oscillator (ECO) Power Supplies with tubes The Diode, Half-wave rectifying, Full-wave rectifying, The Filter, The Voltage Divider, The Voltage Regulator, The Voltage Doubler, AC/DC Power Supplies, Vibrator Power Supplies 🔗 External reference
Electron tubes, also known as vacuum tubes, are electronic devices that control the flow of electric current in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied. The fundamental operation of these tubes hinges on the principles of thermionic emission, where electrons are emitted from a heated cathode and travel towards an anode, creating a flow of current. Early historical developments in electron tubes paved the way for advancements in electronics, leading to the invention of various types of tubes, including triodes, which introduced the concept of amplification through grid control.
Triodes consist of three electrodes: the cathode, anode, and control grid. The grid allows for the modulation of the current flowing from the cathode to the anode, effectively amplifying the input signal. Tetrodes and pentodes further enhance this design by adding additional grids to improve performance and reduce unwanted capacitance, thus allowing for greater frequency response and power handling capabilities.
Beam power tubes are specialized pentodes designed to deliver high output power, making them suitable for audio amplification and radio frequency applications. Combination tubes integrate multiple functions, such as amplification and rectification, into a single package, optimizing space and performance in electronic circuits.
Ionization tubes, which include gas-filled tubes, utilize gas to create a conductive path for current when ionized. This principle is applied in various display technologies, such as neon lights and cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), where visual output is achieved through controlled electron beams striking phosphorescent surfaces.
The comparison between electron tubes and semiconductors highlights the evolution of electronic components, with semiconductors often offering greater efficiency and miniaturization. However, electron tubes are still valued in certain applications, particularly in high-power RF transmission and audio amplification, due to their unique characteristics.
Power supply designs utilizing electron tubes encompass a variety of rectification methods, including half-wave and full-wave configurations. Filters are employed to smooth the output voltage, while voltage dividers and regulators ensure stable operation across varying loads. The integration of LC oscillators within tube circuits allows for the generation of oscillating signals, crucial for radio frequency applications.
Overall, electron tubes represent a significant chapter in the history of electronics, with ongoing relevance in niche applications despite the widespread adoption of semiconductor technology. The study of these devices continues to offer insights into the fundamentals of electronic signal control and amplification.Electron tubes How Electron tubes work, Early tube history, The triode, The tetrode, Beam power tubes, The pentode, Combination tubes, Tube parameters, Ionization (gas-filled) tubes, Display tubes, Microwave tubes, Tubes versus Semiconductors Electron tubes This site is dedicated to Electron Tubes of all kinds. Here you will find information about the construction of tubes and what some of them were used for, a tip Fun With Tubes Electronic emission, tubes, and power introduction to electron tubes, the diode tube, grid bias operating, classifications of tube amplifiers, the pentode, beam power and power pentode tues, power amplifier, planar tubes, gas-filled tubes, the cathode-ray tube (CRT), electrostatic deflection, power supplies, rectifiers, full wave rectifier, bridge rectifier, filters, half-wave rectifier with an LC choke-input filter, voltage regulation, basic VR tube regulator circuit, VR tubes Connected in parallel, current regulation Kilokat`s antique light bulb antique light bulbs, antique radio tubes, tube bulb box art, Crookes tubes, Geissler tubes, view classic vacuum tube and incandescent lamp packaging LC Oscillators with tubes The LC Oscillator, Armstrong Oscillator, Hartley Oscillator, Colpitts Oscillator, Crystal Oscillator, Electron-coupled Oscillator (ECO) Power Supplies with tubes The Diode, Half-wave rectifying, Full-wave rectifying, The Filter, The Voltage Divider, The Voltage Regulator, The Voltage Doubler, AC/DC Power Supplies, Vibrator Power Supplies 🔗 External reference