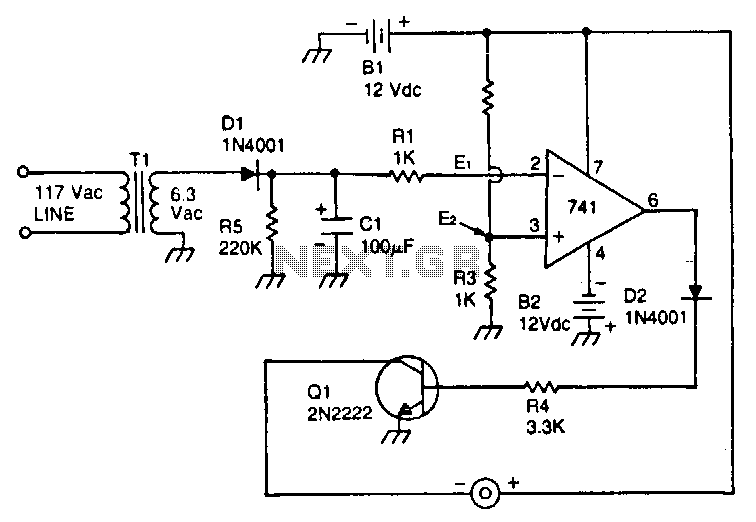
TV LINE DECODER I
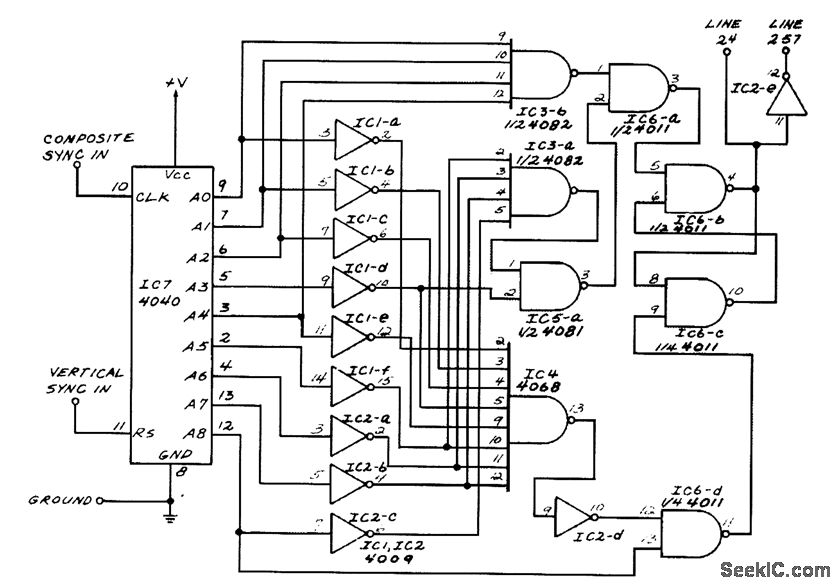
This circuit generates outputs on TV lines 24 and 257. It was utilized for a decoder circuit and employs a CMOS counter along with gate logic. Only one pin is designated for the output line indicator.
The circuit described serves a specific function in television signal processing, particularly in the context of decoding signals for display. The use of CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) technology is significant due to its low power consumption and high noise immunity, making it suitable for applications in consumer electronics.
The CMOS counter is responsible for counting pulses and generating specific output signals corresponding to the desired TV lines, which in this case are lines 24 and 257. These lines are critical in the vertical synchronization of video signals, ensuring that the output matches the timing requirements of the television display.
Gate logic is employed to control the flow of signals within the circuit. Logic gates, such as AND, OR, and NOT gates, are used to manipulate the binary signals generated by the CMOS counter, determining when the output should be activated. The design may incorporate a combination of these gates to achieve the desired functionality.
The single pin designated for the output line indicator is a crucial aspect of the circuit, as it simplifies the design and reduces the number of connections required. This pin can be connected to an LED or another type of indicator, providing a visual representation of the active output state.
In summary, this circuit is an efficient solution for generating specific outputs in decoder applications, utilizing CMOS technology and gate logic to achieve precise timing and control in television signal processing. The design's simplicity, with only one output line indicator pin, enhances its usability in various electronic applications.This circuit will produce outputs on TV lines 24 and 257. It was used for a decoder circuit. It uses a CMOS counter and gate logic. Only one pin is used for the output line indicator. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described serves a specific function in television signal processing, particularly in the context of decoding signals for display. The use of CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) technology is significant due to its low power consumption and high noise immunity, making it suitable for applications in consumer electronics.
The CMOS counter is responsible for counting pulses and generating specific output signals corresponding to the desired TV lines, which in this case are lines 24 and 257. These lines are critical in the vertical synchronization of video signals, ensuring that the output matches the timing requirements of the television display.
Gate logic is employed to control the flow of signals within the circuit. Logic gates, such as AND, OR, and NOT gates, are used to manipulate the binary signals generated by the CMOS counter, determining when the output should be activated. The design may incorporate a combination of these gates to achieve the desired functionality.
The single pin designated for the output line indicator is a crucial aspect of the circuit, as it simplifies the design and reduces the number of connections required. This pin can be connected to an LED or another type of indicator, providing a visual representation of the active output state.
In summary, this circuit is an efficient solution for generating specific outputs in decoder applications, utilizing CMOS technology and gate logic to achieve precise timing and control in television signal processing. The design's simplicity, with only one output line indicator pin, enhances its usability in various electronic applications.This circuit will produce outputs on TV lines 24 and 257. It was used for a decoder circuit. It uses a CMOS counter and gate logic. Only one pin is used for the output line indicator. 🔗 External reference