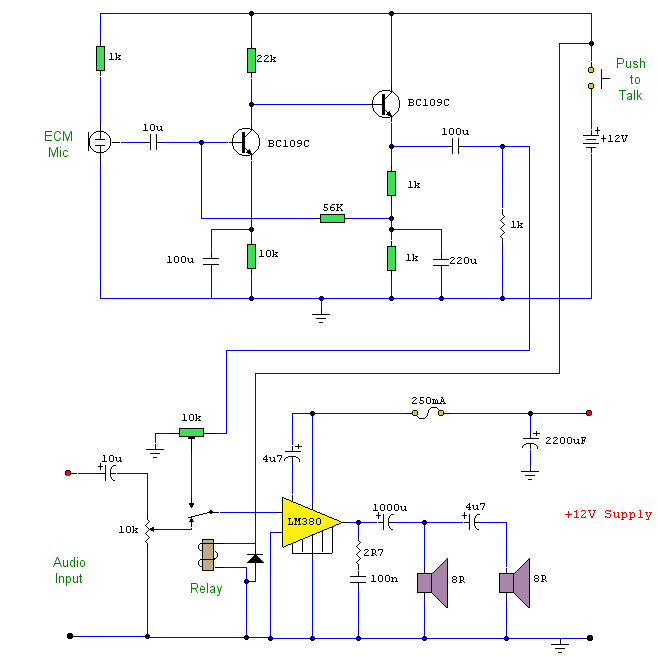
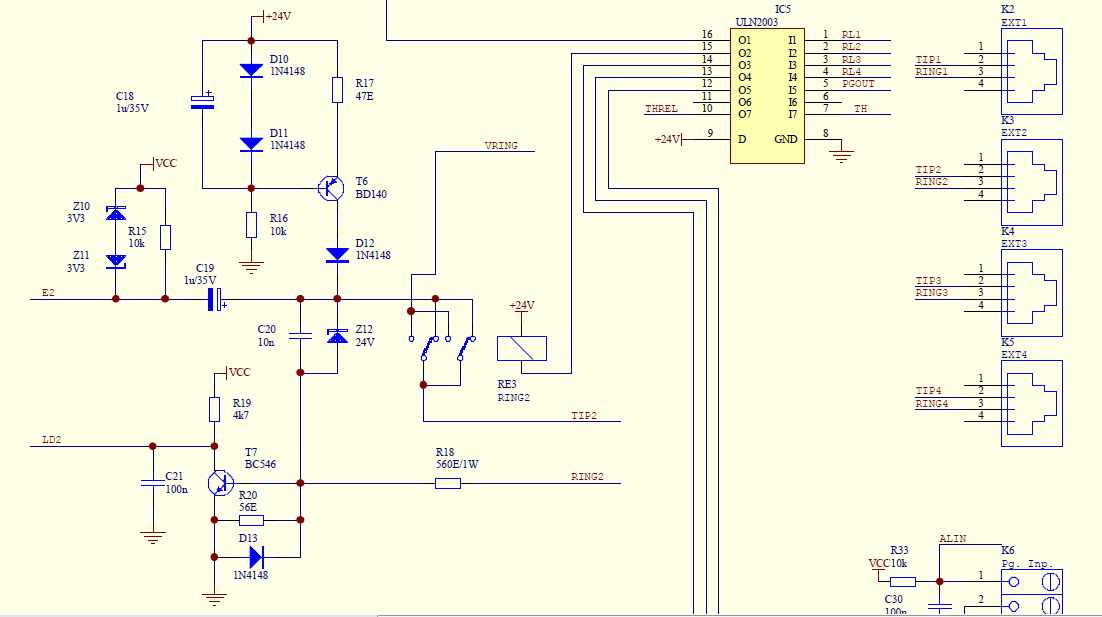
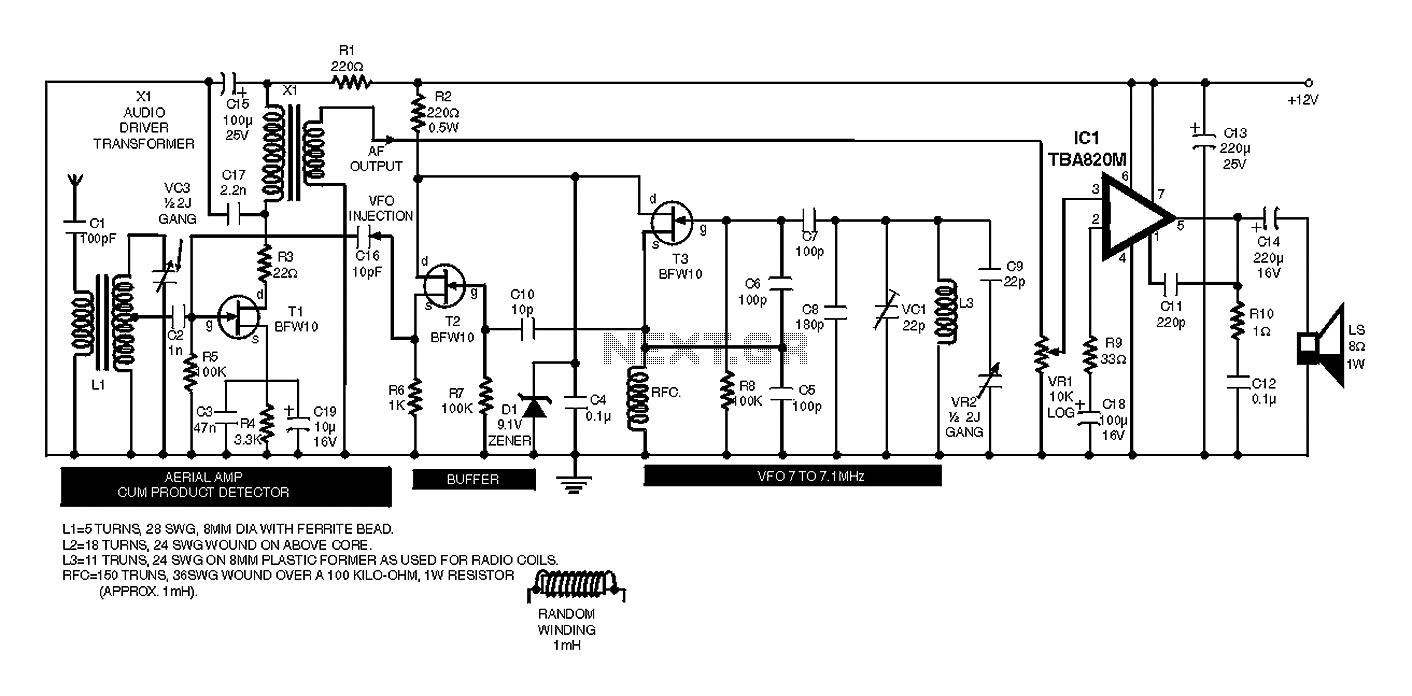
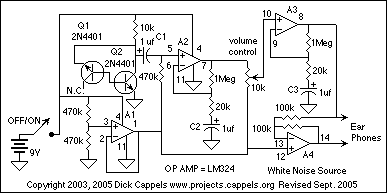
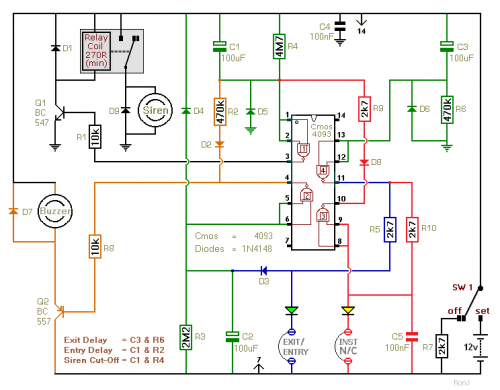
TWO CHANNEL AUDIO MIXER
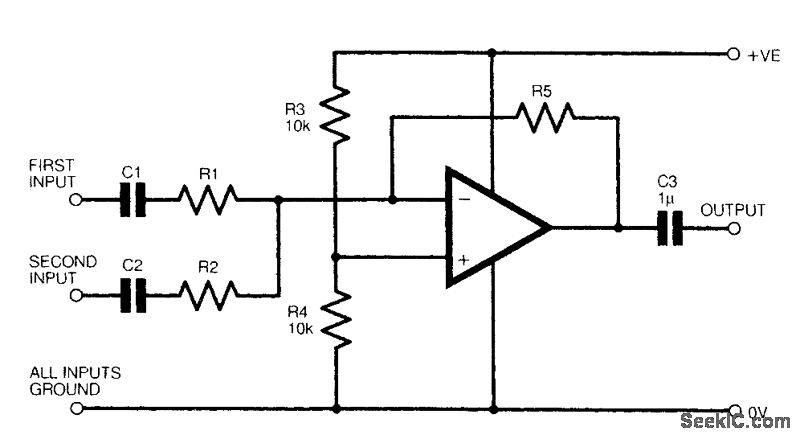
The figure illustrates a fundamental two-channel operational amplifier (op-amp) mixer circuit. The gain for channel 1 is determined by the ratio of resistors R5 to R1, while for channel 2, it is determined by the ratio of R5 to R2. Typically, the values for R1 and R2 range from 2.2 kΩ to 22 kΩ, whereas R5 is selected from a range of 10 kΩ to 100 kΩ. The op-amp used in this circuit can be any suitable type, such as the 741 or its various derivatives.
This two-channel op-amp mixer circuit is designed to combine two audio signals into a single output. The circuit operates by utilizing the properties of the operational amplifier to sum the input signals, thereby allowing for control over the gain of each channel independently. The gain for each channel can be adjusted by changing the resistor values, providing flexibility in the circuit's response.
In this configuration, R1 and R2 serve as input resistors for channels 1 and 2, respectively. These resistors establish the input impedance and influence the gain of the corresponding channel. The feedback resistor, R5, is connected from the output of the op-amp back to the inverting input, setting the overall gain of the circuit. The gain formula for each channel can be expressed as:
- Gain for Channel 1 (G1) = R5 / R1
- Gain for Channel 2 (G2) = R5 / R2
By selecting appropriate values for R1, R2, and R5, the circuit designer can achieve desired amplification levels while maintaining signal integrity. The choice of op-amp, such as the widely used 741, offers a balance of performance and availability, making it suitable for various applications in audio mixing.
The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components such as capacitors for filtering, which can help reduce noise and improve signal quality. For instance, adding capacitors in parallel with R1 and R2 can create a low-pass filter effect, allowing only desired frequencies to pass through while attenuating higher frequencies.
In summary, this basic two-channel op-amp mixer circuit provides a versatile platform for audio signal mixing, with adjustable gain and the potential for further refinements to enhance performance.The figure shows a basic two-channel op-amp mixer circuit. The gain is equal to R5/R1 or R5/R2 for channel 1 or 2, respectively. Typically R1 and R2 are 2. 2 to 22 k © and R5 is 10 to 100 k ©, and the op amp is any suitable type, such as a 741 or its numerous variations. 🔗 External reference
This two-channel op-amp mixer circuit is designed to combine two audio signals into a single output. The circuit operates by utilizing the properties of the operational amplifier to sum the input signals, thereby allowing for control over the gain of each channel independently. The gain for each channel can be adjusted by changing the resistor values, providing flexibility in the circuit's response.
In this configuration, R1 and R2 serve as input resistors for channels 1 and 2, respectively. These resistors establish the input impedance and influence the gain of the corresponding channel. The feedback resistor, R5, is connected from the output of the op-amp back to the inverting input, setting the overall gain of the circuit. The gain formula for each channel can be expressed as:
- Gain for Channel 1 (G1) = R5 / R1
- Gain for Channel 2 (G2) = R5 / R2
By selecting appropriate values for R1, R2, and R5, the circuit designer can achieve desired amplification levels while maintaining signal integrity. The choice of op-amp, such as the widely used 741, offers a balance of performance and availability, making it suitable for various applications in audio mixing.
The circuit can be further enhanced by incorporating additional components such as capacitors for filtering, which can help reduce noise and improve signal quality. For instance, adding capacitors in parallel with R1 and R2 can create a low-pass filter effect, allowing only desired frequencies to pass through while attenuating higher frequencies.
In summary, this basic two-channel op-amp mixer circuit provides a versatile platform for audio signal mixing, with adjustable gain and the potential for further refinements to enhance performance.The figure shows a basic two-channel op-amp mixer circuit. The gain is equal to R5/R1 or R5/R2 for channel 1 or 2, respectively. Typically R1 and R2 are 2. 2 to 22 k © and R5 is 10 to 100 k ©, and the op amp is any suitable type, such as a 741 or its numerous variations. 🔗 External reference