Ultrasonic Mosquito Repeller Circuit Using CMOS IC

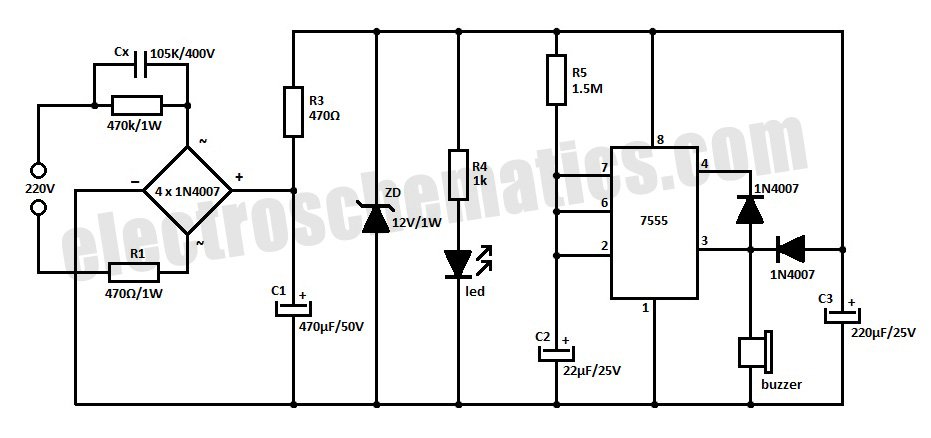
This is the design circuit diagram of an ultrasonic mosquito repeller. The circuit operates based on the theory that insects, such as mosquitoes, can be repelled by sound frequencies in the ultrasonic range (above 20 kHz). The circuit utilizes a CMOS IC CD4047, which is configured as an oscillator working at 22 kHz. A complementary symmetry amplifier, consisting of four transistors, is employed to amplify the sound. The piezo buzzer converts the output of the amplifier into ultrasonic sound that can be detected by insects. The circuit can be powered from a 12V DC source. The IC must be mounted on a holder, and the buzzer can be any general-purpose piezo buzzer.
The ultrasonic mosquito repeller circuit is designed to emit sound waves that are inaudible to humans but can disrupt the behavior of mosquitoes and other insects. The core component, the CD4047 CMOS IC, is configured to function as a free-running oscillator. This oscillator generates a square wave signal at a frequency of 22 kHz, which is within the ultrasonic range.
The output from the CD4047 is fed into a complementary symmetry amplifier, which consists of four transistors arranged to provide the necessary gain for the signal. This configuration ensures that the output signal is strong enough to drive the piezo buzzer effectively. The complementary symmetry amplifier is advantageous as it enhances efficiency and reduces distortion in the amplified signal.
The piezo buzzer serves as the transducer that converts the amplified electrical signal into ultrasonic sound waves. The choice of a general-purpose piezo buzzer allows for flexibility in component selection while ensuring adequate performance for the application. The ultrasonic sound produced is intended to interfere with the sensory perception of mosquitoes, thereby repelling them from the area.
Powering the circuit with a 12V DC supply is a common choice, providing sufficient voltage for the operation of the CMOS IC and the amplifier. It is important to ensure that the IC is securely mounted on a holder to prevent mechanical stress that could affect its performance. Overall, the design of this circuit is straightforward and effective for individuals seeking a non-chemical method of pest control.This is the design circuit diagram of an ultrasonic mosquito repeller. The circuit is work with based on the theory that insects like mosquito can be repelled by using sound frequencies in the ultrasonic (above 20KHz) range. This is the figure of the circuit. This circuit is operated using CMOS IC CD4047. The circuit is nothing but a PLL IC CMOS 4 047 wired as an oscillator working at 22KHz. A complementary symmetry amplifier consisting of four transistor is used to amplify the sound. The piezo buzzer converts the output of amplifier to ultrasonic sound that can be heard by the insects. The circuit can be powered from 12V DC. The IC1 must be mounted on a holder. The buzzer can be any general purpose piezo buzzer. 🔗 External reference
The ultrasonic mosquito repeller circuit is designed to emit sound waves that are inaudible to humans but can disrupt the behavior of mosquitoes and other insects. The core component, the CD4047 CMOS IC, is configured to function as a free-running oscillator. This oscillator generates a square wave signal at a frequency of 22 kHz, which is within the ultrasonic range.
The output from the CD4047 is fed into a complementary symmetry amplifier, which consists of four transistors arranged to provide the necessary gain for the signal. This configuration ensures that the output signal is strong enough to drive the piezo buzzer effectively. The complementary symmetry amplifier is advantageous as it enhances efficiency and reduces distortion in the amplified signal.
The piezo buzzer serves as the transducer that converts the amplified electrical signal into ultrasonic sound waves. The choice of a general-purpose piezo buzzer allows for flexibility in component selection while ensuring adequate performance for the application. The ultrasonic sound produced is intended to interfere with the sensory perception of mosquitoes, thereby repelling them from the area.
Powering the circuit with a 12V DC supply is a common choice, providing sufficient voltage for the operation of the CMOS IC and the amplifier. It is important to ensure that the IC is securely mounted on a holder to prevent mechanical stress that could affect its performance. Overall, the design of this circuit is straightforward and effective for individuals seeking a non-chemical method of pest control.This is the design circuit diagram of an ultrasonic mosquito repeller. The circuit is work with based on the theory that insects like mosquito can be repelled by using sound frequencies in the ultrasonic (above 20KHz) range. This is the figure of the circuit. This circuit is operated using CMOS IC CD4047. The circuit is nothing but a PLL IC CMOS 4 047 wired as an oscillator working at 22KHz. A complementary symmetry amplifier consisting of four transistor is used to amplify the sound. The piezo buzzer converts the output of amplifier to ultrasonic sound that can be heard by the insects. The circuit can be powered from 12V DC. The IC1 must be mounted on a holder. The buzzer can be any general purpose piezo buzzer. 🔗 External reference