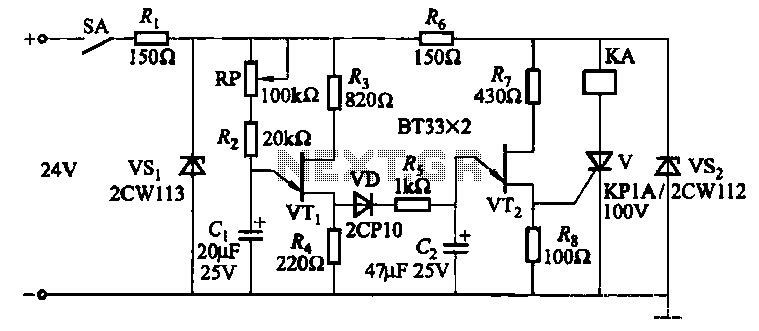
Power Resumption Alarm circuit
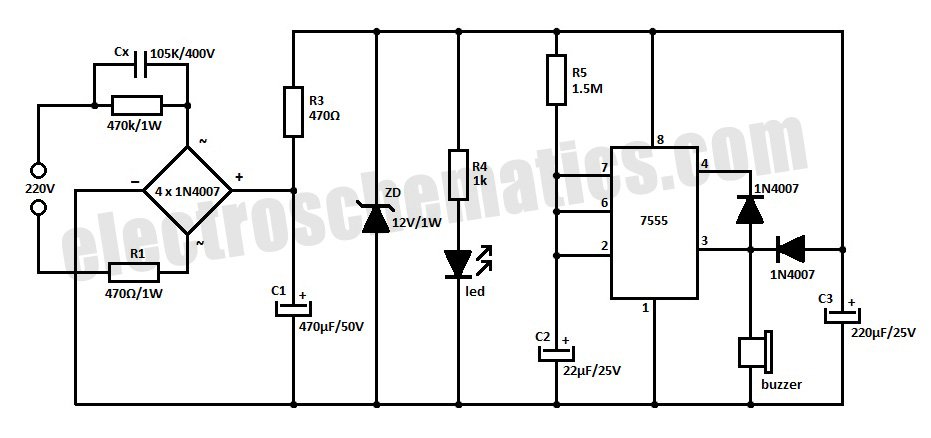
This is a simple power resumption alarm circuit that can be installed within the switch box. It emits beeping sounds when power is restored following a power failure.
The power resumption alarm circuit is designed to provide an audible alert upon the restoration of electrical power after an interruption. The circuit typically consists of a few essential components: a power supply, a microcontroller or a simple timer, a piezo buzzer, and various passive components such as resistors and capacitors.
Upon the restoration of power, the circuit is activated. A capacitor may be used to hold a charge temporarily, allowing the microcontroller or timer to initiate the beeping sequence. The microcontroller can be programmed to control the duration and frequency of the beeps, ensuring that the alarm is both effective and not overly intrusive.
The piezo buzzer serves as the output device, generating sound when triggered by the control circuit. The design may also incorporate a push-button switch that allows users to silence the alarm if desired. Additionally, a resistor-capacitor (RC) network could be implemented to create a delay before the alarm activates, preventing false alarms due to brief power fluctuations.
This circuit can be compactly housed within a switch box, making it convenient for residential or commercial applications. The installation process involves connecting the circuit to the existing power lines, ensuring proper insulation and safety measures are observed. The simplicity and effectiveness of this alarm circuit make it a valuable addition to any electrical system, providing peace of mind during power outages.Here is a simple power resumption alarm circuit that can be fixed inside the switch box itself. It gives beeps when the power resumes after a power failure.. 🔗 External reference
The power resumption alarm circuit is designed to provide an audible alert upon the restoration of electrical power after an interruption. The circuit typically consists of a few essential components: a power supply, a microcontroller or a simple timer, a piezo buzzer, and various passive components such as resistors and capacitors.
Upon the restoration of power, the circuit is activated. A capacitor may be used to hold a charge temporarily, allowing the microcontroller or timer to initiate the beeping sequence. The microcontroller can be programmed to control the duration and frequency of the beeps, ensuring that the alarm is both effective and not overly intrusive.
The piezo buzzer serves as the output device, generating sound when triggered by the control circuit. The design may also incorporate a push-button switch that allows users to silence the alarm if desired. Additionally, a resistor-capacitor (RC) network could be implemented to create a delay before the alarm activates, preventing false alarms due to brief power fluctuations.
This circuit can be compactly housed within a switch box, making it convenient for residential or commercial applications. The installation process involves connecting the circuit to the existing power lines, ensuring proper insulation and safety measures are observed. The simplicity and effectiveness of this alarm circuit make it a valuable addition to any electrical system, providing peace of mind during power outages.Here is a simple power resumption alarm circuit that can be fixed inside the switch box itself. It gives beeps when the power resumes after a power failure.. 🔗 External reference