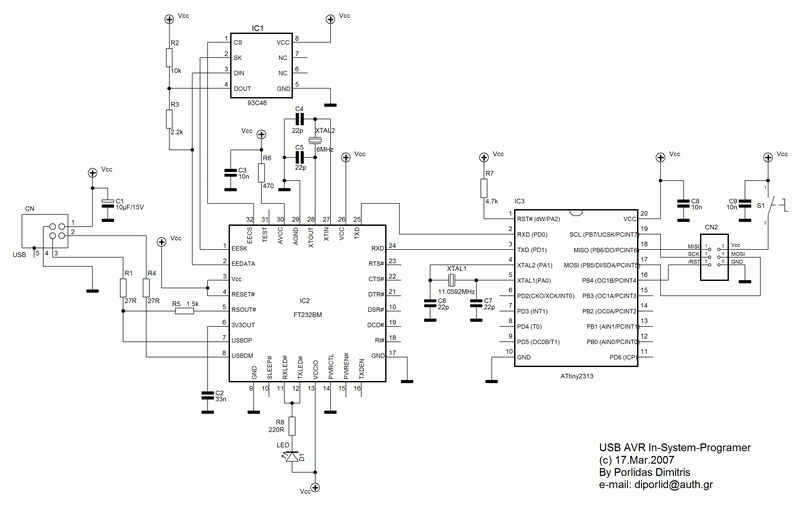
Upgrade Your USB Hub
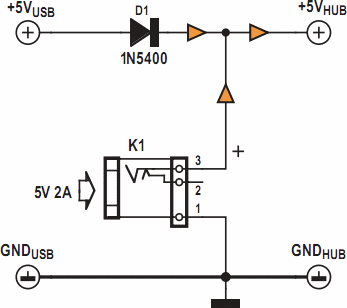
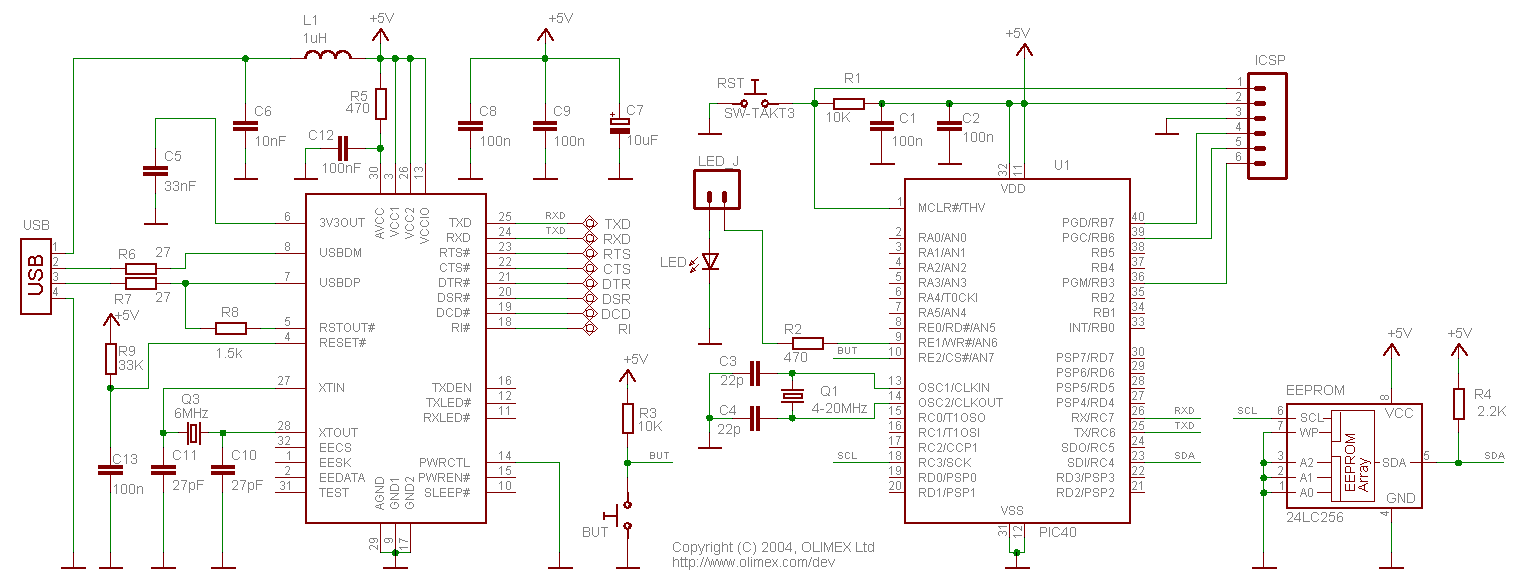
Problems can arise with USB hubs powered from a PC when devices connected to them draw excessive current. This situation often occurs with devices that use USB cables that are either too long or too thin, leading to voltage drops. However, it is not necessary to discard an old USB hub; instead, it can be upgraded using a simple circuit and an external power supply. To implement this upgrade, cut the 5-V power wire of the USB cable inside the hub and solder a diode (D1) in the forward direction. Connect the 5 V wire from the external power supply to the cathode of this diode. The diode D1 prevents any current from the power supply from flowing back into the PC.
To enhance the functionality of a USB hub that experiences current draw issues, a modification can be performed to incorporate an external power supply. The main objective of this upgrade is to ensure that the USB hub can adequately power devices without risking damage to the PC's USB port due to excessive current draw.
The circuit modification begins with the identification of the 5-V power wire within the USB hub. This wire is typically red in color and is responsible for supplying power to the connected devices. By cutting this wire, the internal power supply of the hub is effectively isolated, allowing for the introduction of an external power source.
A diode, specifically designated as D1, is then soldered in the forward-biased configuration across the cut wire. The diode is crucial for preventing reverse current flow; it allows current to flow from the external power supply to the hub while blocking any potential backflow into the PC's USB port. The cathode of the diode, marked with a stripe, should be connected to the 5 V wire from the external power supply, while the anode is connected to the side of the cut wire leading to the devices.
An appropriate external power supply must be selected to ensure that it meets the voltage and current requirements of the devices being powered. It is recommended to use a regulated 5 V power supply capable of providing sufficient current to handle the combined load of all connected devices.
Upon completion of this modification, the USB hub will be able to reliably power devices without the risk of current overload affecting the PC. This solution not only extends the life of the USB hub but also enhances its performance, allowing for the connection of multiple devices without concern for voltage drop or inadequate power delivery.Problems can arise with USB hubs that are powered from a PC when gadgets plugged into them draw too much current. This is often the case with devices fitted with USB cables that are too long or too thin, causing voltage drop.
There`s no need to scrap your old USB hub, however, if you upgrade it using this little circuit and an external power suppl y. Just cut the 5-V power wire of the USB cable inside the hub and solder a diode (D1) in the pass-through direction. Now connect the 5 V wire from the external power supply to the cathode of this diode. D1 prevents any current from the power supply from flowing back into the PC. 🔗 External reference
To enhance the functionality of a USB hub that experiences current draw issues, a modification can be performed to incorporate an external power supply. The main objective of this upgrade is to ensure that the USB hub can adequately power devices without risking damage to the PC's USB port due to excessive current draw.
The circuit modification begins with the identification of the 5-V power wire within the USB hub. This wire is typically red in color and is responsible for supplying power to the connected devices. By cutting this wire, the internal power supply of the hub is effectively isolated, allowing for the introduction of an external power source.
A diode, specifically designated as D1, is then soldered in the forward-biased configuration across the cut wire. The diode is crucial for preventing reverse current flow; it allows current to flow from the external power supply to the hub while blocking any potential backflow into the PC's USB port. The cathode of the diode, marked with a stripe, should be connected to the 5 V wire from the external power supply, while the anode is connected to the side of the cut wire leading to the devices.
An appropriate external power supply must be selected to ensure that it meets the voltage and current requirements of the devices being powered. It is recommended to use a regulated 5 V power supply capable of providing sufficient current to handle the combined load of all connected devices.
Upon completion of this modification, the USB hub will be able to reliably power devices without the risk of current overload affecting the PC. This solution not only extends the life of the USB hub but also enhances its performance, allowing for the connection of multiple devices without concern for voltage drop or inadequate power delivery.Problems can arise with USB hubs that are powered from a PC when gadgets plugged into them draw too much current. This is often the case with devices fitted with USB cables that are too long or too thin, causing voltage drop.
There`s no need to scrap your old USB hub, however, if you upgrade it using this little circuit and an external power suppl y. Just cut the 5-V power wire of the USB cable inside the hub and solder a diode (D1) in the pass-through direction. Now connect the 5 V wire from the external power supply to the cathode of this diode. D1 prevents any current from the power supply from flowing back into the PC. 🔗 External reference