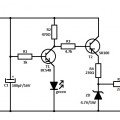
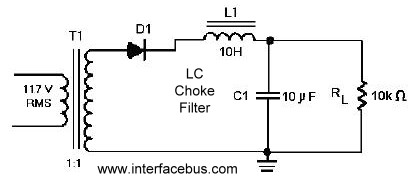
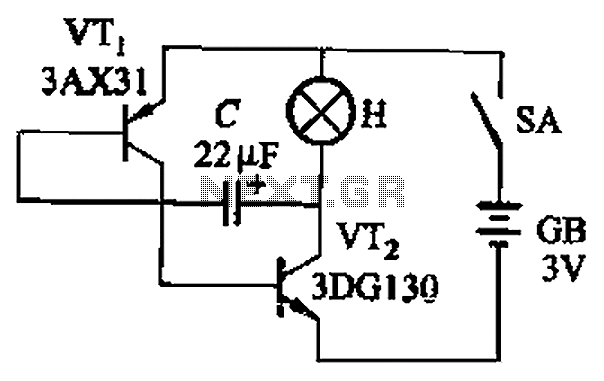
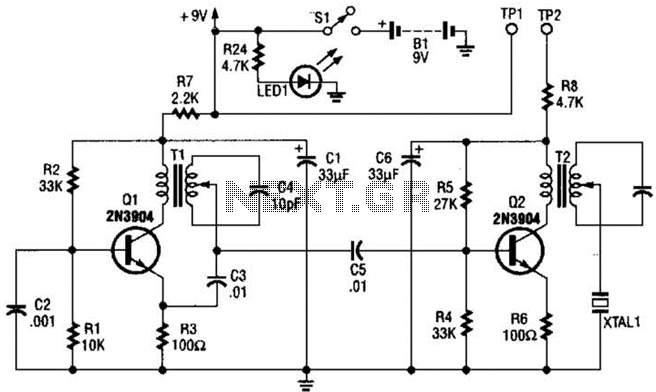
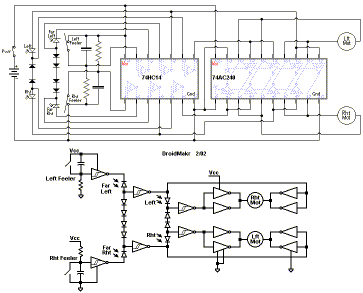
UPS_design_2 16f84 based UPS circuit
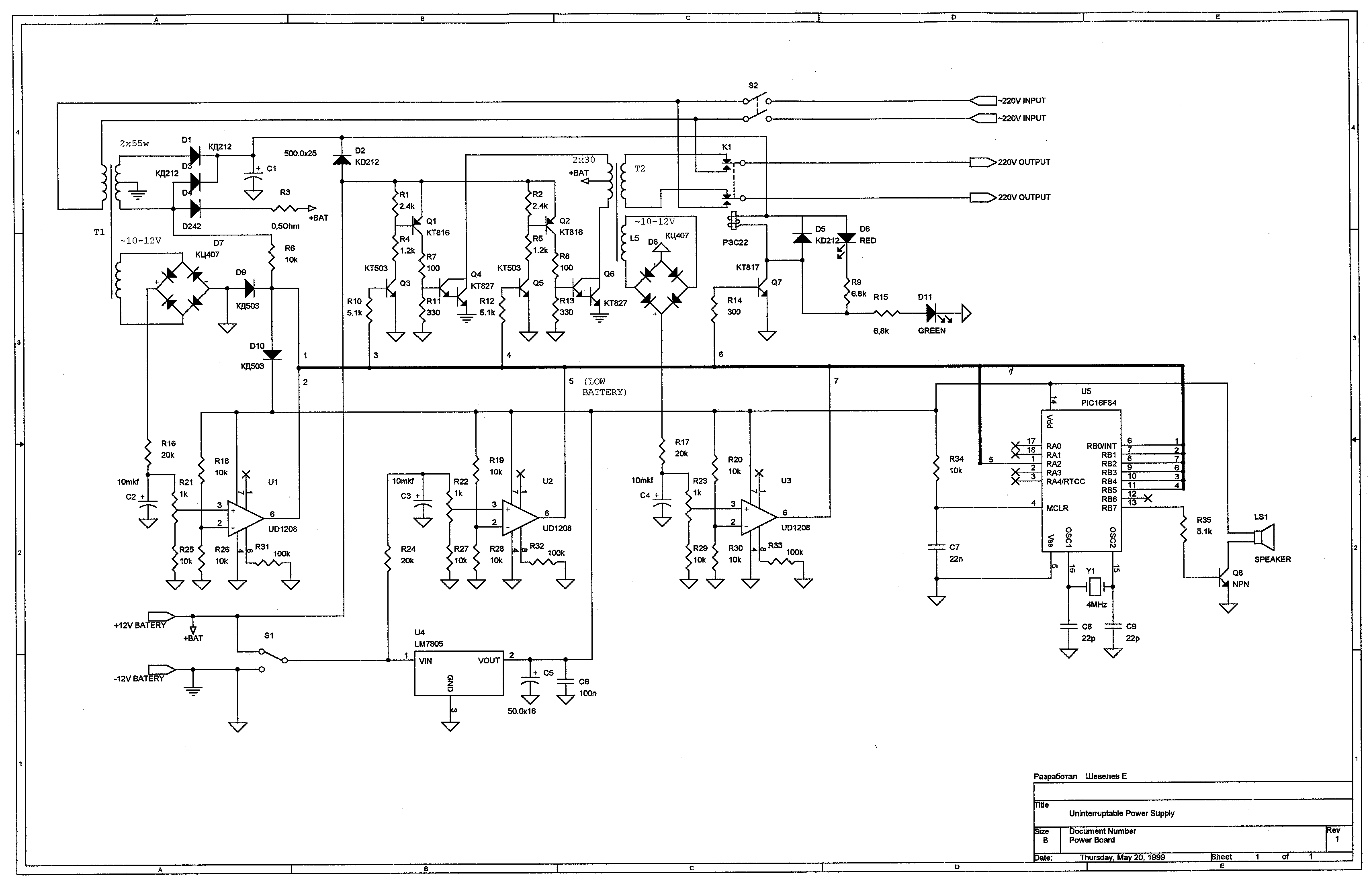
Full sine wave UPS information in English, along with detailed C language source code. English proficiency may be a concern, so caution is advised.
A full sine wave Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is designed to provide a stable and continuous power output that closely resembles the characteristics of a standard AC sine wave. This type of UPS is essential for sensitive electronic equipment that requires a pure sine wave for optimal performance, such as audio/video equipment, medical devices, and computer systems.
The UPS operates by converting stored DC power from batteries into AC power through an inverter circuit. The inverter is typically controlled by a microcontroller that executes a C language source code program. This program is responsible for managing the battery charging process, monitoring the input and output voltages, and ensuring that the output waveform is a pure sine wave.
The C language source code for a full sine wave UPS includes functions for generating the sine wave signal, controlling the inverter switches (such as MOSFETs or IGBTs), and implementing protection features like over-voltage, under-voltage, and thermal shutdown. The sine wave generation is often achieved using a lookup table or a Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS) technique, which allows for precise control of the waveform frequency and amplitude.
In addition to the sine wave generation, the code handles real-time monitoring of battery status and load conditions. It may also include user interface elements for displaying operational parameters such as battery voltage, load current, and output frequency.
Overall, a full sine wave UPS system is critical for ensuring that sensitive electronic devices operate reliably during power interruptions, and the integration of C programming allows for sophisticated control and monitoring capabilities.full sine wave ups information, in English, with a detailed C language source code, English may be the weak to be careful of, a little 🔗 External reference
A full sine wave Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is designed to provide a stable and continuous power output that closely resembles the characteristics of a standard AC sine wave. This type of UPS is essential for sensitive electronic equipment that requires a pure sine wave for optimal performance, such as audio/video equipment, medical devices, and computer systems.
The UPS operates by converting stored DC power from batteries into AC power through an inverter circuit. The inverter is typically controlled by a microcontroller that executes a C language source code program. This program is responsible for managing the battery charging process, monitoring the input and output voltages, and ensuring that the output waveform is a pure sine wave.
The C language source code for a full sine wave UPS includes functions for generating the sine wave signal, controlling the inverter switches (such as MOSFETs or IGBTs), and implementing protection features like over-voltage, under-voltage, and thermal shutdown. The sine wave generation is often achieved using a lookup table or a Direct Digital Synthesis (DDS) technique, which allows for precise control of the waveform frequency and amplitude.
In addition to the sine wave generation, the code handles real-time monitoring of battery status and load conditions. It may also include user interface elements for displaying operational parameters such as battery voltage, load current, and output frequency.
Overall, a full sine wave UPS system is critical for ensuring that sensitive electronic devices operate reliably during power interruptions, and the integration of C programming allows for sophisticated control and monitoring capabilities.full sine wave ups information, in English, with a detailed C language source code, English may be the weak to be careful of, a little 🔗 External reference