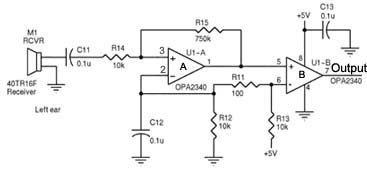
Analog Milliamp Meter Used as Voltmeter circuit
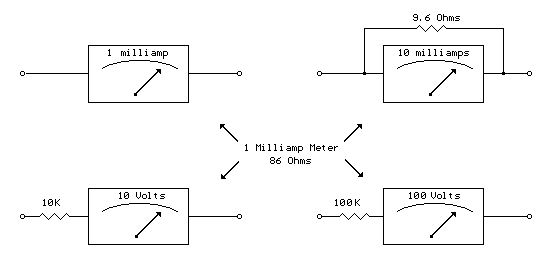
A milliamp meter can function as a voltmeter by incorporating a series resistance. The required resistance is calculated by dividing the full-scale voltage reading by the full-scale current of the meter movement. For instance, using a 1 milliamp meter to measure a voltage range of 0-10 volts necessitates a total resistance of 10 volts divided by 0.001 amps, resulting in 10K ohms.
To implement this conversion effectively, the circuit design must ensure that the milliamp meter is properly calibrated to operate within the desired voltage range. The series resistor, which is critical for this adaptation, should be connected in series with the meter. The resistor's value is determined based on the maximum voltage to be measured and the full-scale current rating of the meter.
In the example provided, the 1 milliamp meter has a full-scale current of 0.001 A. To measure up to 10 volts, the series resistor can be calculated as follows:
\[ R = \frac{V_{max}}{I_{full-scale}} = \frac{10V}{0.001A} = 10,000 \, \Omega \]
This means a 10K ohm resistor must be used in series with the meter. When a voltage of 10 volts is applied across the combination of the resistor and the meter, the current flowing through the circuit will be 1 milliamp, which corresponds to the full-scale reading of the meter.
It is essential to select a resistor that can handle the power dissipation, calculated using the formula:
\[ P = I^2 \cdot R \]
For this application:
\[ P = (0.001A)^2 \cdot 10,000 \, \Omega = 0.01W \]
A resistor rated for at least 1/8 watt (0.125W) would be suitable, providing a safety margin.
When constructing the circuit, ensure that the connections are secure and that the resistor is rated for the appropriate power level. The meter should be calibrated after assembly to confirm accuracy across the intended voltage range. This configuration allows for a simple yet effective method to extend the functionality of a milliamp meter into the realm of voltage measurement, making it a versatile tool in various electronic applications.A milliamp meter can be used as a volt meter by adding a series resistance. The resistance needed is the full scale voltage reading divided by the full scale current of the meter movement. So, if you have a 1 milliamp meter and you want to read 0-10 volts you will need a total resistance of 10/.001 = 10K ohms..
🔗 External reference
To implement this conversion effectively, the circuit design must ensure that the milliamp meter is properly calibrated to operate within the desired voltage range. The series resistor, which is critical for this adaptation, should be connected in series with the meter. The resistor's value is determined based on the maximum voltage to be measured and the full-scale current rating of the meter.
In the example provided, the 1 milliamp meter has a full-scale current of 0.001 A. To measure up to 10 volts, the series resistor can be calculated as follows:
\[ R = \frac{V_{max}}{I_{full-scale}} = \frac{10V}{0.001A} = 10,000 \, \Omega \]
This means a 10K ohm resistor must be used in series with the meter. When a voltage of 10 volts is applied across the combination of the resistor and the meter, the current flowing through the circuit will be 1 milliamp, which corresponds to the full-scale reading of the meter.
It is essential to select a resistor that can handle the power dissipation, calculated using the formula:
\[ P = I^2 \cdot R \]
For this application:
\[ P = (0.001A)^2 \cdot 10,000 \, \Omega = 0.01W \]
A resistor rated for at least 1/8 watt (0.125W) would be suitable, providing a safety margin.
When constructing the circuit, ensure that the connections are secure and that the resistor is rated for the appropriate power level. The meter should be calibrated after assembly to confirm accuracy across the intended voltage range. This configuration allows for a simple yet effective method to extend the functionality of a milliamp meter into the realm of voltage measurement, making it a versatile tool in various electronic applications.A milliamp meter can be used as a volt meter by adding a series resistance. The resistance needed is the full scale voltage reading divided by the full scale current of the meter movement. So, if you have a 1 milliamp meter and you want to read 0-10 volts you will need a total resistance of 10/.001 = 10K ohms..
🔗 External reference